1. 配置管理:state和file
https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/topics/states/index.html
1.state状态模块
希望主机,apache ,启动状态,关闭状态,
写法1
[root@linux-node1 web]# pwd /srv/salt/base/web [root@linux-node1 web]# vim apache.sls apache: pkg.installed: - name: httpd service.running: - name: httpd file.managed: - name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf - source: salt://apache/files/httpd.conf - usr: root - group: root - mode: 644
Id声明,全局(test,dev,base环境)唯一
Pkg 状态模块
. 引用方法
Installed 模块方法
Name: httpd 参数
2.file 文件管理模块
Name :管理文件的路径
在id,Apache下,每个模块只能用一次
写法2
[root@linux-node1 web]# vim apache.sls apache-install: pkg.installed: - name: httpd apache-service: service.running - name: httpd apache-config: file.managed: - name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf - source: salt://apache/files/httpd.conf - usr: root - group: root - mode: 644
写法3
没有声明name,id就是name

apache: pkg.installed: - name: httpd service.running: - name: httpd file.managed: - name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf - source: salt://apache/files/httpd.conf - usr: root - group: root - mode: 644 /etc/httpd/conf/php.conf file.managed: - source: salt://apache/files/php.conf - user: root - group: root - mode: 644

2.自动化安装LAMP:状态设计
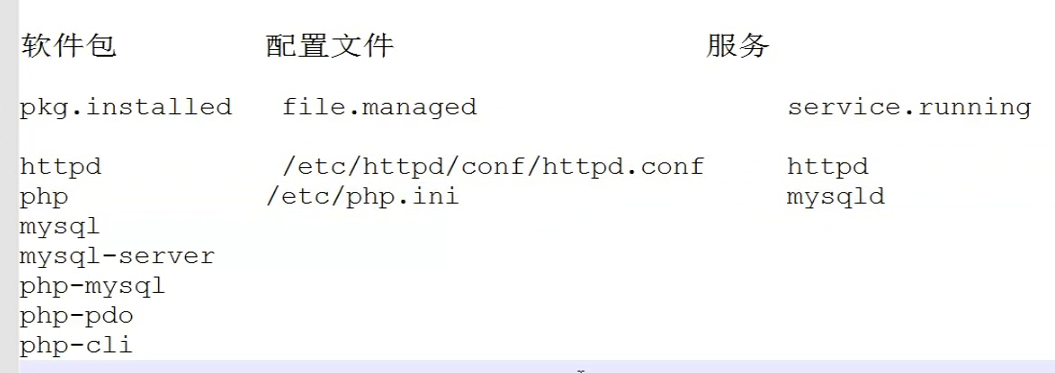
1. Pkg模块
指定版本
指定仓库
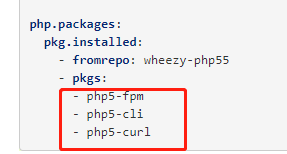
需要安装的软件包
[root@linux-node1 web]# yum install -y httpd php mysql-server php-mysql php-pdo php-cli
2. jinja模板
监控本地的mac ip
用模板的实现jinja
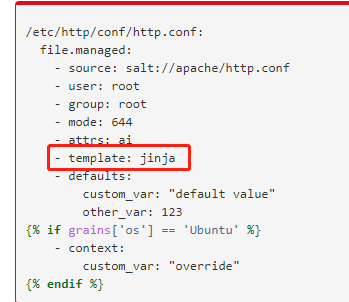
3.file模块
File可以使用grains
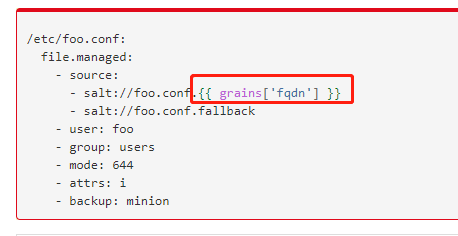
4.Service模块
监控文件,文件更新,自动重载服务
3.LAMP的状态实现
学saltstack,学的是思路,三段式
前期版本:
学习状态,先把安装,配置写在一起
三段式: 安装 配置 启动
创建目录
[root@linux-node1 prod]# pwd
/srv/salt/prod
[root@linux-node1 prod]# mkdir apache
[root@linux-node1 prod]# mkdir php
[root@linux-node1 prod]# mkdir mysql
1.apache
# sls 配置文件
[root@linux-node1 prod]# cd apache/
[root@linux-node1 apache]# vim apache.sls

