1.打开文件(ofstream || ifstream)。
如果想读文件则需要建立 ifstream类的对象。
如果想写文件则需要建立ofstream类的对象。
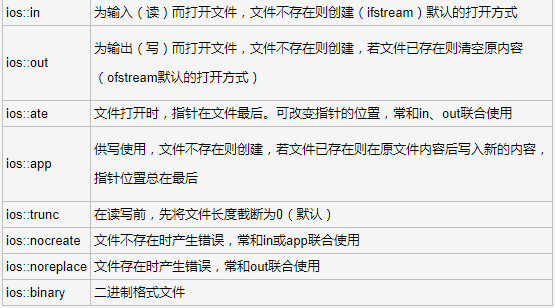
打开文件的方式有多种具体如下:
读文件一般以 ios::in 方式打开
写文件一般以 ios::out方式打开,这种打开方式会清空原数据,如果不想清空则需要以ios::app方式打开
eg:
题目:打开当前目录下的data.txt文件(以读的方式打开)
答案:ifstream fin;
fin.open("data.txt",ios::in | ios::app);
......
fin.close();
为了数据安全,每次打开文件执行完操作后,都建议人为关闭文件.
2.用ifstream函数读取文件数据(get || getline || read || )。
(1).get函数的使用.
ifstream fin;
fin.open("data.txt",ios::in);
while(!fin.eof()){
/*char info;
info = fin.get();
按字节获取数据
*/
string info;
info = fin.get();
按字符串获取数据
}
fin.close():
(2).getline函数的使用.
ifstream fin;
fin.open("data.txt",ios::in);
string info;
getline(fin,info);
fin.close():
该程序段会获取data文件的第一行数据以字符串的形式赋值给info。
(3).read函数的使用。
ifstream fin;
fin.open("data.txt",ios::in);
char info [50]"; fin.read(info,50 * sizeof(char));
fin.close():
该程序段会从文件开头获取50个字符长度的数据到info变量中.
3.用ofstream函数写入文件数据(put || write).
(1).put函数的使用.
ofstream fout;
fout.open("data.txt",ios::out);
char info = 'H';
fout.put(info);
fout.close();
(2).write函数的使用.
ofstream fout;
fout.open("data.txt",ios::out);
char info[50] = "The data of test";
fout.write(info,50 * sizeof(char));
fout.close();
4.定位函数的使用(tellg || tellp || seekg || seekp).
tellg和seekg需要结合ifstream对象使用,tellp和seekp需要结合ofstream函数使用.
具体使用方法,在本文最下面的示列代码中有详细步骤。
示例代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<fstream>
#include<sstream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void menu();
void init(){
ofstream fout;
fout.open("test.txt",ios::out);
fout << "The first row: These data is using for test,you should not change!
The second row: These data is using for test,you should not change!";
fout.close();
}
void ly_ofstream(){
system("cls");
ofstream fout;
fout.open("test.txt",ios::out);
fout << "ofstream函数测试数据,请勿更改";
fout.close();
system("pause");
}
void ly_ifstream(){
system("cls");
ifstream fin;
fin.open("test.txt",ios::in);
string info;
fin >> info;
if(info == ""){
info = "指定文件不存在数据,获取内容成功!";
}
cout << "ifstream函数使用结果展示: " << info << endl;
fin.close();
system("pause");
}
void ly_get(){
system("cls");
ifstream fin;
fin.open("test.txt",ios::in);
cout << "get函数使用结果展示(string类型读取): " << endl;
while(!fin.eof()){
string data;
fin >> data;
cout << data << " ";
}
fin.seekg(0,ios::beg);
cout << endl << "get函数使用结果展示(char类型读取): " << endl;
while(!fin.eof()){
char data;
fin >> data;
cout << data << " ";
}
fin.close();
cout << endl;
system("pause");
}
void ly_getline(){
system("cls");
ifstream fin;
fin.open("test.txt",ios::in);
cout << "getline函数使用结果展示: " << endl;
string data;
getline(fin,data);
cout << data << endl;
fin.close();
system("pause");
}
void ly_eof(){
system("cls");
ifstream fin;
fin.open("test.txt",ios::in);
cout << "eof函数使用结果展示: " << endl;
int nums = 0;
while(!fin.eof()){
char byte;
byte = fin.get();
