1. SaltStack数据系统
Grains (谷物)
Pillar (支柱)
2.Grains
Grains存放着Salt命令启动时收集的信息,运行时不收集
2.1 信息查询
收集资产
网卡,ip,cpu ....
(1)收集系统底层的msg
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' grains.ls [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' grains.items
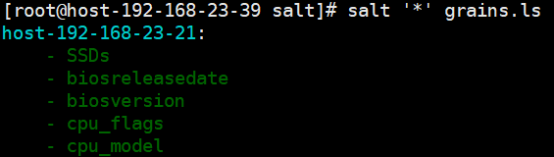
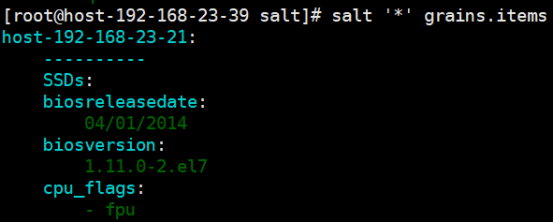
(2)查询单个
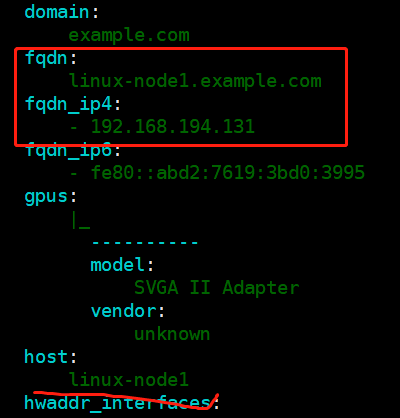
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' grains.item fqdn [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' grains.get fqdn [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' grains.get ip4_interfaces
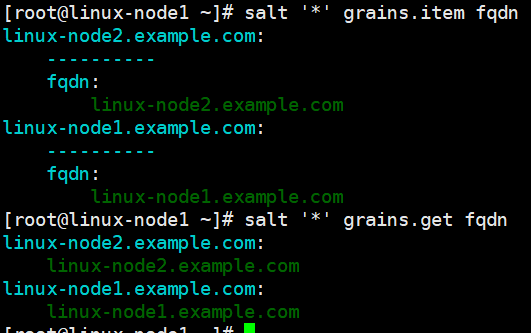
2.2 匹配minion
在所有centos上执行,
所有开机的虚拟机上执行
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt -G 'os:CentOS' cmd.run 'uptime' [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt -G 'init:systemd' cmd.run 'uptime'
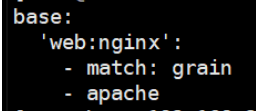
2.3 top.sls中匹配minion
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /srv/salt/base/top.sls

2.4 配合模板来做判断
在pillar中使用
2.5 如何配置?
1.Minion配置文件中的grains (不推荐了)
(1)修改配置文件
vim /etc/minion
systemctl restart salt-minion
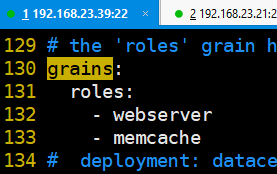
(2)在所有角色是memcache上执行

(3)grians配置文件
新建 grins
:后面必须有空格

(4)重启服务minion
[root@host-192-168-23-39 master]# systemctl restart salt-minion
[root@host-192-168-23-39 master]# systemctl status salt-minion
(5)执行命令

2.自定制grains
# vim grains文件
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/grains test-grains: linux-node2 [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' grains.get test-grains linux-node2.example.com: linux-node1.example.com:
# 重启或者重新获取grains
[root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl restart salt-minion
# 执行命令
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' grains.get test-grains linux-node2.example.com: linux-node1.example.com: linux-node2
3.Pillar
官方文档:https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/topics/pillar/index.html
github中pillar的配置: https://github.com/saltstack-formulas?utf8=✓&q=&type=&language=
3.1 Grains与pillar对比
Grains的问题
1:静态数据,要刷新 2.用户名密码,不太安全
Pillar好处
敏感data,比如配置文件设定密码
处理变量差异性
给minion指定它想要的数据 安全性比较好,给谁指定谁能看到,其他的看不到 安全,只有指定的人才能看到key-value 在master端设定 不用每次重启服务
pillar解析后是个python的字典
直接在salt中 写python的语法
3.2 打开默认pillar
# 默认关闭的
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' grains.get test-grains linux-node1.example.com: ---------- linux-node2.example.com: ----------
# 配置master文件
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master

# 重启master服务
[root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl restart salt-master
# 执行命令

3.3 配置pillar
1.配置master文件,创建目录
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master
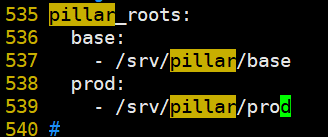
[root@linux-node1 ~]# mkdir -p /srv/pillar/{base,prod}
[root@linux-node1 ~]# tree /srv/pillar/
/srv/pillar/
├── base
└── prod
2 directories, 0 files
[root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl restart salt-master
2. vim apache.sls
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /srv/pillar/base/apache.sls {% if grains['os'] == 'CentOS' %} apache: httpd {% elif grains['os'] == 'Debian'%} apache: apache2 {% endif %}
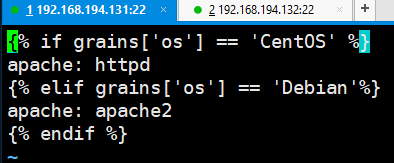
apache: 空格注意空格
[root@linux-node1 pillar]# tree . ├── base │ └── apache.sls └── prod 2 directories, 1 file
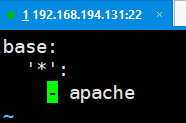
3. 指定哪个minion可以看到
[root@linux-node1 pillar]# vim /srv/pillar/base/top.sls
[root@linux-node1 pillar]# salt '*' pillar.items
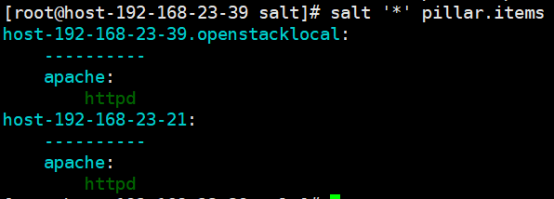
3.4 pillar在状态文件中如何引用的
[root@linux-node1 base]# vim /srv/salt/base/web/apache.sls
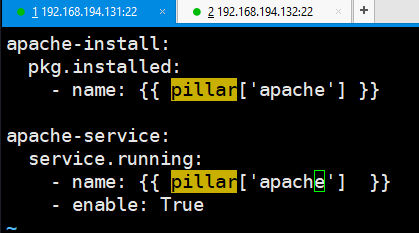
执行命令

4.总结与展望
1. Grains与Pillar对比


2. 报错:Pillar报错
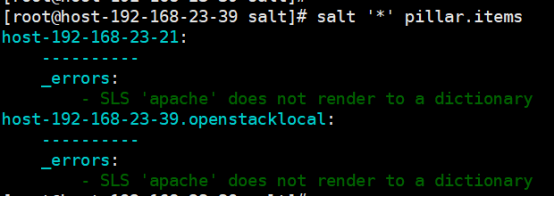
报错信息:apache: 空格注意空格

3.配置中心
https://www.infoq.cn/article/basis-frameworkto-implement-micro-service/