apache-install: pkg.installed: - name: httpd apache-config: file.managed: - name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf - source: salt://apache/files/httpd.conf - user: root - group: root - mode: 644 apache-service: service.running: - name: httpd - enable: True
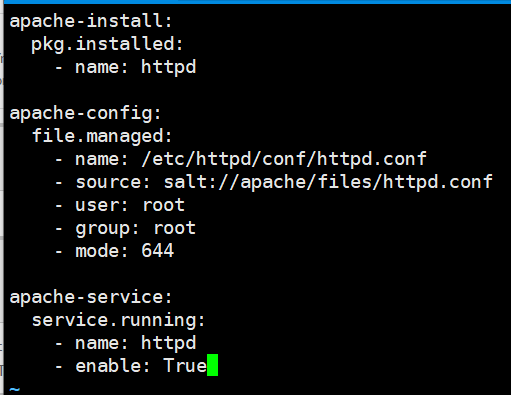
source :对应当前目录,相对路径
- source: salt://apache/files/httpd.conf
你这个环境的根路径 salt: /srv/salt/
# 配置文件,cp
[root@linux-node1 apache]# mkdir files
[root@linux-node1 apache]# cd files/
[root@linux-node1 files]# cp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf .
# 执行命令
默认base目录
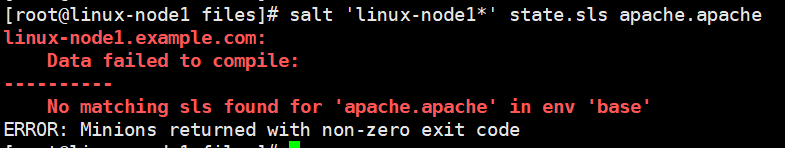
[root@linux-node1 files]# salt 'linux-node1*' state.sls apache.apache saltenv=prod
# test
# init.sls
[root@linux-node1 apache]# pwd
/srv/salt/prod/apache
[root@linux-node1 apache]# mv apache.sls init.sls
2.php
# php目录
Php不需要启动服务,以模块的方式通信
安装多个,查看文档
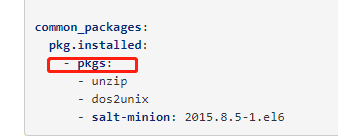
[root@linux-node1 prod]# ls
apache mysql php
[root@linux-node1 prod]# cd php/
[root@linux-node1 php]# mkdir files
[root@linux-node1 php]# vim init.sls
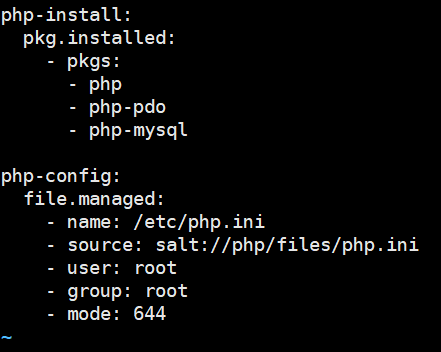
# cp php配置文件
[root@linux-node1 php]# cp /etc/php.ini files/
3.mysql
安装 配置 启动
[root@linux-node1 prod]# vim mysql/init.sls

