VUE文档 https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/
1、vue的介绍
尤雨溪
1、vue的优点


2、vue的介绍


3、vue的安装




4、声明式渲染
<body> <div id="app1"> <!-- 插值语法 react {} angular {{}} {%%} <% = %> 你可以任意插 --> <h3>{{title}}</h3>
<h3>{{ 1>2?"true":"false"}}</h3>
</div> <script src="vue.js"> </script> <script> // vue实例化对象 var app = new Vue({ el: "#app1", // 所有的数据都放在数据属性中 data:{ title:"土豆" } }) // 不推荐 console.log(app) console.log(app.$el) console.log(app.$data) console.log(app.$data.title) </script> </body>

2、指令系统介绍
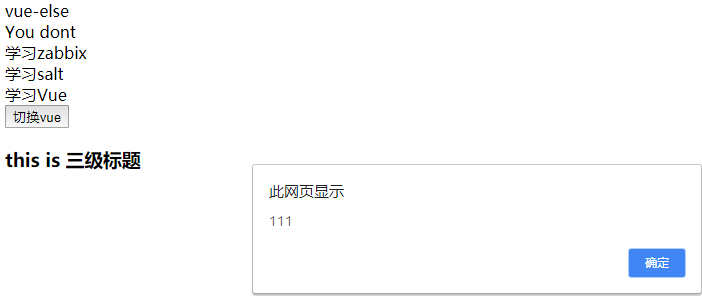
1、v-if v-for v-on v-show
<body> <div id="app"> <!-- v-if --> <div v-if='show'>vue-if</div> <div v-else>vue-else</div> <div v-if='Math.random() > 0.5'>Now you see </div> <div v-else>You dont</div> <!-- v-for --> <div v-for="todo in todolist">{{todo.text}}</div> <!-- v-show --> <h3 v-show='isShow'>this is 三级标题</h3> <!-- v-on --> <button v-on:click="clickHandler">切换vue</button> </div> <script src="vue.js"></script> <script> // vue的实例对象 // 指令系统 v-* var app = new Vue({ el: "#app", data:{ show: false, todolist:[ {text:"学习zabbix"}, {text:"学习salt"}, {text:"学习Vue"}, ], isShow:true }, methods:{ clickHandler:function(){ alert(111) console.log(this) //整个网页就一个实例化对象 this.show = !this.show this.isShow = !this.isShow } } }) // MVVM Model View ViewModel // MTV Model Template View </script> </body>


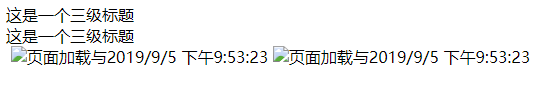
2、v-bind
<body> <div id="app"> <!-- v-bind --> <div title="嘿嘿">这是一个三级标题</div> <div v-show='isShow' v-bind:title='data'>这是一个三级标题</div> <img src="" alt=""> <img v-bind:src='imgSrc' v-bind:alt="imgAlt"> <!-- 简便写法 v-bin:src :src v-on:click @click --> <img :src='imgSrc' :alt="imgAlt"> </div> <script src="vue.js"></script> <script> // vue的实例对象 // 指令系统 v-* var app = new Vue({ el: "#app", data:{ isShow:true, data:"hahah", imgSrc:'./images/shiyun.jp', imgAlt: `页面加载与${new Date().toLocaleString()}` }, }) </script> </body>
3、v-bind: class与style绑定
传个 v-bind:class 一个对象,以动态地切换class
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> <style type="text/css"> .box{ width:100px; height: 100px; background: red; } .box2{ width:100px; height: 100px; background: green; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <div class="box" v-bind:class={box2:isGreen} ></div> <button @click='changeColor'>切换颜色</button> </div> <script src="vue.js"></script> <script> // vue的实例对象 // 指令系统 v-* var app = new Vue({ el: "#app", data:{ isGreen:false }, methods:{ changeColor:function(){ this.isGreen = !this.isGreen }, } }) </script> </body> </html>


