一、Hard Voting 与 Soft Voting 的对比
1)使用方式
- voting = 'hard':表示最终决策方式为 Hard Voting Classifier;
- voting = 'soft':表示最终决策方式为 Soft Voting Classifier;
2)思想
- Hard Voting Classifier:根据少数服从多数来定最终结果;
- Soft Voting Classifier:将所有模型预测样本为某一类别的概率的平均值作为标准,概率最高的对应的类型为最终的预测结果;
-
Hard Voting
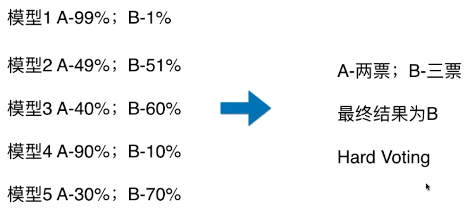
- 模型 1:A - 99%、B - 1%,表示模型 1 认为该样本是 A 类型的概率为 99%,为 B 类型的概率为 1%;
-
Soft Voting
- 将所有模型预测样本为某一类别的概率的平均值作为标准;

- Hard Voting 投票方式的弊端:
- 如上图,最终的分类结果不是由概率值更大的模型 1 和模型 4 决定,而是由概率值相对较低的模型 2/3/5 来决定的;
二、各分类算法的概率计算
- Soft Voting 的决策方式,要求集合的每一个模型都能估计概率;
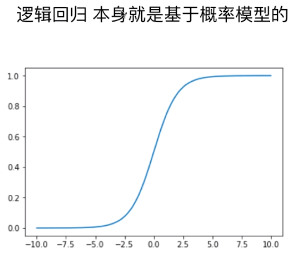
1)逻辑回归算法
- P = σ( y_predict )
2)kNN 算法
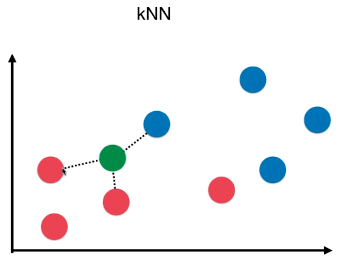
- k 个样本点中,数量最多的样本所对应的类别作为最终的预测结果;
- kNN 算法也可以考虑权值,根据选中的 k 个点距离待预测点的距离不同,k 个点的权值也不同;
- P = n / k
- n:k 个样本中,最终确定的类型的个数;如下图,最终判断为 红色类型,概率:p = n/k = 2 / 3;
3)决策树算法
- 通常在“叶子”节点处的信息熵或者基尼系数不为 0,数据集中包含多种类别的数据,以数量最多的样本对应的类别作为最终的预测结果;(和 kNN 算法类似)
- P = n / N
- n:“叶子”中数量最多的样本的类型对应的样本数量;
- N:“叶子”中样本总量;
4)SVM 算法
- 在 scikit-learn 中的 SVC() 中的一个参数:probability
- probability = True:SVC() 返回样本为各个类别的概率;(默认为 False)
from sklearn.svm import SVC svc = SVC(probability=True)
- 计算样本为各个类别的概率需要花费较多时间;
三、scikit-learn 中使用集成分类器:VotingClassifier
1)模拟数据集
-
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split X, y = datasets.make_moons(n_samples=500, noise=0.3, random_state=42) X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=42)
2)voting = 'hard':使用 Hard Voting 做决策
-
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression from sklearn.svm import SVC from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifier # 实例化 voting_clf = VotingClassifier(estimators=[ ('log_clf', LogisticRegression()), ('svm_clf', SVC()), ('dt_clf', DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=666)) ], voting='hard') voting_clf.fit(X_train, y_train) voting_clf.score(X_test, y_test) # 准确率:0.896
3)voting = 'soft':使用 Soft Voting 做决策
-
voting_clf = VotingClassifier(estimators=[ ('log_clf', LogisticRegression()), ('svm_clf', SVC(probability=True)), ('dt_clf', DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=666)) ], voting='soft') voting_clf.fit(X_train, y_train) voting_clf.score(X_test, y_test) # 准确率:0.912
- 使用 Soft Voting 时,SVC() 算法的参数:probability=True