mysql-install: pkg.installed: - pkgs: - mariadb - mariadb-server mysql-config: file.managed: - name: /etc/my.cnf - source: salt://mysql/files/my.cnf - user: root - group: root - mode: 644 mysql-service: service.running: - name: mariadb - enable: True
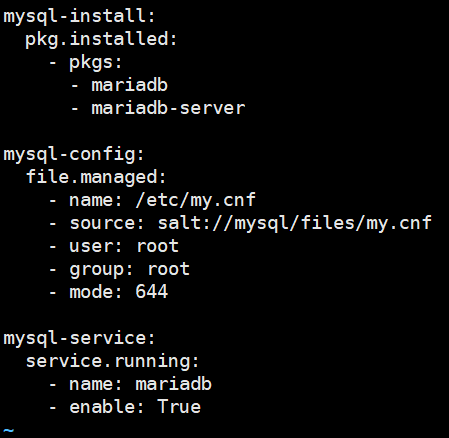
# 配置文件
[root@linux-node1 mysql]# mkdir files
[root@linux-node1 mysql]# cd files/
[root@linux-node1 files]# cp /etc/my.cnf .
4.执行state
文件目录
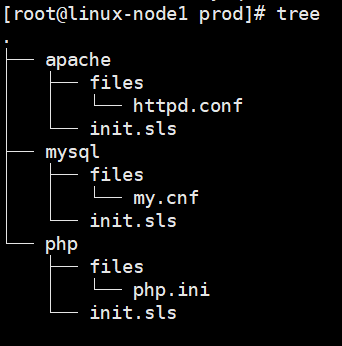
执行
[root@linux-node1 salt]# salt -S '192.168.194.131' state.sls php.init saltenv=prod
[root@linux-node1 salt]# salt -S '192.168.194.131' state.sls mysql.init saltenv=prod
5. 高级状态.
[root@linux-node1 base]# vim top.sls
[root@linux-node1 base]# pwd
/srv/salt/base
[root@linux-node1 base]# salt 'linux-node1*' state.highstate
4. 配置管理:状态间的关系
1. Include功能
https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/topics/tutorials/states_pt3.html
[root@linux-node1 prod]# pwd
/srv/salt/prod
[root@linux-node1 prod]# vim lamp.sls
include: - apache.init - php.init - mysql.init
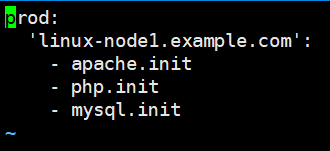
[root@linux-node1 prod]# vim ../base/top.sls
prod: 'linux-node1.example.com': - lamp
[root@linux-node1 prod]# salt -S '192.168.194.131' state.highstate
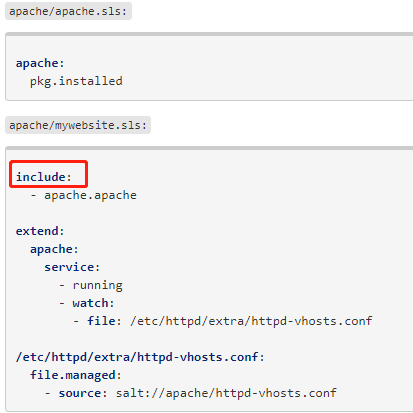
2.Extend扩展功能
- 增加其他功能,修改配置文件,到最终版本
- Extend 语法
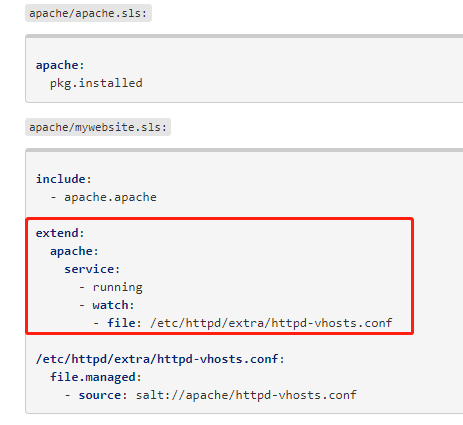
需求:只能在机器1上php-mbstring 包
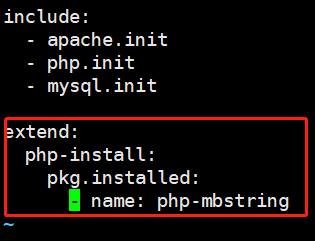
[root@linux-node1 prod]# vim lamp.sls include: - apache.init - php.init - mysql.init extend: php-install: pkg.installed: - name: php-mbstring [root@linux-node1 prod]# salt -S '192.168.194.131' state.highstate
3.Require依赖
需求:if 上个操作,安装不成功或者配置不成功,下一个不执行
(1)反例子
[root@linux-node1 apache]# vim init.sls
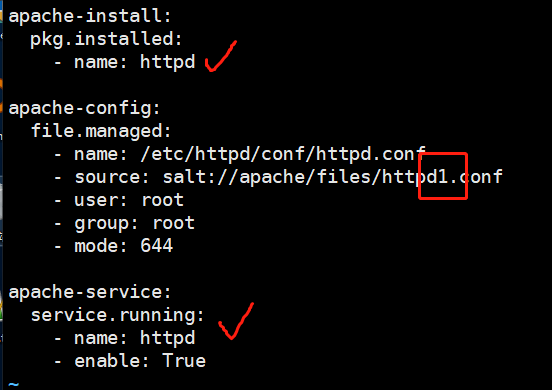
[root@linux-node1 apache]# salt -S '192.168.194.131' state.highstate
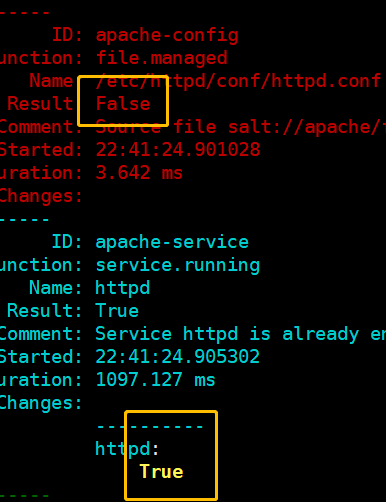
(2)依赖于上个操作
[root@linux-node1 apache]# systemctl stop httpd

