java.util.concurrent : 提供了并发编程的解决方案
1、CAS 是java.util.concurrent.atomic包的基础
2、AQS是java.util.concurrent.locks包以及一些常用类,比如:Semophore ,ReentrantLock等类的基础
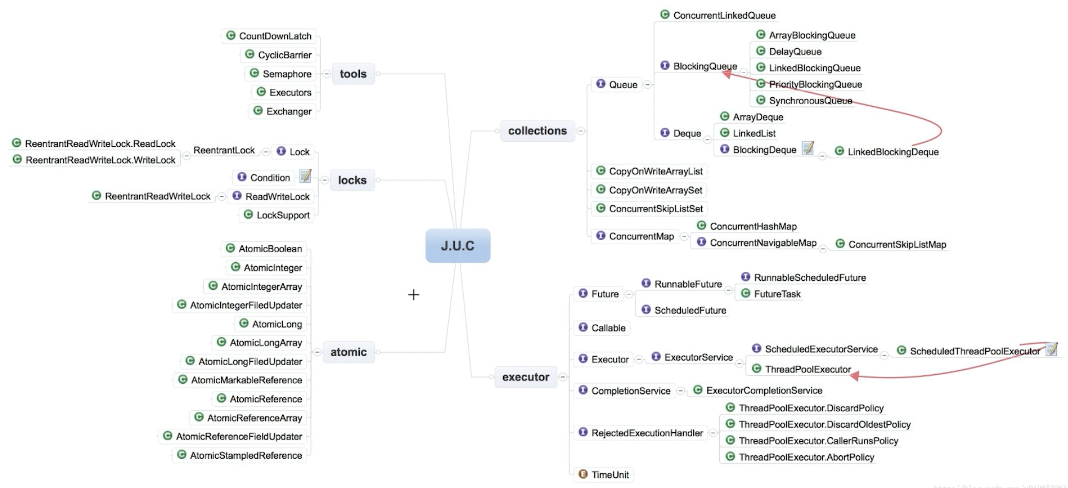
J.U.C包的分类
1、线程执行器executor
2、锁locks
3、原子变量类atomic
4、并发工具类 tools
5、并发集合collections
并发工具类
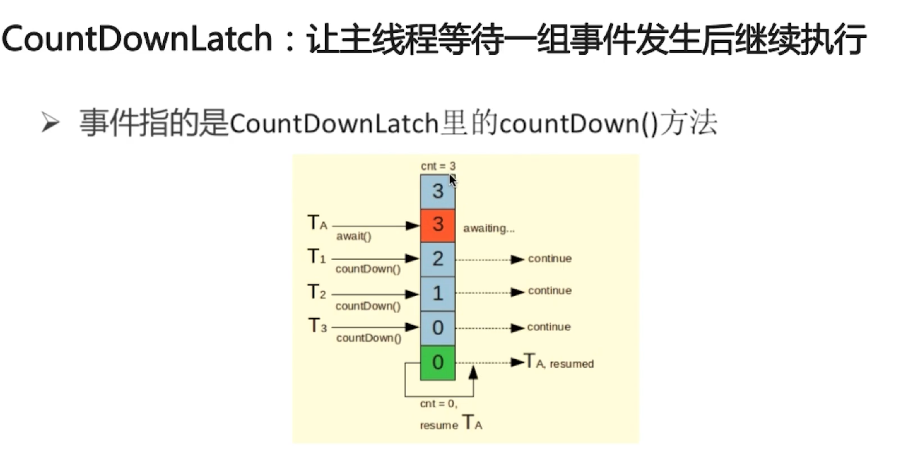
1、闭锁 CountDownLatch
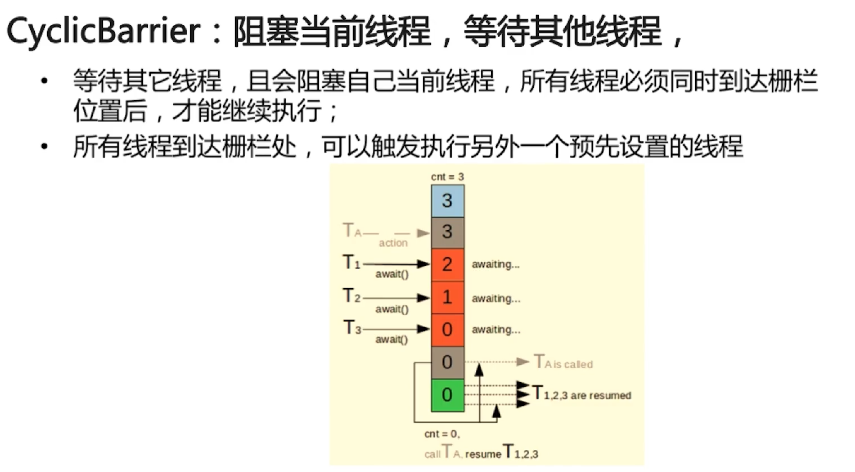
2、栅栏 CyclicBarrier
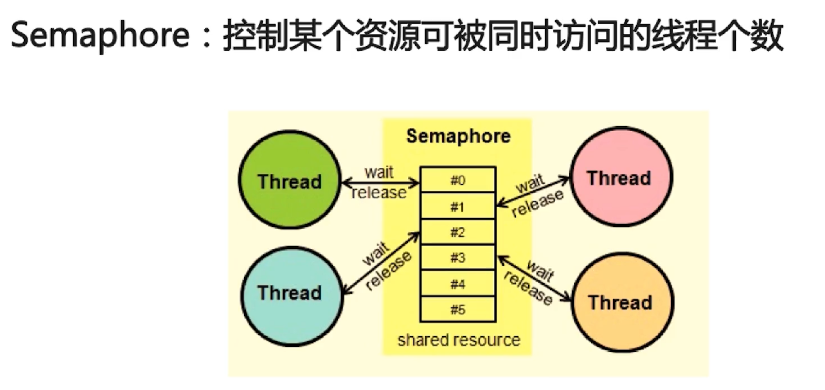
3、信号量Semaphore
4、交换器 Exchanger
public class CountDownLatchDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new CountDownLatchDemo().go();
}
private void go() throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(3);
// 依次创建3个线程,并启动
new Thread(new Task(countDownLatch), "Thread1").start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
new Thread(new Task(countDownLatch), "Thread2").start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
new Thread(new Task(countDownLatch), "Thread3").start();
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println("所有线程已到达,主线程开始执行" + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
class Task implements Runnable {
private CountDownLatch countDownLatch;
public Task(CountDownLatch countDownLatch) {
this.countDownLatch = countDownLatch;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已经到达" + System.currentTimeMillis());
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}
}
public class CyclicBarrierDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new CyclicBarrierDemo().go();
}
private void go() throws InterruptedException {
// 初始化栅栏的参与者数为3
CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(3);
// 依次创建3个线程,并启动
new Thread(new Task(cyclicBarrier), "Thread1").start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
new Thread(new Task(cyclicBarrier), "Thread2").start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
new Thread(new Task(cyclicBarrier), "Thread3").start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("main");
