1.css层叠样式表
1.什么是CSS?
CSS是指层叠样式表(Cascading Style Sheets),样式定义如何显示HTML元素,样式通常又会存在于样式表中。 也就是说把HTML元素的样式都统一收集起来写在一个地方或一个CSS文件里。
2.css的优势
1.内容与表现分离 2.网页的表现统一,容易修改 3.丰富的样式,使页面布局更加灵活 4.减少网页的代码量,增加网页浏览器速度,节省网络带宽 5.运用独立页面的css,有利于网页被搜索引擎收录
2.css的引入方式
1.内嵌式 一般不写内嵌式,以后不好维护 <h1 style="font-size: 10px;color: yellow">我是h1路飞学城</h1> 2.内链式 <style type="text/css"> h2{font-size:30px;color:red;} </style> 3.外链式 链接式 link css 同时加载的! <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="./css/index.css"> 导入式 实际用的很少,先加载html,在加载css import 是css2.1特有的,对于不兼容css2.1的浏览器是无效的eg:IE5以下 <style type="text/css"> @import url('./css/index.css'); </style> 注意:@import url()必须写在文件最开始的位置。 链接式与导入式的区别: 1、<link/>标签属于XHTML,@import是属性css2.1 2、使用<link/>链接的css文件先加载到网页当中,再进行编译显示 3、使用@import导入的css文件,客户端显示HTML结构,再把CSS文件加载到网页当中 4、@import是属于CSS2.1特有的,对于不兼容CSS2.1的浏览器来说就是无效的 生效优先级:内嵌式 > 内链式 > 外链式
css样式优先级: 行内样式 > 内部样式表 > 外部样式表 ID选择器 > 类选择器 > 标签选择器
3.基本选择器
/*1.标签选择器 p { color: red; }
/*2.id选择器:
#user { background-color: yellow; } /*3.类选择器 .c1 { color: blue; } .c2{ background-color: red; } .c3{ font-size: 12px; } /*4.通配符选择器*/ *{ margin: 0; padding: 0; }
4、高级选择器
/*5.子代选择器 (选择器之间用 > )*/ ul > li { color: red; } /*6.后代选择器 (选择器之间用 空格)*/ ul a { color: green; } /*7.群组选择器 (中间用,)*/ .title, .content, .footer { width: 900px; margin: 0 auto; background-color: red; border: 1px solid red; } /*8.交集选择器 (选择器之间不能有空格,第一个标签必须是标签选择器,第二个标签可以是id或者类选择器)*/ p.p1 { color: red; } p#title1 { font-size: 30px; color: red; } /*9.毗邻选择器 (选择器之间用 + 紧跟着h3标题的标签)*/ h3 + p { color: red; } /*10.兄弟选择器 (选择器之间用~)*/ h3 ~ p { color: red; }
5.属性选择器
^ 以...开头,
$ 以...结尾,
* 包含...,
~ 有多个值中的其中一个
[class="baidu"]{ color:red; } [class^="btn"]{ color:yellow; font-size:12px; } [class$="ault"]{ font-size:12px; color:red; } [class]{ color:red; } [class*='baidu']{ color:red; } [class~='baidu']{ color:red; } input[input="text"]{ background-color:red; }
6、伪类选择器
a标签的 lover hate
a:link{ } 超链接 未被访问时的状态 a:hover{ color: green;} 鼠标悬停时的状态 a:visited{ color: yellow;} 鼠标单击时的状态 a:active{ color:blue;} 鼠标不松手的状态 input:focus{ background-color:red;} 获取焦点时的状态
nth-child(n)