apache-install: pkg.installed: - name: httpd apache-config: file.managed: - name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf - source: salt://apache/files/httpd1.conf - user: root - group: root - mode: 644 apache-service: service.running: - name: httpd - enable: True - require: - file: apache-config
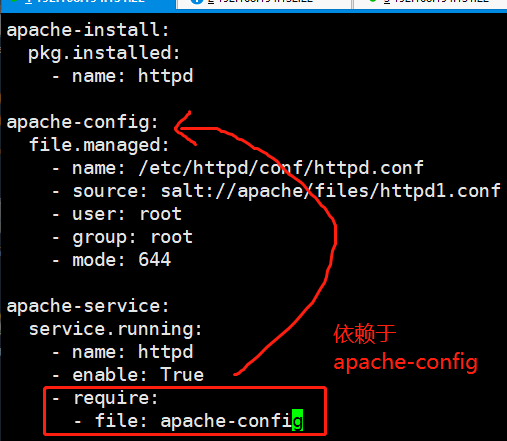
[root@linux-node1 apache]# salt -S '192.168.194.131' state.highstate
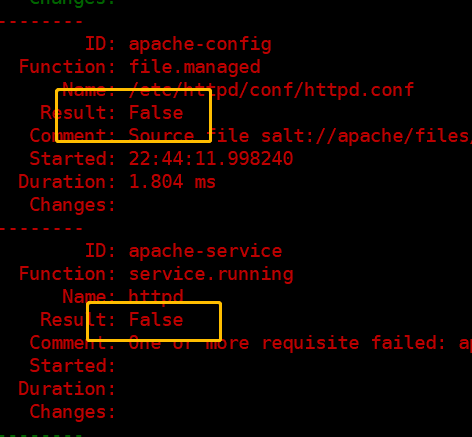
(3)最终版本:
启动 依赖于 安装,配置
[root@linux-node1 apache]# vim init.sls
[root@linux-node1 apache]# salt -S '192.168.194.131' state.highstate

apache-install: pkg.installed: - name: httpd apache-config: file.managed: - name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf - source: salt://apache/files/httpd.conf - user: root - group: root - mode: 644 apache-service: service.running: - name: httpd - enable: True - require: - pkg: apache-install - file: apache-config
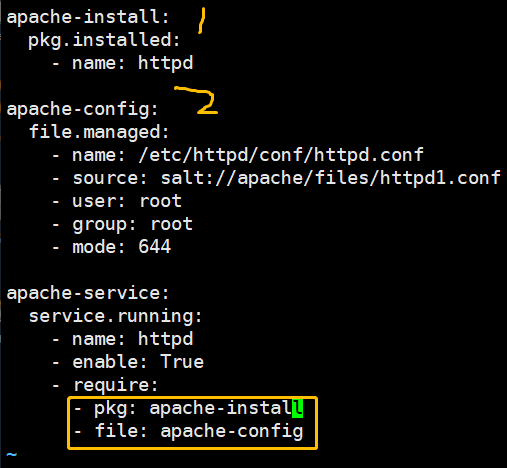
(4)Require 我依赖于谁
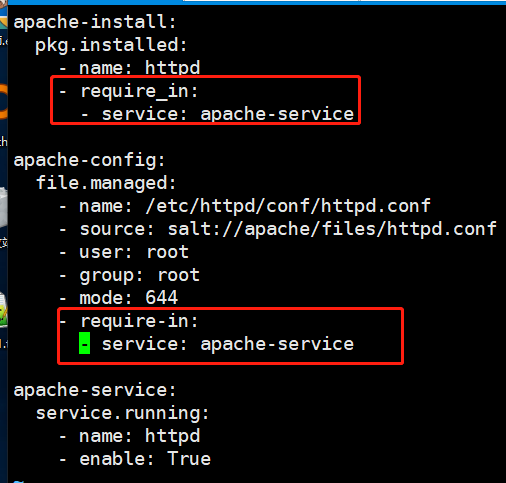
Require_in 我被谁依赖
[root@linux-node1 apache]# vim init.sls