4、vue核心思想:数据驱动视图,双向数据绑定
<body> <div id="app"> <!-- 核心思想概念:数据驱动视图 --> <!-- 双向数据绑定 --> <button v-on:click = 'count+=1'> 加 {{count}}</button> </div> <script src="vue.js"></script> <script> // vue的实例对象 // 指令系统 v-* var app = new Vue({ el: "#app", data:{ count:0 }, methods:{ } }) </script> </body>
声明式的指令 :之前写的html,都是
命令式的:Vue
5、监听事件

6、应用:轮播图
版本1

<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 列表渲染 :轮播图 -->
<!-- 传统写法 -->
<div>
<img src="./images/vue.png" alt="">
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
</ul>
</div>
<!-- Vue -->
<div>
<img :src="imgSrc" >
<ul>
<li v-for = "(item,i) in imgArr" @click='ChangeImgSrc(item)'>{{ i+1 }}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<button @click='nextImg'>下一张</button>
</div>
<script src="vue.js"></script>
<script>
// vue的实例对象
// 指令系统 v-*
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data:{
imgSrc:'./images/1.png',
imgArr:[
{id:1, src:'./images/1.png'},
{id:2, src:'./images/2.png'},
{id:3, src:'./images/3.png'},
{id:4, src:'./images/4.png'}
],
currentIndex:0
},
methods:{
ChangeImgSrc(item){
this.imgSrc = item.src
},
nextImg(){
if (this.currentIndex==this.imgArr.length-1){
this.currentIndex=-1
}
this.currentIndex ++
this.imgSrc = this.imgArr[this.currentIndex].src
}
}
})
</script>
</body>


版本2:添加定时器

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> <style type="text/css"> ul{ width:180px; overflow: hidden; list-style: none; } ul li{ float: left; width: 30px; height: 30px; background: peachpuff; margin-left: 10px; line-height: 30px; text-align: center; color: black } </style> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <!-- 列表渲染 :轮播图 --> <!-- 传统写法 --> <div> <img src="./images/vue.png" alt=""> <ul> <li>1</li> <li>2</li> <li>3</li> <li>4</li> </ul> </div> <!-- Vue --> <div> <img :src="imgSrc" @mouseenter="closeTimer" @mouseleave="openTimer"> <ul> <li v-for = "(item,i) in imgArr" @click='ChangeImgSrc(item)'>{{ i+1 }}</li> </ul> </div> <button @click='nextImg'>下一张</button> </div> <script src="vue.js"></script> <script> // vue的实例对象 // 指令系统 v-* var app = new Vue({ el: "#app", data:{ imgSrc:'./images/1.png', imgArr:[ {id:1, src:'./images/1.png'}, {id:2, src:'./images/2.png'}, {id:3, src:'./images/3.png'}, {id:4, src:'./images/4.png'} ], currentIndex:0, timer:null // 3.0 鼠标移到停止 }, created(){ // 生命周期方法 // 开启定时器 // 提前获取cookie和session this.timer = setInterval(this.nextImg,2000) console.log(1111) }, methods:{ ChangeImgSrc(item){ this.imgSrc = item.src }, nextImg(){ if (this.currentIndex==this.imgArr.length-1){ this.currentIndex=-1 } this.currentIndex ++ this.imgSrc = this.imgArr[this.currentIndex].src }, closeTimer(){ clearInterval(this.timer) // 鼠标enter,停止定时器 }, openTimer(){ this.timer = setInterval(this.nextImg,2000) // 重新开启定时器 } } }) </script> </body> </html> 作业: 1、标号颜色 2、下一张
7、v-html:解析标签

<body> <div id="app"> <!-- 为什么需要v-html,解析标签 --> <div>{{str}}</div> <div v-html="str"></div> </div> <script src="vue.js"></script> <script> // vue的实例对象 // 指令系统 v-* var app = new Vue({ el: "#app", data:{ str:"<p>为什么需要v-html,解析标签</p>" }, methods:{ } }) </script> </body>
8、计算属性 :getter setter
(1)getter

