Java,C#已经比较熟悉,最近在从0开始自学C++。学习过程中必然会与Java,C#进行对比,有吐槽,也有点赞。
先来讲讲最基本也是最重要的部分:参数传递的方式。
对于类型, Java分基本类型、复合类型,从另外一个角度分是值类型,引用类型。在展开对比前, 我们先来看看三个关键方式:
-
值
- 创建新的副本,与原来的没有关系
-
地址(指针)
- 把对象所在内存的地址传递过去
-
引用
- 可以理解为变量的别名
举个例子:
1 void testMethodA(int input) { 2 input = 999; 3 } 4 5 void testMethodB(int* input) { 6 //int newValue = 888; 7 *input = 888; 8 } 9 10 void testMethodC(int& input) { 11 input = 777; 12 } 13 14 int main() { 15 16 int input = 111; 17 cout << "Original: " << input << endl; 18 testMethodA(input); 19 cout << "After testMethodA: " << input << endl; 20 cout << input; 21 testMethodB(&input); 22 cout << "After testMethodB: " << input << endl; 23 cout << input; 24 testMethodC(input); 25 cout << "After testMethodC: " << input << endl; 26 27 std::cin.get(); 28 29 // What is the value of input? 30 31 }
运行后的结果:
Original: 111 After testMethodA: 111 111After testMethodB: 888 888After testMethodC: 777
解释一下:
函数 testMethodA 的参数是值传递的,调用函数后,创建了一个input的副本,副本的值改变了, 但是input值没有被改变。
函数 testMethodB 的参数是地址(指针)传递的,函数内修改了input指向的那块内存区域,所以input的值也被改变了。
函数 testMethodC的行为看起来是和函数 testMethodB是一样的, input值也被改变了,他们有什么区别呢?
区别在于:
传递地址,函数内改变的是变量指向的那块内存区域的内容。
传递引用,函数内改变的是变量的指向,换句话说,input指向的内存地址都变了。
如下图:
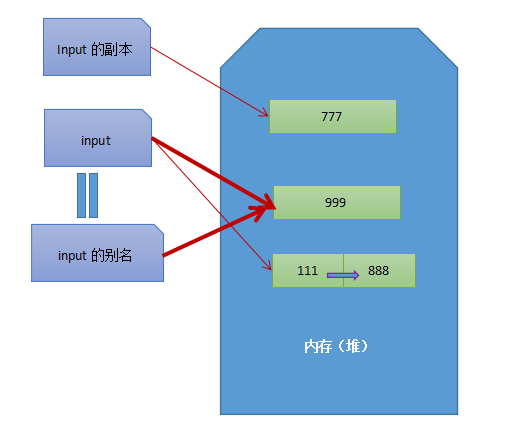
在C++里面,所有的类型,不管是基础数据类型,结构体,还是类,默认都是“值”传递的;显式声明为指针,才是传地址;显式声明为引用,可以认为就是给变量起了一个别名。
在Java里面,只有基础数据类型(int, double, float等),是值传递的,所有的类对象,都是传地址(注意,不是传引用), 实际上,java里面没有引用传递的概念。
在C#里面, 基础数据类型,结构体, 默认都是值传递;所有的对象, 默认都是传地址;如果想传引用,在参数前面加ref关键字,例如:
1 void testMethodC(ref int input) { 2 input = 777; 3 }