div ul li:first-child{color: red;} /*选中第一个元素*/ div ul li:last-child{color: yellow;} /*选中最后一个元素*/ div ul li:nth-child(3){color: purple;} /*选中当前指定的元素 数值从1开始*/ div ul li:nth-child(n){color: red;} /*n表示选中所有 从0开始的 0的时候表示没有选中*/ div ul li:nth-child(2n){color: gold;} /*偶数*/ div ul li:nth-child(2n-1){color: yellow;} /*奇数*/ div ul li:nth-child(5n+1){color: red;} /*隔几换色 隔行换色*/
7、伪元素选择器
p:first-letter{ font-size:30px;} p段落 为文本的首字母设置特殊样式 p:before{ 用于在元素的内容前面插入新内容 content:"开头"; color:red; } p:after{ 用于在元素的内容后面插入新内容(清除浮动) content:"结尾"; color:green; } 使用此伪元素选择器一定要结合content属性
8、字体样式,文本属性,背景图片
(1)字体样式
默认字体大小: 16px = 1em 12px = 0.75em 1) font-size:30px; 注:文字大小:如果设置成inherit表示继承父元素的字体大小值。 2) font-style:oblique; 注:文字的样式:italic 也表示斜体; 推荐设置斜体的时候使用oblique 3) font-weight:bolder; 字体的粗细 注: 文字的粗细:normal 默认值,标准粗细 bord 粗体 border 更粗 lighter 更细 100~900 设置具体粗细,400等同于normal,而700等同于bold inherit 继承父元素字体的粗细值 4) font-family:"微软雅黑"; font-family: "Microsoft Yahei", "微软雅黑", "Arial", "sans-serif"; 注:文字的类型: 如果浏览器不支持第一个字体,则会尝试下一个。浏览器会使用它可识别的第一个值。 如果设置成inherit,则表示继承父元素的字体。 5) color:red; 注:文字颜色:支持三种颜色值: #FF0000 RGB(255,0,0) red
(2)文本属性
(1)# text-decoration:underline; 注:线:overline 上 line-through 中 underline 下 none 无(默认 定义标准的文本) inherit 继承父元素的text-decoration属性的值。 (2)# text-indent:20px; 注:首行缩进:20px (3)# text-align:center; 注:文本对齐可水平居中:left(默认值) right center justify(两端对齐只针对英文) (4)# text-shadow: 10px 10px 0.5px #fff; 注:阴影:左右,上下,0-1,颜色 (5)# cursor:pointer; 注: 鼠标形状:pointer 指针, cell 十字, default 鼠标 (6)# height:200px; # line-height:200px; 注:文本垂直居中:height = line-height
(3)背景属性
(1)# background-color:red; 注:背景颜色。 (2)# background-image:url("./images/***.png"); 注:背景图像 (3)# background-size: 300px 300px; 注:背景图片的尺寸 (4)# background-repeat:no-repeat; 注: 如何重复背景图像 repeat 默认。背景图像将在垂直方向和水平方向重复。 repeat-x 背景图像将在水平方向重复。 repeat-y 背景图像将在垂直方向重复。 no-repeat 背景图像将仅显示一次。 inherit 规定应该从父元素继承background-repeat属性的设置。 (5)# background-attachment:fixed; 注: 背景图像是否固定或者滚动 scroll 默认值。背景图像会随着页面其余部分的滚动而移动。 fixed 当页面的其余部分滚动时,背景图像不会移动。 inherit 规定应该从父元素继承background-attachment属性的设置。 (6)# background-position:10px 20px; 注: 背景图像的位置 top left 如果只设置了一个关键词,那么第二个值就是"center"。 top center top right center left center center center right bottom left bottom center bottom right