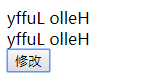
<body> <!-- 计算属性 --> <div id="computed"> <!-- 1.0 版本1 --> <div> {{ msg.split('').reverse().join('') }} </div> <!-- 2.0 版本 --> <div> {{ recverseStr }} </div> <!-- 3.0 修改字符串 --> <button @click="clickHandler">修改</button> </div> <script type="text/javascript" src="vue.js"></script> <script> // vue的实例对象 var com = new Vue({ el: "#computed", data:{ msg:"Hello world" }, computed:{ // 计算属性 watch 监听 // 默认只有getter方法 recverseStr(){ return this.msg.split('').reverse().join('') } }, methods:{ clickHandler(){ this.msg = "Hello Luffy" } } }) </script> </body>
(2) setter

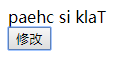
<body> <!-- 计算属性 --> <div id="computed"> <!-- setter --> <div> {{ recverseStr }} </div> <button @click="clickHandler">修改</button> </div> <script type="text/javascript" src="vue.js"></script> <script> // vue的实例对象 var com = new Vue({ el: "#computed", data:{ msg:"Hello world" }, computed:{ // 计算属性 watch 监听 // 默认只有getter方法 // 如何添加set方法 recverseStr:{ set:function(newValue){ this.msg = newValue }, get:function(){ return this.msg.split('').reverse().join(''); } } }, methods:{ clickHandler(){ // this.msg = "Hello Luffy" console.log(this.recverseStr) // GET this.recverseStr = "Talk is cheap" //SET } } }) </script> </body>
9、v-model :双向绑定
(1) v-model 只适用于表单控件 form
<body> <form id="computed"> <!-- v-model --> <!-- 数据的双向绑定 = 单向数据绑定+UI事件监听 --> <input type="text" v-model="msg"> <h3>{{ msg }}</h3> </form> <script type="text/javascript" src="vue.js"></script> <script> // vue的实例对象 var com = new Vue({ el: "#computed", data:{ msg:"123", getValue:"233" }, }) </script> </body>
(2)数据的双向绑定 = 单向数据绑定+UI事件监听
<body> <form id="computed"> <!-- v-model --> <!-- 数据的双向绑定 = 单向数据绑定+UI事件监听 --> <!-- 等价于 --> <input type="text" v-bind:value="getValue" @input="msgChange"> <h3>{{ getValue }}</h3> </form> <script type="text/javascript" src="vue.js"></script> <script> // vue的实例对象 var com = new Vue({ el: "#computed", data:{ getValue:"233" }, methods:{ msgChange(e){ console.log(e) this.getValue = e.target.value } }, computed:{ getValue:{ set:function(newValue){ this.getValue = newValue }, get:function(){ return this.getValue } } } }) </script> </body>

(3)计算属性应用
10、vue表单
https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/forms.html



<body> <form id="computed"> <!-- v-model --> <!-- 数据的双向绑定 = 单向数据绑定+UI事件监听 --> <input type="text" v-model="msg"> <!-- 使用 change 事件进行同步 --> <input type="text" v-model.lazy="msg"> <!-- 输入值转为数值类型 --> <input type="text" v-model.number="msg"> <!-- 首尾空白字符 --> <input type="text" v-model.trim="msg"> <h3>{{ msg }}</h3> </form> <script type="text/javascript" src="vue.js"></script> <script> // vue的实例对象 var com = new Vue({ el: "#computed", data:{ msg:"123", getValue:"233" }, }) </script> </body>
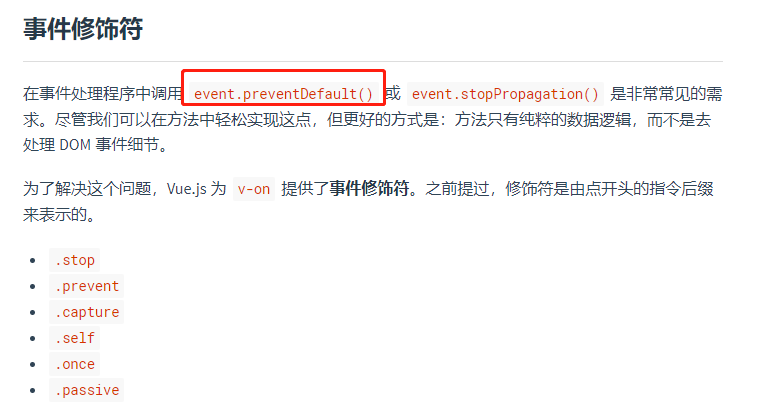
11、事件处理
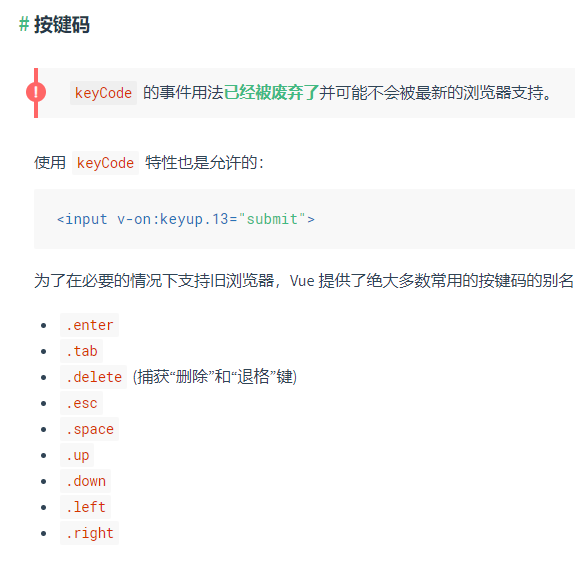
https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/events.html#事件修饰符

