1.选择器
首先来说一下,什么是选择器。在一个HTML页面中会有很多很多的元素,不同的元素可能会有不同的样式,某些元素又需要设置相同的样式,选择器就是用来从HTML页面中查找特定元素的,找到元素之后就可以为它们设置样式了。 选择器为样式规则指定一个作用范围。

2.基础选择器
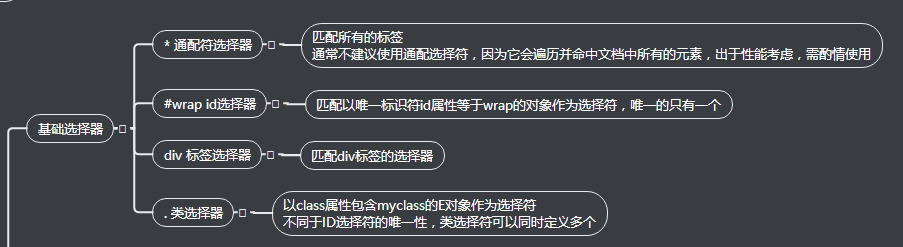
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>基本选择器</title> <style type="text/css"> /*CSS的选择器分为:1.基本选择器 2.高级选择器*/ /*1.标签选择器 可以选中所有的标签元素,比如div li ul p 不管标签藏的多深,都能选中 选中的是所有的,而不是某一个,是共性 */ p { color: red; } /*2.id选择器: id是唯一的,同一个页面id不能重复 任何的标签都可以设置id id命名规范,字母数字下划线,严格区分大小写aaAA */ #user { background-color: yellow; } /*3.类选择器 1.所谓类 就是class . class与id非常相似 任何的标签都可以加类 但是类是可以重复 归类 2.同一个标签中可以携带多个类 用空格隔开 类的使用 能够决定前端工程师的css水平到底有多牛逼? 一定要有”公共类“的概念 */ .c1 { color: blue; } .c2{ background-color: red; } .c3{ font-size: 12px; } /*通用选择器*/ *{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } </style> </head> <body> <div> <p>我是哪一个段落</p> </div> <div> <label for="user">用户名</label> <input type="text" id="user" /> <label for="USER"> 密码</label> <input type="text" id="USER" /> </div> <div class="c1"> 我有c1 </div> <div class="c1 c2"> <h2>我是c1 c2类</h2> </div> <div class="c2 c3"> <h3>我有c2 c3类</h3> </div> </body> </html>

3.类选择器:解耦
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>类选择器</title> <style type="text/css"> /*总结:解耦,耦合 1.不要去试图用一个类将我们的页面写完。这个标签要携带多个类,共同设置样式 2.每个类要尽可能的小,有公共的概念,能够让更多的标签使用 玩好了类 就等于玩好了css中的1/2 到底使用id还是用class? 答案:尽可能的用class。除非一些特殊情况可以用id 原因:id一般是用在js的。也就是说 js是通过id来获取到标签 */ .lv1{ color: green; text-decoration: underline; } .lv2{ font-size:24px; text-decoration: underline; } .lv3{ color: green; font-size:24px; } .c-green{ color: green; } .font-size{ font-size:24px; } .line{ text-decoration: underline; } </style> </head> <body> <div> <p class="lv1">段落1</p> <p class="lv2">段落2</p> <p class="lv3">段落3</p> </div> <div> <p class="c-green line">解耦1</p> <p class="font-size line">解耦2</p> <p class="font-size c-green">解耦3</p> </div> </body> </html>

4.高级选择器



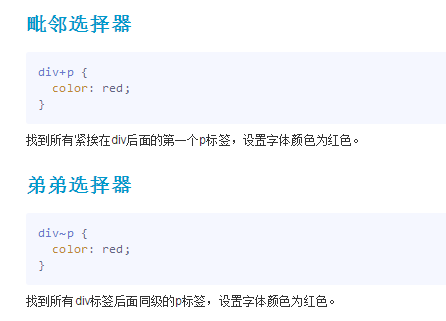
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>高级选择器</title> <style type="text/css"> /*后代选择器 在css中使用非常频繁*/ div p{ color: red; } .container div p{ color: green; } /*子代选择器,必须是父子关系*/ .container2>p{ color: #f0ad4e; } /*交集选择器 必须是h3 必须有active属性*/ h3{ width:300px; color: red; } .active{ font-size: 30px; } h3.active{ background-color: yellow; } /*分组选择器 并集选择器(组合) 相比通用选择器,效率更好 设置多个标签中的统一样式 */ body,div,ol,ul{ margin:0; padding: 0; } /*通用选择器: 性能比较差*/ *{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } </style> </head> <body> <div> <p>this is 段落</p> </div> <div class="container"> <div> <p>this is parg</p> </div> </div> <div class="container2"> <p>this is 父子关系</p> </div> <h3>我是h3</h3> <span class="active">我是h3</span> <h3 class="active">我是h3</h3> </body> </html>