background: green; background: url("./homesmall1.png") no-repeat 10px 12px red; background: url("./homesmall1.png") no-repeat center red fixed; 注: 简写 body { background-color: red; backgraound-image: url(xx.png); background-size: 300px 300px; background-repeat: no-repeat; background-position: center }
body { background: red url(xx.png) no-repeat fixed center/300px 300px; }
9.盒子模型
HTML文档中的每个元素都被描绘成矩形盒子,这些矩形盒子通过一个模型来描述其占用空间,这个模型称为盒子模型。
盒子模型通过四个边界来描述:margin(外边距),border(边框),padding(内填充),content(内容区域)
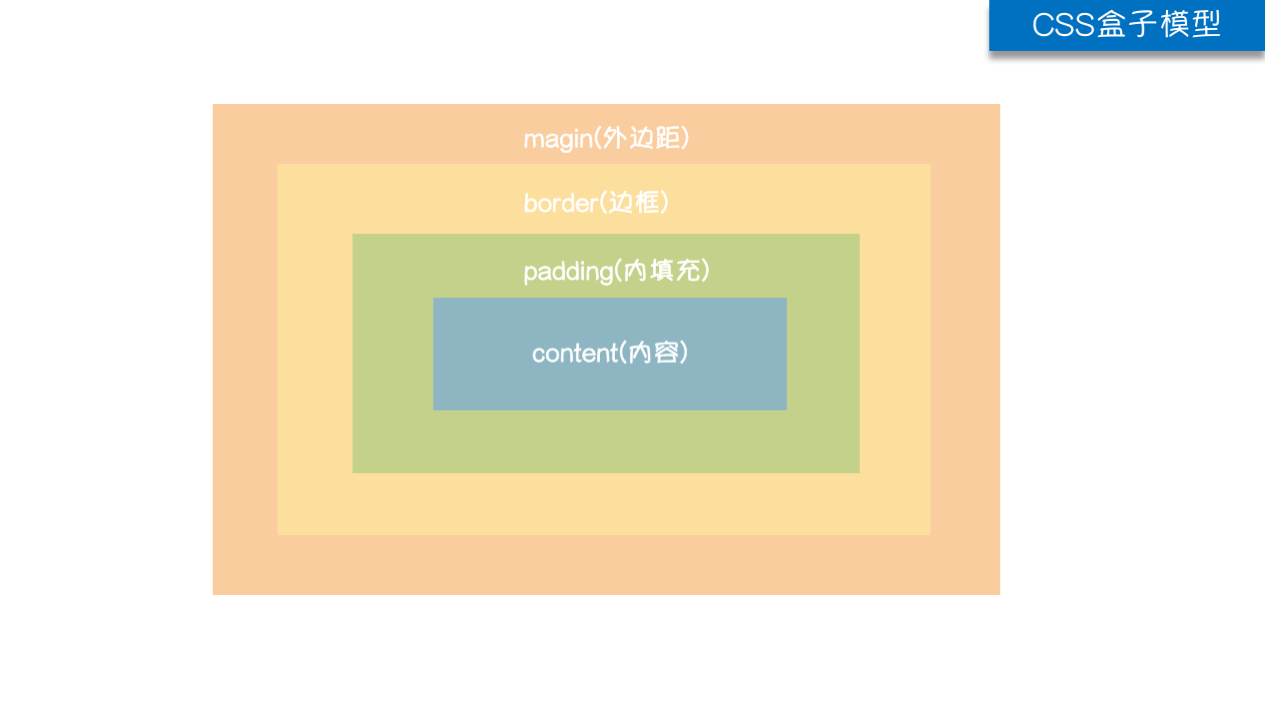
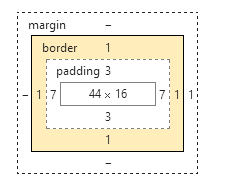
(1)padding
内边距:控制内容到边框的距离,内边距会扩大元素所在的区域,width+padding;
注意:为元素设置内边距,只能影响自己,不会影响其他的元素,padding不支持负值。
/*小属性设置*/ padding-top: 30px; padding-right: 30px; padding-bottom: 30px; padding-left: 30px; /*上 右 下 左*/ padding: 20px 30px 40px 50px ; /*上 左右 下*/ padding: 20px 30px 40px; /* 上下 左右*/ padding: 20px 30px; /*上下左右*/ padding: 20px;
(2) border
border-top- 5px;
border-bottom- 10px;
border-left- 15px;
border-right- 20px;
border-top-color: red;
border-bottom-color: yellowgreen;
border-left-color: yellow;
border-right-color: blue;
border-top-style: solid; 实线
border-bottom-style: dashed; 矩形虚线边框
border-left-style: dotted; 点状虚线边框
border-right-style: double; 两条实线
简写:
border: none 无边框
border: 10px solid yellow;
border-radius: 50%; # 设置圆
border-radius: 10px 20px 30px 40px; # 设置边角
/*小三角 箭头指向下方*/ div{ width: 0; height: 0; border-bottom: 20px solid red; border-left: 20px solid transparent; border-right: 20px solid transparent; }
(3)margin
外边距: 控制元素与元素之间的距离
注意:margin会改变实际大小,背景色不会渲染到margin区域 这个区域会以空白显示,但是也属于盒子的一部分。
margin-top: 20px; margin-left: 40px; margin-bottom: 20px; margin-right: 40px; #上 右 下 左 margin: 20px 30px 40px 50px; #上 左右 下 margin: 20px 30px 40px; #上下 左右 margin: 20px 40px; #上下左右 margin-bottom: 50px; #水平居中 盒子元素 margin: 0 auto;
注意:
margin塌陷:当给两个兄弟盒子 设置垂直方向上的margin 那么以较大的为准,那么我们称这种现象叫塌陷
善用父级的padding,而不是使用margin :因为父亲没有border,那么儿子margin实际上踹的是“流” 踹的是行
所以父亲就掉下来
10、display visibility 属性