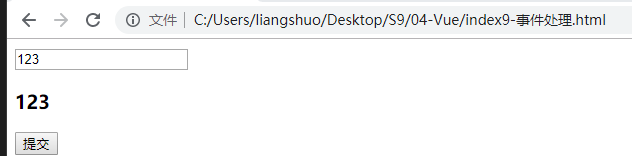
<body> <!-- 阻止表单提交 --> <!-- <form id="computed" > --> <form id="computed" @submit.prevent> <input type="text" v-model="msg"> <h3>{{ msg }}</h3> <input type="submit" name="" value="提交"> </form> <script type="text/javascript" src="vue.js"></script> <script> // vue的实例对象 var com = new Vue({ el: "#computed", data:{ msg:"123", getValue:"233" }, methods:{ // ajax技术 // jquery ---> $ajax() 封装了(xmlhttpRequest) // vue --> axios } }) </script> </body>
3、音乐播放器
1、目录结构,rest css
reset css
https://meyerweb.com/eric/tools/css/reset/
2、v-for,@click:点击切换歌曲

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> <style type="text/css"> *{ padding:0 } ul{ list-style: none; } li{ border-bottom: 1px solid gray; } </style> </head> <body> <!-- 1.0 死写法 --> <audio src="./audios/1.mp3" autoplay="" controls=""></audio> <!-- 2.0 循环指令 --> <div id="music"> <audio :src="currentSong" autoplay="" controls="" ></audio> <ul> <li v-for="(item,index) in songs" @click='clickHandler(index)'> <h3>歌名:{{ item.name }}</h3> <p>歌手:{{ item.author }}</p> </li> </ul> </div> <script type="text/javascript" src="vue.js"> </script> <script> var songs = [ {id:1, src:"./audios/1.mp3", name:"la la la", author:"Rla"}, {id:2, src:"./audios/2.mp3", name:"kkkk kkk", author:"kkaa"}, {id:3, src:"./audios/3.mp3", name:"thththt", author:"thth"}, {id:4, src:"./audios/4.mp3", name:"four four", author:"Four"} ] var musci = new Vue({ el: "#music", data:{ songs:songs, currentSong:"./audios/1.mp3", currentIndex:0 }, methods:{ // 点击,切换下一首歌曲 clickHandler(index){ this.currentSong = this.songs[index].src; }, }, computed:{ }, created(){ // 通常都用来做页面的初始化 } }) </script> </body> </html>
3、@ended :播放结束,切换下一首
<body> <!-- 2.0 循环指令 --> <div id="music"> <audio :src="currentSong" autoplay="" controls="" @ended='nextSong'></audio> <ul> <li v-for="(item,index) in songs" @click='clickHandler(index)'> <h3>歌名:{{ item.name }}</h3> <p>歌手:{{ item.author }}</p> </li> </ul> </div> <script type="text/javascript" src="vue.js"> </script> <script> var