apache-install: pkg.installed: - name: httpd - require_in: - service: apache-service apache-config: file.managed: - name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf - source: salt://apache/files/httpd.conf - user: root - group: root - mode: 644 - require-in: - service: apache-service apache-service: service.running: - name: httpd - enable: True
4.Watch功能:同时有require功能
https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/ref/states/all/salt.states.service.html#salt.states.service.mod_watch
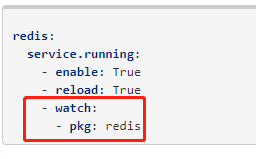
该配置文件变化,这个服务重启,重载
[root@linux-node1 apache]# vim files/httpd.conf
[root@linux-node1 apache]# salt -S '192.168.194.131' state.highstate
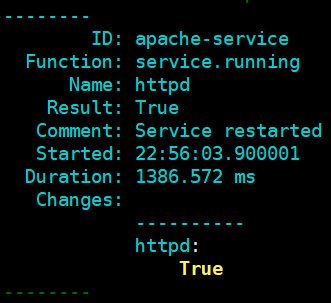
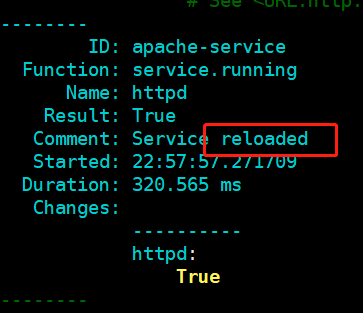
重载
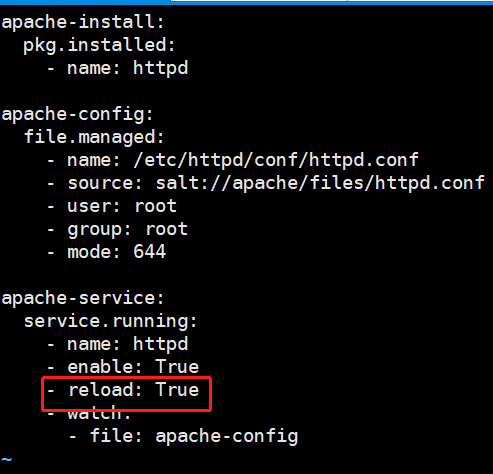

apache-install: pkg.installed: - name: httpd apache-config: file.managed: - name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf - source: salt://apache/files/httpd.conf - user: root - group: root - mode: 644 apache-service: service.running: - name: httpd - enable: True - reload: True - watch: - file: apache-config
Watch_in
[root@linux-node1 apache]# cat init.sls

apache-install: pkg.installed: - name: httpd apache-config: file.managed: - name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf - source: salt://apache/files/httpd.conf - user: root - group: root - mode: 644 - watch_in: - service: apache-service apache-service: service.running: - name: httpd - enable: True - reload: True
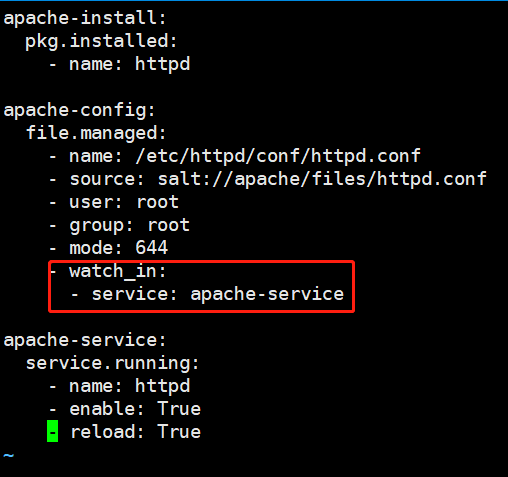
5. 配置管理,状态间的条件判断
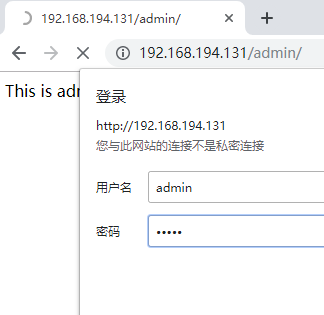
需求:Admin输入用户名,密码才能登陆
1.Apache认证登陆
https://blog.csdn.net/alexander_phper/article/details/52242474
- 修改配置
- 用户名密码文件
(1)配置admin页面
[root@linux-node1 apache]# cd /var/www/html/
[root@linux-node1 html]# mkdir admin
[root@linux-node1 html]# cd admin/
[root@linux-node1 admin]# vim index.html
This is admin
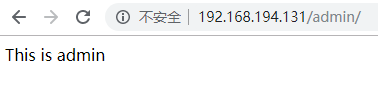
(2)配置
# 配置httpd
[root@linux-node1 files]# pwd
/srv/salt/prod/apache/files
[root@linux-node1 files]# vim httpd.conf

