首先,贴上整个测试Project的构造:
接下来、贴上代码段:
package com.example.servicetest;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private Button startButton, stopButton;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
startButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.startService);
stopButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.stopService);
startButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, MyService.class);
MainActivity.this.startService(intent);
}
});
stopButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent("closeService");
MainActivity.this.sendBroadcast(intent);
}
});
}
}
package com.example.servicetest;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.IntentFilter;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
public class MyService extends Service {
private BroadcastReceiver stopService = new BroadcastReceiver() {
// 当发送广播消息sendBroadcast()时、相应的广播接收消息并且执行这个onReceive()方法,
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
MyService.this.stopSelf();
MyService.this.unregisterReceiver(stopService);
}
};
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Log.v("Show_V", "onCreate");
// 创建Service时、注册广播Receiver,其中stopService是个内部实现类。
IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter();
filter.addAction("closeService");
MyService.this.registerReceiver(stopService, filter);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Log.v("Show_V", "onDestroy");
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.v("Show_V", "onStartCommand");
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.servicetest"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8"
android:targetSdkVersion="16" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name="com.example.servicetest.MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service android:name=".MyService" >
</service>
</application>
</manifest>
主要界面是:
当我们点击start_service按钮时,使用startService()方法启动一个service,首先需要调用Service里面的onCreate()方法,紧接着调用了onStartCommand()方法,接着我们继续点击start_service按钮时,仅仅调用onStartCommand()方法,不再调用onCreate()方法。
此时的Logcat显示为:
此时我们点击back按钮、退出程序回到桌面,此时的LogCat还是显示上面的内容,说明我们的service还在运行,接着我们找到我们的应用程序,点击进入,我们继续点击start_service按钮,此时的Logcat也还是打印出来了一条onStartCommand语句,验证我们前面的猜测,即应用程序退出以后,我们的service还是在继续运行,此时我们点击stop_service按钮,控制台的输出是:
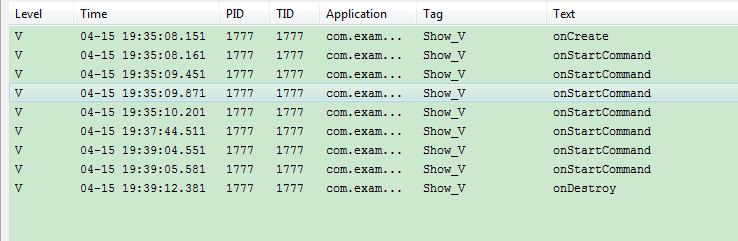
我们看到了onDestroy()这个函数执行了,说明我们的service确实是停止销毁了,再点击start_service按钮,直接看Logcat结果:
如前面的叙述,不过需要注意的时、我们在使用service时,需要在manifest文件中进行一定的声明,如我上面的声明一样。
启动service是通过的Intent来表明意图的,然后调用startService()方法启动service:
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, MyService.class);
MainActivity.this.startService(intent);
关闭service我们是通过广播机制实现的,这里我们是动态的注册了广播的接收者,在onCreate()方法里面实现的。通过点击stop_service按钮,发送一个带有Action的intent广播,注册了该Action的广播的都必须要通过onReceive()方法来实现。在onReceive()方法里,我们成功的停止了服务,调用的是stopSelf()方法。我们还可以使用stopService()方法来实现停止服务。至此,我们就实现了怎么启动一个service和关闭一个service的操作,并且对service的生命周期有了一个初步的了解。
看看主要的startService()方法的谷歌说明,进一步了解一下service:
上面的意思是:请求一个给出的应用程序的service启动。这个Intent可以是包含该service的完整类名,然后执行启动service,或者是一个抽象的定义通过action或者其他域的service启动。如果这个service不是正在运行的话,它会实例化和启动service(如果需要的话,创建一个进程),如果service已经是正在运行的,那么他继续运行。
每次调用这个方法时,会引起目标service一个通信调用,即onStartCommand方法,而且intent也是在这个方法参数中。这样提供了一个方便的方式去提交一个工作给service,因为不需要绑定和调用它的接口。
使用startService()覆盖默认的service生命周期,而这个有bindService来管理。它需要service来保留运行状态知道stopService被调用。无论是否有任何客户端与它连接。需要注意的是,调用startService()并不是嵌套的,也就是无论你调用了多少次startService()方法,只需要一次的调用stopService方法就可以停止service.
操作系统会尽最大努力去保持service处于运行状态,除非是当前的前台与用户交互的程序使用太多资源,才会把service销毁掉。如果有任何错误发生在service进程中,service会自动的重新启动。
翻译的不是很好,不过大概意思很明朗,有助于理解service。