二叉查找树定义
二叉查找树(英语:Binary Search Tree),也称二叉搜索树、有序二叉树(英语:ordered binary tree),排序二叉树(英语:sorted binary tree),是指一棵空树或者具有下列性质的二叉树:
- 若任意节点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有节点的值均小于它的根节点的值;
- 若任意节点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有节点的值均大于它的根节点的值;
- 任意节点的左、右子树也分别为二叉查找树;
- 没有键值相等的节点。
二叉查找树相比于其他数据结构的优势在于查找、插入的时间复杂度较低。为O(log n)。
 三层二叉查找树
三层二叉查找树
二叉查找树的操作主要是运用的递归的思想,可操作的Object类必须继承了Comparable接口,个人实现查找树主要是参考了《数据结构与算法分析》这本书。因为遍历涉及到三种遍历方式,所以届时单独开一篇。
树的结点定义
1 private static class BinaryNode<T>{ 2 BinaryNode(T theElement) { 3 this(theElement,null,null); 4 } 5 BinaryNode(T theElement,BinaryNode<T> lt,BinaryNode<T> rt) { 6 element=theElement; 7 left=lt; 8 right=rt; 9 } 10 T element;//根节点 11 BinaryNode<T> left;//左子树 12 BinaryNode<T> right;//右子树 13 }
contains方法
1 private boolean contains(T x,BinaryNode<T> t){ 2 if(t==null) 3 return false; 4 int compareResult=x.compareTo(t.element); 5 if(compareResult<0) 6 return contains(x,t.left); //递归 7 else if (compareResult>0) { 8 return contains(x, t.right); 9 } 10 else { 11 return true; 12 } 13 }
contains方法主要是查找当前二叉树是否还有某个节点,利用了comparaTo方法递归调用。
findMin()与findMax()方法
1 private BinaryNode<T> findMin(BinaryNode<T> t){ 2 //非递归写法 3 if(t!=null) 4 while(t.left!=null) 5 t=t.left; 6 return t; 7 //递归写法 8 /*if(t==null) 9 return null; 10 else if (t.left==null) { 11 return t; 12 } 13 return findMin(t.left);*/ 14 }
findMin与findMax方法类似,这里只列出一种即可。然后仍有两种方法解决此问题,一种为递归,一种非递归。
非递归方法就是采用了while循坏思想,直到找出最左的节点即可。
insert方法
1 private BinaryNode<T> insert(T x,BinaryNode<T> t){ 2 if(t==null)//生成新的节点 3 return new BinaryNode<T>(x, null, null); 4 if(contains(x))//如果二叉树中已经有x元素,则不进行任何操作 5 return t; 6 else { 7 int compareResult=x.compareTo(root.element); 8 if(compareResult<0){ 9 t.left=insert(x, t.left); 10 } 11 else { 12 t.right=insert(x, t.right); 13 } 14 return t; 15 } 16 }
remove方法
1 private BinaryNode<T> remove(T x,BinaryNode<T> t){ 2 if(t==null) 3 return t; 4 int compareResult=x.compareTo(t.element); 5 if(compareResult<0){ 6 t.left=remove(x, t.left); 7 } 8 else if(compareResult>0){ 9 t.right=remove(x, t.right); 10 } 11 else if (t.left!=null&&t.right!=null) { //两个孩子情况,采取懒惰删除 12 t.element=findMin(t.right).element; 13 t.right=remove(t.element, t.right); 14 } 15 else { //单个孩子情况 16 t=(t.left!=null)?t.left:t.right; 17 } 18 return t; 19 }
删除节点时需要考虑两种情况,一种为两个孩子的情况,一种为单个孩子的情况。
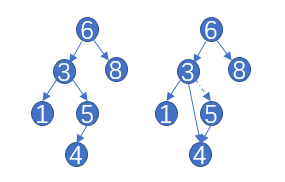 如图为删除5节点为单个孩子情况
如图为删除5节点为单个孩子情况
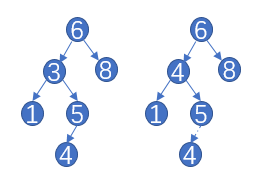 此图是删除3节点两个孩子的情况,具体做法是找出该节点右子树中最小的节点替换当前删除的节点
此图是删除3节点两个孩子的情况,具体做法是找出该节点右子树中最小的节点替换当前删除的节点
