一、state
1.1 引入vuex 以后,我们需要在state中定义变量,类似于vue中的data,通过state来存放状态
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex) export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { //存放状态 nickname:'Simba', age:20, gender:'男' }, mutations: {}, actions: {}, modules: {} })
注册两个组件分别引入到app.vue中
<div id="app"> <vabout> </vabout> <vhome> </vhome> </div>
vhome组件内容
<div class="home">{{$store.state.nickname}}</div>
vabout组件内容
<h1>{{$store.state.nickname}}:{{$store.state.age}}</h1>

如图,显示出相应的内容,有了vuex,我们不必在考虑组件之间的传值,直接就可以通过$store来获取不同的数据,但是如果需要vuex中的多个数据的这时候,这样写就太啰嗦了,我们可以将它定义在computed中。
Props,methods,data和computed的初始化都是在beforeCreated和created之间完成的。
<template> <div class="home"> {{nickname}} </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'home', computed:{ nickname(){ return this.$store.state.nickname } } } </script>
这样引入就方便了很多。
1.2 mapState 辅助函数
1.1中的方法虽然引入的时候方便了,但是computed中定义的代码还是很多,而这时候vuex又给我们提供了更简便的方法mapState方法
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'home',
computed: mapState(['nickname','age','gender'])
}
mapState(['nickname','age','gender']) //映射哪些字段就填入哪些字段
这一句代码就相当于下面这些
nickname(){return this.$store.state.nickname}
age(){return this.$store.state.age}
gender(){return this.$store.state.gender}
记住:用mapState等这种辅助函数的时候,前面的方法名和获取的属性名是一致的。
如果我们需要自定义一个计算属性怎么办呢?怎么添加呢?
毕竟现在已经成这样了 computed: mapState(['nickname','age','gender'])
这时候我们就需要es6中的展开运算符:...
computed: { //computed是不能传参数的
value(){
return this.val/7
},
...mapState(['nickname','age','gender'])
}
二、getters
2.1 getters相当于vue中的计算属性,通过getters进一步处理,得到我们想要的值,而且允许传参,第一个参数就是state
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex) export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { //存放状态 nickname:'Simba', firstname:'张', lastname:'三丰', age:20, gender:'男', money:1000 }, getters:{ realname(state){ return state.firstname+state.lastname }, money_us(state){ return (state.money/7).toFixed(2) } }, mutations: {}, actions: {}, modules: {} })
vue组件
computed: { //computed是不能传参数的
valued(){
return this.value/7
},
...mapGetters(['realname','money_us'])// 把 `this.realname` 映射为 `this.$store.getters.realname`
}
三、Mutation
3.1 我们代码中定义的时候需要些mutations,它类似于vue中的methods,
mutations需要通过commit来调用其里面的方法,它也可以传入参数,第一个参数是state,第二个参数是载荷(payLoad),也就是额外的参数
代码如下
mutations: { //类似于methods
addAge(state,payLoad){
state.age+=payLoad.number
}
}
template部分
<div class="home"> <div><button @click="test">测试</button></div> </div>
js部分
methods:{ test(){ this.$store.commit('addAge',{ number:5 }) } }
调用的时候第二个参数最好写成对象形式,这样我们就可以传递更多信息。
但是,这样写还是会遇到同样的问题,就是如果需要操作多个数据,就会变的麻烦,这时候我们就需要mapMutations,通过它将方法映射过来
3.2 mapMutations
跟mapState、mapGetters一样
methods:{ ...mapMutations(['addAge']) }
mapMutations(['addAge'])这一句就相当于下面的代码
addAge(payLoad){ this.$store.commit('addAge',payLoad) }
参数我们可以在调用这个方法的时候写入
<button @click="addAge({number:5})">测试</button>
为什么要绕一圈,从mutations里面去改state呢?能不能直接改state呢?
比如这样:
addAge(){ this.$store.state.age +=5; }
实际看结果也可以,那我为什么从mutations里面中转一下呢?
原因如下:
① 在mutations中不仅仅能做赋值操作
② 作者在mutations中做了类似埋点操作,如果从mutations中操作的话, 能被检测到,可以更方便用调试工具调试,调试工具可以检测到实时变化,而直接改变state中的属性,则无法实时监测
注意:mutations只能写同步方法,不能写异步,比如axios、setTimeout等,这些都不能写,mutations的主要作用就是为了修改state的。
原因类似:如果在mutations中写异步,也能够调成功,但是由于是异步的,不能被调试工具追踪到,所有不推荐这样写,不利于调试,这是官方的约定。
四、actions
4.1 action类似于mutation
区别:action可以提交mutation
action也不要直接去操作state,而是去操作mutation
action包含异步操作,类似于axios请求,可以都放在action中写
action中的方法默认的就是异步,并且返回promise
代码如下
store部分
actions: { getUserInfo(){ return { nickname:'Simba', age:20 } } }
在actions中定义一个方法:getUserInfo,并且返回一个对象
vue部分
created(){ var res = this.getUserInfo() console.log(res) }, methods:{ ...mapActions(['getUserInfo']) }
在created中调用此方法,并将结果赋值给res,打印res,结果打印出Promise
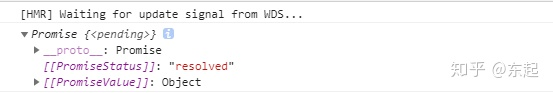
这表明,在actions中的方法,默认就是异步的,通过then获取数据
mapActions(['getUserInfo']) 相当于以下代码
getUserInfo(){ return this.$store.dispatch(‘getUserInfo’) }
在实际开发当中,state里面的属性值是空的,当登录以后,再进行获取对应的信息。
登录以后,需要得到用户信息,那如何得到呢?
首先进入页面的时候调用actions中的getUserInfo方法
代码如下
vue部分
created(){ this.getUserInfo()}
methods:{ ...mapActions([‘getUserInfo’])}
store部分
首先要想得到数据,那就相当于给state赋值,那首先想到的就是mutations来操作state,但是请求的接口都是axios异步,所以就不能用mutations而是用actions,通过actions来操作mutations从而操作state
export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { nickname:‘’, age:0, gender:'', money:0 }, mutations: { setUerInfo(state,payLoad){ state.nickname = payLoad.nickname state.age = payLoad.age state.gender = payLoad.gender state.money = payLoad.money } }, actions: { //actions没有提供state当参数 async getToken({commit}){ var res = await axios.get('/token接口') commit('setToken',res) }, async getUserInfo(context){ //context可以理解为它是整个Store的对象.类似于this.$store, 他里面包含了state,getter,mutations,actions const res = await axios.get('/接口url') context.commit('setUerInfo',res) //相当于 this.$store.commit,第一个参数是方法名,第二个参数是要传入的数据 context.dispatch('getToken') //actions也可以调用自己的其他方法 }, } })
运行过程,调用getUserInfo方法以后,进入actions,然后通过commit调用setUserInfo,将res(用户信息)作为参数传入传入进去,并将相对应的属性值赋值给state,完成这一过程的操作。
getUserInfo的参数也可以用解构,这样更方便
async getUserInfo({commit,dispatch}){ const res = await axios.get('/接口url') commit('setUerInfo',res) dispatch('getToken') }
五、总结:
mapState(['nickname'])映射为:
nickname(){ return this.$store.state.nickname }
mapGetters(['realname'])映射为:
realname(){ return this.$store.getters.realname }
mapMutations(['addAge'])映射为:
addAge(payLoad){ this.$store.commit('addAge',payLoad) }
mapActions(['getUserInfo']) 映射为:
getUserInfo(){ return this.$store.dispatch(‘getUserInfo’) }