5.属性选择器
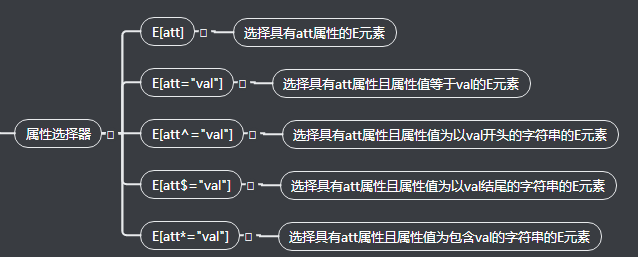
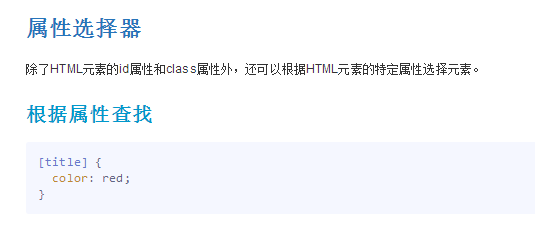


<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>属性选择器</title> <style type="text/css"> label[for]{ color: red; font-size: 20px; } label[for='pwd']{ color: yellow; } /*以...开头*/ label[for^='vip']{ font-size: 30px; } /*以...结尾*/ label[for$='p2']{ font-size: 20px; } label[for*='ser']{ color: green; } input[type='text']{ background-color: purple; } </style> </head> <body> <!-- 属性选择器 通常在 表单控件中 使用比较频繁--> <div class="box"> <form action=""> <label for="user">用户名:</label> <input type="text" name="" id="user"> <label for="pwd">密码:</label> <label for="vip1">vip1</label> <label for="vip2">vip2</label> <label for="user2">用户名2:</label> <label for="user3">用户名3:</label> </form> </div> </body> </html>

6.伪类选择器
(1)a标签的love hate
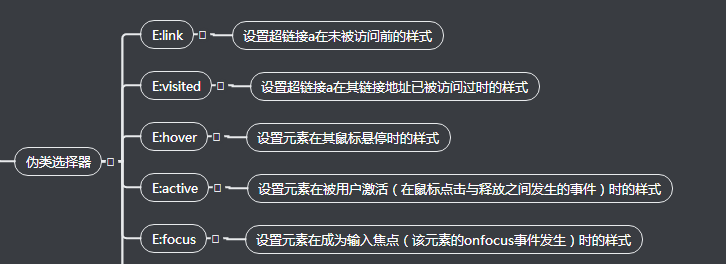

(2)nth-child用法
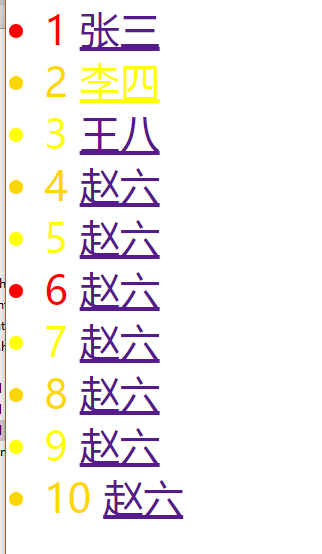
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>伪类选择器</title> <style type="text/css"> /*1.伪类选择器*/ /*'爱恨原则' love hate*/ /*没有被访问的a标签的样式*/ .box ul li.item1 a:link{ color: #666; } /*访问过后的a标签的样式*/ .box ul li.item2 a:visited{ color: yellow; } /*鼠标悬停时a标签的样式*/ .box ul li.item3 a:hover{ color: green; } /*鼠标点住的时候a标签的样式*/ .box ul li.item4 a:active{ color: yellowgreen; } input:focus { outline: none; background-color: darkred; } /*选中第一个元素*/ div ul li:first-child{ font-size: 20px; color: red; } /*选中最后一个元素*/ div ul li:last-child{ font-size: 20px; color: yellow; } /*选中当前指定的元素 数值从1开始*/ div ul li:nth-child(3){ font-size: 30px; color: purple; } /*n表示选中所有 从0开始的 0的时候表示没有选中*/ div ul li:nth-child(n){ font-size: 40px; color: red; } /*偶数*/ div ul li:nth-child(2n){ font-size: 50px; color: gold; } /*奇数*/ div ul li:nth-child(2n-1){ font-size: 50px; color: yellow; } /*隔几换色 隔行换色*/ div ul li:nth-child(5n+1){ font-size: 50px; color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"> <ul> <li class="item1"> 1 <a href="#">张三</a> </li> <li class="item2"> 2 <a href="#">李四</a> </li> <li class="item3"> 3 <a href="#">王八</a> </li> <li class="item4"> 4 <a href="#">赵六</a> </li> <li class="item4"> 5 <a href="#">赵六</a> </li> <li class="item4"> 6 <a href="#">赵六</a> </li> <li class="item4"> 7 <a href="#">赵六</a> </li> <li class="item4"> 8 <a href="#">赵六</a> </li> <li class="item4"> 9 <a href="#">赵六</a> </li> <li class="item4"> 10 <a href="#">赵六</a> </li> </ul> </div> </body> </html>
7.伪元素选择器