全部的代码如下(暂缺遍历)

1 package Tree; 2 3 public class BinarySearchTree<T extends Comparable<? super T>> { 4 private static class BinaryNode<T>{ 5 BinaryNode(T theElement) { 6 this(theElement,null,null); 7 } 8 BinaryNode(T theElement,BinaryNode<T> lt,BinaryNode<T> rt) { 9 element=theElement; 10 left=lt; 11 right=rt; 12 } 13 T element;//根节点 14 BinaryNode<T> left;//左子树 15 BinaryNode<T> right;//右子树 16 } 17 private BinaryNode<T> root;//定义根节点 18 public BinarySearchTree() { 19 root=null; 20 } 21 public void makeEmpty(){ 22 root=null; 23 } 24 public boolean isEmpty(){ 25 return root==null; 26 } 27 public boolean contains(T x){ 28 return contains(x,root); 29 } 30 public T findMin() throws Exception{ 31 if(isEmpty()) 32 throw new Exception(); 33 return findMin(root).element; 34 } 35 public T findMax() throws Exception{ 36 if(isEmpty()) 37 throw new Exception(); 38 return findMax(root).element; 39 } 40 public void insert(T x){ 41 root=insert(x,root); 42 } 43 public void remove(T x){ 44 root=remove(x,root); 45 } 46 private boolean contains(T x,BinaryNode<T> t){ 47 if(t==null) 48 return false; 49 int compareResult=x.compareTo(t.element); 50 if(compareResult<0) 51 return contains(x,t.left); //递归 52 else if (compareResult>0) { 53 return contains(x, t.right); 54 } 55 else { 56 return true; 57 } 58 } 59 private BinaryNode<T> findMin(BinaryNode<T> t){ 60 //非递归写法 61 if(t!=null) 62 while(t.left!=null) 63 t=t.left; 64 return t; 65 //递归写法 66 /*if(t==null) 67 return null; 68 else if (t.left==null) { 69 return t; 70 } 71 return findMin(t.left);*/ 72 } 73 private BinaryNode<T> findMax(BinaryNode<T> t){ 74 if(t!=null) 75 while(t.right!=null) 76 t=t.right; 77 return t; 78 } 79 private BinaryNode<T> insert(T x,BinaryNode<T> t){ 80 if(t==null)//生成新的节点 81 return new BinaryNode<T>(x, null, null); 82 if(contains(x))//如果二叉树中已经有x元素,则不进行任何操作 83 return t; 84 else { 85 int compareResult=x.compareTo(root.element); 86 if(compareResult<0){ 87 t.left=insert(x, t.left); 88 } 89 else { 90 t.right=insert(x, t.right); 91 } 92 return t; 93 } 94 } 95 private BinaryNode<T> remove(T x,BinaryNode<T> t){ 96 if(t==null) 97 return t; 98 int compareResult=x.compareTo(t.element); 99 if(compareResult<0){ 100 t.left=remove(x, t.left); 101 } 102 else if(compareResult>0){ 103 t.right=remove(x, t.right); 104 } 105 else if (t.left!=null&&t.right!=null) { //两个孩子情况,采取懒惰删除 106 t.element=findMin(t.right).element; 107 t.right=remove(t.element, t.right); 108 } 109 else { //单个孩子情况 110 t=(t.left!=null)?t.left:t.right; 111 } 112 return t; 113 } 114 115 }
也可访问我的gihub数据结构的部分,暂时内容较少。