songs = [ {id:1, src:"./audios/1.mp3", name:"la la la", author:"Rla"}, {id:2, src:"./audios/2.mp3", name:"kkkk kkk", author:"kkaa"}, {id:3, src:"./audios/3.mp3", name:"thththt", author:"thth"}, {id:4, src:"./audios/4.mp3", name:"four four", author:"Four"} ] var musci = new Vue({ el: "#music", data:{ songs:songs, currentSong:"./audios/1.mp3", currentIndex:0 }, methods:{ // 点击,切换下一首歌曲 clickHandler(index){ this.currentSong = this.songs[index].src; }, // 音频播放完成,切换下一首 方法1 nextSong(){ alert(111) this.currentIndex++; this.currentSong = this.songs[this.currentIndex].src } }, computed:{ }, created(){ // 通常都用来做页面的初始化 } }) </script> </body>
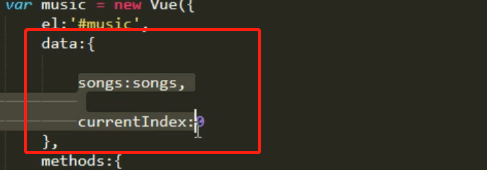
4、computed:实时监控,计算数据属性***
<body> <!-- 1.0 死写法 --> <audio src="./audios/1.mp3" autoplay="" controls=""></audio> <!-- 2.0 循环指令 --> <div id="music"> <!-- 方法2 --> <audio :src="currSong" autoplay="" controls="" @ended='nextSong'></audio> <ul> <li v-for="(item,index) in songs" @click='clickHandler(index)'> <h3>歌名:{{ item.name }}</h3> <p>歌手:{{ item.author }}</p> </li> </ul> <button @click="addOneSong">添加1首歌</button> </div> <script type="text/javascript" src="vue.js"> </script> <script> var songs = [ {id:1, src:"./audios/1.mp3", name:"la la la", author:"Rla"}, {id:2, src:"./audios/2.mp3", name:"kkkk kkk", author:"kkaa"}, {id:3, src:"./audios/3.mp3", name:"thththt", author:"thth"}, {id:4, src:"./audios/4.mp3", name:"four four", author:"Four"} ] var musci = new Vue({ el: "#music", data:{ songs:songs, currentIndex:0 }, methods:{ // 点击,切换下一首歌曲 clickHandler(index){ this.currentIndex = index; }, // 音频播放完成,切换下一首 nextSong(){ this.currentIndex++; }, // 添加1首歌 addOneSong(){ this.songs.push({id:5, src:"./audios/5.mp3", name:"qqq", author:"qqq"}) } }, computed:{ // 方法2 currsong 实时监听,数组 index // 计算属性:计算数据属性,data中的数据 // 数据驱动视图 currSong(){ return this.songs[this.currentIndex].src } }, created(){ // 通常都用来做页面的初始化 } }) </script> </body>
计算属性:data中的数据
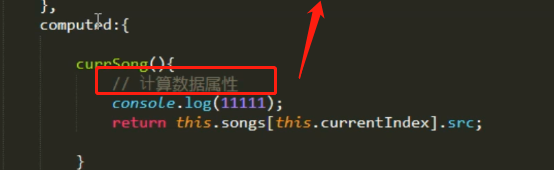
网页中的实时监控
4、作业与总结
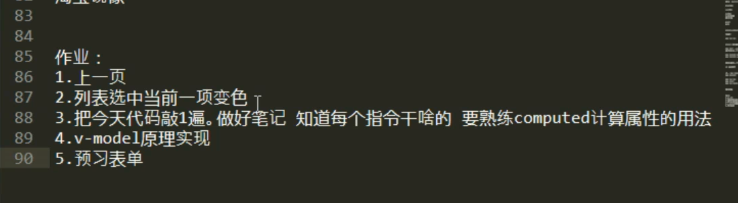
1、作业

2、总结