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>伪元素</title> <style type="text/css"> /*设置第一个首字母的样式*/ div:first-letter{ color: red; font-size:22px; } /* 在....之前 添加内容 这个属性使用不是很频繁 了解 使用此伪元素选择器一定要结合content属性 */ p:before{ content:'alex'; } /*在....之后 使用非常频繁 通常与咱们后面要讲到布局 有很大的关联(清除浮动)*/ p:after{ content: '&&&&'; color: red; font-size: 40px; } </style> </head> <body> <div> 我是一个段落 </div> <p> 我是一个段落2 </p> </body> </html>

8.css的继承性
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>继承性</title> <style type="text/css"> .father{ font-size: 30px; background-color: green; } .child{ color: purple; } </style> </head> <body> <!-- 继承:给父级设置一些属性,子级继承了父级的该属性,这就是我们的css中的继承 有一些属性是可以继承下来 : color 、 font-*、 text-*、line-* 文本元素 像一些盒子元素,定位的元素(浮动,绝对定位,固定定位)不能继承 --> <div class="father" id="egon"> <div class="child"> <p>alex</p> </div> </div> <p>小马哥</p> </body> </html>

9.选择器的优先级
我们现在已经学过了很多的选择器,也就是说我们有很多种方法从HTML中找到某个元素,那么就会有一个问题:如果我通过不用的选择器找到了相同的一个元素,并且设置了不同的样式,那么浏览器究竟应该按照哪一个样式渲染呢?也就是不同的选择器它们的优先级是怎样的呢?
是先来后到呢还是后来居上呢?统统不是,它是按照下面的选择器的权重规则来决定的。

注意:
还有一种不讲道理的!import方式来强制让样式生效,但是不推荐使用。因为大量使用!import的代码是无法维护的。

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> p{ color: red !important; font-size: 30px; } .spe1{ color: yellow ; font-size: 40px; } .spe2{ color: green; font-size: 40px; } ul{ color: red; } .list{ color: purple !important; } </style> </head> <body> <!-- !important:设置权重为无限大 !important 不影响继承来的权重,只影响选中的元素 --> <div> <p class="spe1 spe2">我是什么颜色</p> <p class="spe2 spe1">我是什么颜色</p> </div> <div class="list"> <ul> <li> 我是一个li标签 </li> </ul> </div> </body> </html>

10.CSS的层叠性
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>层叠性</title> <style type="text/css"> /*1 0 0*/ #box{ color: red; } /*0 1 0*/ .container{ color: yellow; } /*0 0 1*/ p{ color: purple; } </style> </head> <body> <!-- 层叠性: 权重的标签覆盖掉了权重小的标签,说白了 ,就是被干掉了 权重: 谁的权重大,浏览器就会显示谁的属性 谁的权重大? 非常简单 数数 id的数量 class的数量 标签的数量 --> <p id="box" class="container"> 猜猜我是什么颜色 </p> </body> </html>


<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> /*2 0 1*/ #box1 #box2 p{ color: yellow; } /*1 1 1*/ #box2 .wrap3 p{ color: red; } /*1 0 3*/ div div #box3 p{ color: purple; } /*0 3 4*/ div.wrap1 div.wrap2 div.wrap3 p{ color: blue; } </style> </head> <body> <div id='box1' class="wrap1"> <div id="box2" class="wrap2"> <div id="box3" class="wrap3"> <p>再来猜猜我是什么颜色?</p> </div> </div> </div> </body> </html>


<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> /*1 1 1 */ /*#box2 .wrap3 p{ color: yellow; }*/ /*1 1 1*/ /*#box1 .wrap2 p{ color: red; }*/ /* 0*/ /*继承来的*/ #box1 #box2 .wrap3{ color: red; } .wrap1 #box2 .wrap3{ color: green; } /*选中来的*/ /*1 1 1*/ /*#box2 .wrap3 p{ color: green; }*/ </style> </head> <body> <!-- 当权重一样的时候 是以后设置的属性为准。 前提权重一样 ,后来者居上 继承来的属性 权重为0 总结: 1.先看标签元素有没有被选中,如果选中了,就数数 (id,class,标签的数量) 谁的权重大 就显示谁的属性。权重一样大,后来者居上 2.如果没有被选中标签元素,权重为0。 如果属性都是被继承下来的 权重都是0 。权重都是0:"就近原则" : 谁描述的近,就显示谁的属性 --> <div id='box1' class="wrap1"> <div id="box2" class="wrap2"> <div id="box3" class="wrap3"> <p>再来猜猜我是什么颜色?</p> </div> </div> </div> </body> </html>