}
class Task implements Runnable {
private CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier;
public Task(CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier) {
this.cyclicBarrier = cyclicBarrier;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已经到达" + System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
cyclicBarrier.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "开始处理" + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
}
public class SemaphoreDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程池
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// 只能5个线程同时访问
final Semaphore semp = new Semaphore(5);
// 模拟20个客户端访问
for (int index = 0; index < 20; index++) {
final int NO = index;
Runnable run = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
// 获取许可
semp.acquire();
System.out.println("Accessing: " + NO);
Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random() * 10000));
// 访问完后,释放
semp.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
};
exec.execute(run);
}
// 退出线程池
exec.shutdown();
}
}
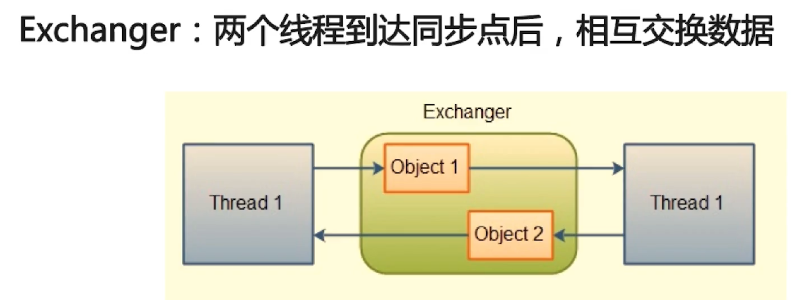
public class ExchangerDemo {
private static Exchanger<String> exchanger = new Exchanger();
public static void main(String[] args) {
//代表男生和女生
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
service.execute(() -> {
try {
//男生对女生说的话
String girl = exchanger.exchange("我其实暗恋你很久了......");
System.out.println("女生说:" + girl);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
service.execute(() -> {
try {
System.out.println("女生慢慢的从教室里走出来......");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
//男生对女生说的话
String boy = exchanger.exchange("我很喜欢你......");
System.out.println("男生说:" + boy);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
service.shutdown();
} }
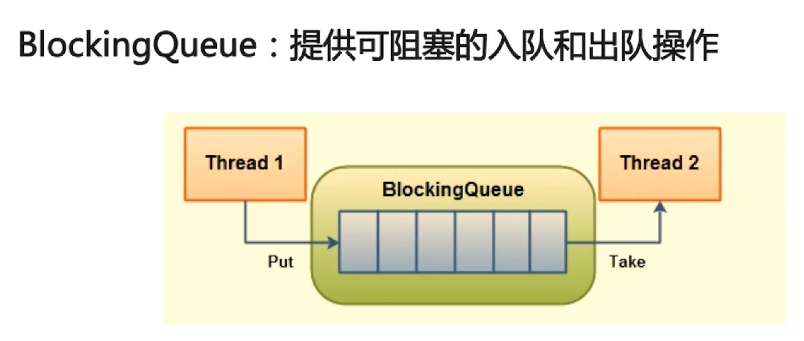
主要用于生产者-消费者模式,在多线程场景时生产者线程在队列尾部添加元素,而消费者线程则在队列头部消费元素,通过这种方式能够达到将任务的生产和消费进行隔离的目的。
注意:BlockingQueue的加入方法,offer(),add(),put()