<Directory "/var/www/html/admin"> AllowOverride All Order allow,deny Allow from all AuthType Basic AuthName "hehe" AuthUserFile /etc/httpd/conf/htpasswd_file Require user admin </Directory>
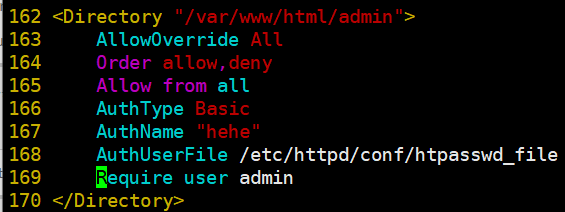
[root@linux-node1 files]# whereis htpasswd
htpasswd: /usr/bin/htpasswd /usr/share/man/man1/htpasswd.1.gz
[root@linux-node1 files]# rpm -qf /usr/bin/htpasswd
httpd-tools-2.4.6-89.el7.centos.x86_64
2. Cmd认证模块
Unless
https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/ref/states/all/salt.states.cmd.html
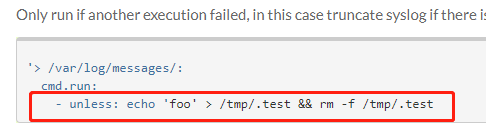
3.配置init.sls
[root@linux-node1 apache]# pwd
/srv/salt/prod/apache
[root@linux-node1 apache]# vim init.sls
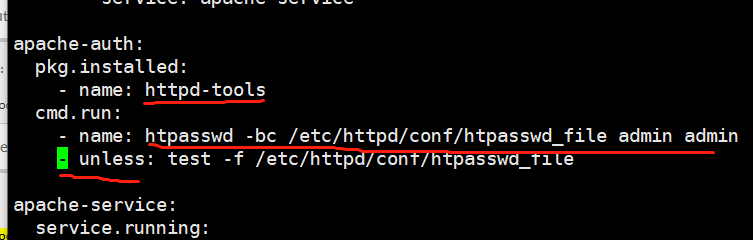
4 unless状态判断
If 文件存在:不执行
Else:不存在,执行

Unless
条件为假,执行
apache-install: pkg.installed: - name: httpd apache-config: file.managed: - name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf - source: salt://apache/files/httpd.conf - user: root - group: root - mode: 644 - watch_in: - service: apache-service apache-auth: pkg.installed: - name: httpd-tools cmd.run: - name: htpasswd -bc /etc/httpd/conf/htpasswd_file admin admin - unless: test -f /etc/httpd/conf/htpasswd_file apache-service: service.running: - name: httpd - enable: True - reload: True
test
6 配置管理 jinja模板
需求:配置文件,监听minion自己本地的ip地址