nums++;
}
cout << "一共有" << nums << "个字符" << endl;
fin.close();
system("pause");
}
void ly_tellg(){
system("cls");
ifstream fin;
fin.open("test.txt",ios::in);
cout << "tellg函数使用结果展示: " << endl;
while(!fin.eof()){
char byte;
byte = fin.get();
cout << "当前指针所在位置为 " << fin.tellg() << " 此处存在的字符为 " << byte << " " << endl;
}
fin.close();
system("pause");
}
void ly_tellp(){
system("cls");
ofstream fout;
fout.open("test.txt",ios::out);
cout << "tellp函数使用结果展示: " << endl;
int sub = 10;
while(sub--){
fout << "此处为第" << fout.tellp() << "字节所在地" << endl;
}
fout.close();
system("pause");
}
void ly_seekg(){
system("cls");
ifstream fin;
fin.open("test.txt",ios::in);
cout << "seekg函数使用结果展示: " << endl;
fin.seekg(10,ios::beg);
char info = fin.get();
cout << "指定文件的第十个字节为 " << info << " " << endl;
fin.close();
system("pause");
}
void ly_seekp(){
system("cls");
ofstream fout;
fout.open("test.txt",ios::out);
cout << "tellp函数使用结果展示: " << endl;
fout.seekp(20,ios::beg);
fout << "此处为第二十个字节所在的位置";
fout.close();
system("pause");
/*
如果以app方式打开文件,文件指针会自动移动到文件尾,
致使seekp函数定位失败,如果不以app函数打开,直接
用seekp函数在指定位置添加数据,则会清空原有数据,解决这个问题的方法是使用fstream函数
*/
}
void ly_write(){
system("cls");
ofstream fout;
fout.open("test.txt",ios::out);
cout << "write函数使用结果展示: " << endl;
char info[50] = "此为write函数输出到文件的数据,请勿修改";
fout.write(info,50 * sizeof(char));
fout.close();
system("pause");
}
void ly_read(){
system("cls");
ifstream fin;
fin.open("test.txt",ios::out);
cout << "read函数使用结果展示: " << endl;
char info[20];
fin.read(info,20 * sizeof(char));
cout << info << endl;
fin.close();
system("pause");
}
void ly_fstream(){
system("cls");
fstream file;
file.open("test.txt", ios::in | ios::out);
cout << "fstream函数使用结果展示: " << endl;
file.seekp(20, ios_base::beg);
file<<"此处为第二十个字节所在的位置";
file.close();
system("pause");
}
int main(int argc,char** argv){
init();
menu();
return 0;
}
void menu(){
int select;
while(true){
system("cls");
cout << "1.ofstream函数的使用" << endl;
cout << "2.ifstream函数的使用" << endl;
cout << "3.get函数的使用" << endl;
cout << "4.getline函数的使用" << endl;
cout << "5.eof函数的使用" << endl;
cout << "6.tellg函数的使用" << endl;
cout << "7.tellp函数的使用" << endl;
cout << "8.seekg函数的使用" << endl;
cout << "9.seekp函数的使用" << endl;
cout << "10.write函数的使用" << endl;
cout << "11.read函数的使用" << endl;
cout << "12.fstream函数的使用" << endl;
cout << "0.退出" << endl;
cout << endl << "请选择功能进行下一步操作" << endl;
cin >> select;
switch(select){
case 1:
ly_ofstream();
break;
case 2:
ly_ifstream();
break;
case 3:
ly_get();
break;
case 4:
ly_getline();
break;
case 5:
ly_eof();
break;
case 6:
ly_tellg();
break;
case 7:
ly_tellp();
break;
case 8:
ly_seekg();
break;
case 9:
ly_seekp();
break;
case 10:
ly_write();
break;
case 11:
ly_read();
case 12:
ly_fstream();
break;
case 0:
exit(1);
break;
default:
cout << "输入有误,请重新输入!" << endl;
}
}
}