# dispaly 1.控制HTML元素的显示和隐藏
2.块级元素与行内元素的转换。
display:block display:inline display:inline-block display:none # visibility visibility:hidden # 区别 visibility:hidden----将元素隐藏,但是还占着位置,影响页面布局 display:none----将元素的显示设为无,不占任何的位置,不影响
11、float浮动
文档流:指的是元素排版布局过程中,元素会自动从左往右,从上往下的流式排列。
浮动特性
1.浮动的元素脱标
2.浮动的元素互相贴靠
3.浮动的元素有“字围”效果
4.收缩的效果
浮动影响:
浮动可以使元素按指定方向排列,直到遇到父元素的边界或另一个浮动元素停止。
float:left:左浮动 左侧为起始,从左向右排列
float:right:右浮动 右侧为起始,从右向左排列
float:none :不浮动,默认不浮动
浮动效果:
1.浮动可以使元素脱离文档流,不占位置
脱离文档流,也就是将元素从普通的布局排版中拿走,
其他盒子在定位的时候,会当做脱离文档流的元素不存在而进行定位。
2.浮动会使元素提升层级
3.浮动可以使块元素在一行内排列,不设置宽高时,可以使元素适应内容
4.浮动可以使行内元素支持宽高
# 浮动产生的问题: 父元素不设置高度时,子元素设置了浮动,不会撑开父元素的高度,此时父盒子没有高度了。因为子元素不占位置了! 如果在父盒子下面还有一个标准流的盒子,那么就会影响页面的布局。------清除浮动 # 解决办法: 1.给父盒子设定固定高度;缺点:不灵活; 2.给浮动元素最后一个加一个空的块级元素,且该元素为不浮动float:none,设置clear:both,就会撑开盒子。 缺点:结构冗余 3.官方推荐:推荐使用: .wrap:after{ content: '.'; display: block; height: 0; visibility: hidden; clear: both; } 4.推荐使用:给父元素添加overflow:hidden eg: .warp{overflow: hidden;}
12、position、z-index 属性
(1)position
position: absolute; top: 20px; bottom: 10px; left: 20px; right: 0px; static : 默认值 relative : 相对定位 有bug 1. 不设置偏移量的时候,对元素没有任何影响。 2. 相对定位可以提升层级关系。 3. 相对定位是相对于自身定位。 absolute : 绝对定位 1. 可以提升层级关系。 2. 脱离文档流。 3. 在没有父级元素定位时,以浏览器的左上角为基准定位的。 4. 有父级的情况下,父级设置相对定位,子集设置绝对定位,是以父盒子进行定位的。 (父相子绝) 来进行位置的调整 fixed : 固定定位(返回顶部)
父相子绝
.box{ width: 300px; height: 300px; border: 5px solid red; margin: 100px; /*父盒子设置相对定位*/ position: relative; padding: 50px; } .box p{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: pink; /*子元素设置了绝对定位*/ position: absolute; top: 10px; left: 20px; }
绝对定位盒子居中
.box .c{ width: 960px; height: 69px; background-color: pink; /*margin: 0 auto;*/ position: relative; left: 50%; margin-left: -480px; /*设置绝对定位之后,margin:0 auto;不起任何作用, 如果想让绝对定位的盒子居中。当做公式记下来 设置子元素绝对定位, 然后left:50%; margin-left等于元素宽度的一半, 实现绝对定位盒子居中*/ }
(2)z-index
position: absolute;
z-index: 3;
z-index: 1000;
注:
数字大的压着数字小的,默认为0
从父现象
13、网页布局
网页布局:
上下 结构
上中下 结构
上左右下 结构: 1-2-1 结构
上左中右下 结构: 1-3-1 结构
一般css先这样写:
*{padding:0;margin:0;}
ul>li{list-style:none;}
a{text-decoration:none;}
.wrap{100%;}
.header{}
.content{}
.footer{}
...
...