1.学习方法
1 官方文档
https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/contents.html
2 配置管理
https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/topics/states/index.html
3 file模块
https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/ref/states/all/index.html#all-salt-states
4 搜索jinja
https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/ref/states/all/salt.states.file.html#module-salt.states.file
2.jinja
Salt默认模板 jinja2
Jinja2 是一个现代的,设计者友好的,仿照 Django 模板的 Python 模板语言。
http://docs.jinkan.org/docs/jinja2/templates.html
两种分隔符: {% ... %} 和 {{ ... }} 。
前者用于执行诸如 for 循环 或赋值的语句,
后者把表达式的结果打印到模板上
如何区分这是一个模板
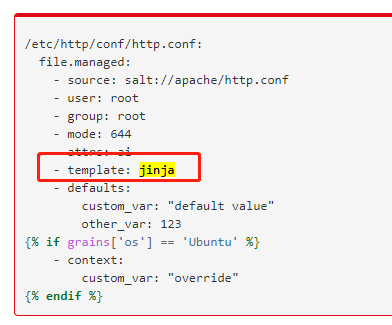
3. 如何配置jinja?
1. 修改模板配置文件
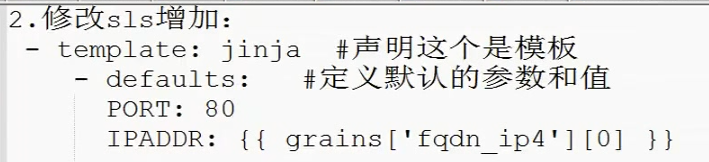
2 修改sls增加
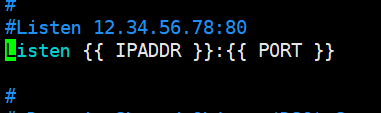
conf配置
[root@linux-node1 apache]# pwd /srv/salt/prod/apache [root@linux-node1 apache]# vim files/httpd.conf Listen {{ IPADDR }}:{{ PORT }}
sls
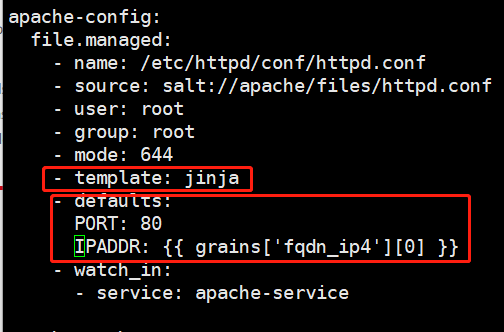
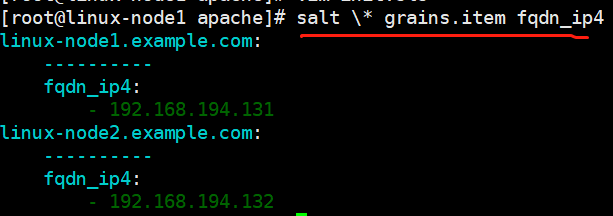
3.验证
[root@linux-node1 apache]# salt -S '192.168.194.131' state.highstate
[root@linux-node1 apache]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
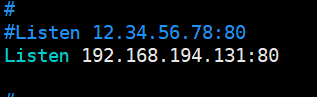
另一个方法:(不推荐)
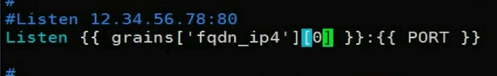
7. job管理
执行1次highstate,会产生1个任务
最近干了什么事
装某个东西,太慢了给我,停止
1.查看job
[root@linux-node1 ~]# cd /var/cache/salt/master/jobs/ [root@linux-node1 jobs]# ls 00 0d 19 27 33 42 50 5a 65 72 7e 8d 9a a5 b4 c0 cd df ea f6 01 0e 1a 28 34 44 51 5b 66 74 80 8e 9b a7 b6 c2 cf e0 eb f8 03 0f 1b 29 35 46 52 5c 67 75 82 8f 9d a8 b8 c4 d2 e1 ec f9 04 10 1c 2a 36 47 53 5d 68 76 83 91 9e a9 b9 c5 d3 e2 ee fa 05 11 1e 2b 37 48 54 5e 69 77 85 93 9f aa ba c6 d4 e3 f0 fb 06 12 1f 2c 38 49 55 5f 6a 78 87 94 a0 ab bb c7 d5 e4 f1 fc 07 13 20 2e 3a 4a 56 61 6b 79 88 95 a1 ac bc c8 d7 e5 f2 fe 0a 14 21 2f 3b 4c 57 62 6c 7a 89 96 a2 ad bd c9 d9 e7 f3 ff 0b 16 22 31 3d 4d 58 63 6e 7b 8a 97 a3 ae be ca da e8 f4 0c 18 25 32 3f 4e 59 64 71 7c 8c 98 a4 b3 bf cc dd e9 f5 [root@linux-node1 jobs]# cd 6c/ [root@linux-node1 6c]# ls 210bdfecd6c424d9d7e1c5bbe2f171 53117bf95a2bea7fbf2d81c8c471ce [root@linux-node1 6c]# ll 210bdfecd6c424d9d7e1c5bbe2f171/ total 4 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 20 Jul 30 22:44 jid drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 35 Jul 30 22:44 linux-node1.example.com [root@linux-node1 6c]# cd 210bdfecd6c424d9d7e1c5bbe2f171/ [root@linux-node1 210bdfecd6c424d9d7e1c5bbe2f171]# cat jid [root@linux-node1 210bdfecd6c424d9d7e1c5bbe2f171]# tree . ├── jid └── linux-node1.example.com ├── out.p └── return.p 1 directory, 3 files
缓存时间默认24h
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master
2.saltutil模块.job
远程执行
https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/topics/execution/index.html
执行模块
https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/ref/modules/all/index.html#all-salt-modules
Saltutil

Test
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt 'linux-node2*' cmd.run 'sleep 160'
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt * saltutil.running
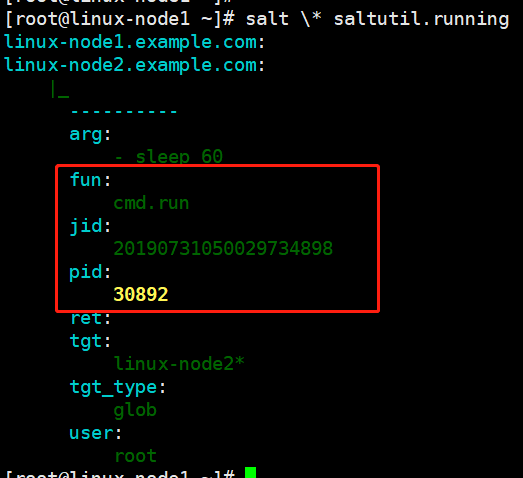
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt 'linux-node2*' saltutil.kill_job 20190731050029734898
案例:每5分钟给所有机器跑一下状态
8.总结
1. 作业:saltstack部署redis主从配置

init.sls
[root@linux-node1 redis]# pwd
/srv/salt/prod/redis
[root@linux-node1 redis]# tree
.
├── files
│ └── redis.conf
├── init.sls
├── master.sls
└── slave.sls
1 directory, 4 files
[root@linux-node1 redis]# vim init.sls
redis-install:
pkg.installed:
- name: redis
redis-config:
file.managed:
- name: /etc/redis.conf
- source: salt://redis/files/redis.conf
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 644
- template: jinja
- defaults:
PORT: 6379
IPADDR: {{ grains['fqdn_ip4'][0] }}
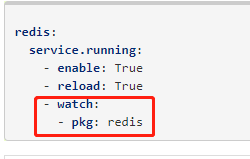
redis-service:
service.running:
- name: redis
- enable: True
- reload: True
- watch:
- file: redis-config
conf
[root@linux-node1 redis]# cp /etc/redis.conf files/
bind {{ IPADDR }}
port {{ PORT }}
daemonize yes
master
slave
[root@linux-node1 redis]# vim master.sls
include:
- redis.init
[root@linux-node1 redis]# vim slave.sls
include:
- redis.init
slave-config:
cmd.run:
- name: redis-cli -h 192.168.194.131 slaveof 192.168.194.132 6379
- unless: redis-cli -h 192.168.194.132 info |grep role:slave
- require:
- service: redis-service
node2上实验命令
[root@linux-node2 modules]# redis-cli -h 192.168.194.132 info
[root@linux-node2 modules]# redis-cli -h 192.168.194.132 slaveof 192.168.194.131 6379
[root@linux-node2 modules]# redis-cli -h 192.168.194.132
192.168.194.132:6379> info [sectio
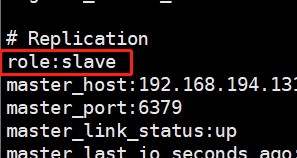
不需要unless
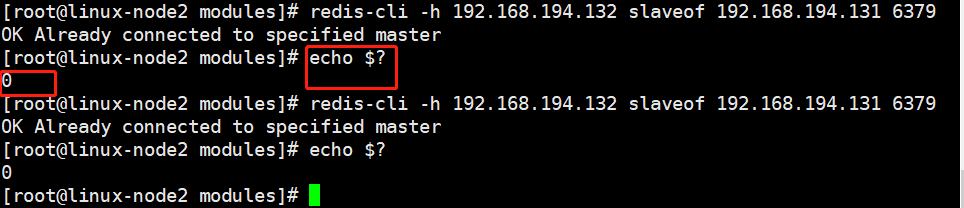
执行top
[root@linux-node1 base]# vim top.sls
prod:
'linux-node1.example.com':
- lamp
- redis.master
'linux-node2.example.com':
- lamp
- redis.slave
[root@linux-node1 base]# pwd
/srv/salt/base
[root@linux-node1 redis]# salt * state.highstate
设置node2为主
[root@linux-node2 modules]# redis-cli -h 192.168.194.132
192.168.194.132:6379>
192.168.194.132:6379> slaveof no one
OK
unless应用
[root@linux-node2 modules]# redis-cli -h 192.168.194.132 info |grep role:slave
role:slave
[root@linux-node2 modules]# echo $?
0
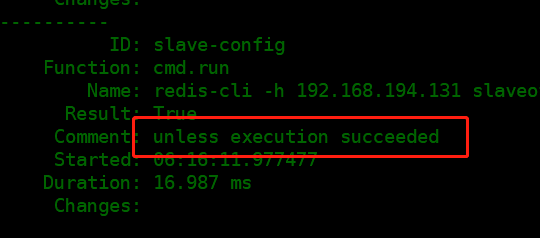
Watch
生产不要watch
生产 test=True
不用* 用1个节点
1.学习saltstack思路:三段式

2.学习模块方法
1 官方文档
https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/contents.html
2 配置管理
https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/topics/states/index.html
3 file模块
https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/ref/states/all/index.html#all-salt-states
4 搜索jinja
https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/ref/states/all/salt.states.file.html#module-salt.states.file
