1.配置管理
1.1 puppet
- /'pʌpɪt/ 木偶;傀儡;受他人操纵的人

使用自有的puppet描述语言,可管理配置文件、用户、cron任务、软件包、系统服务等。
问题:
学习曲线非常陡峭
centos上装个puppet,Ruby环境让人头大
puppet没有远程执行功能(执行100台服务器命令),只能借助Func第三方工具
Func烂,真烂,难用。
1.2 Ansible

1. 优点:
出名原因,被红帽收购,redhat所有东西会附属ansible的自动化部署
轻量级,容易使用,不需要装agent, (salt 需要装minion,也可以不用装,直接使用ssh)
python开发
2.缺点:
没有agent,大规模环境下,通过ssh(串行,10个10个跑)会很慢,(salt是并行的)
3.国内趋势
Ansible + SaltStack(主)
Ansible 200台机器 并发50 CPU负载80 不停报错
2000台就是噩梦
1.3 SaltStack

强化版的FUNC (远程执行),弱化版的Puppet
1. 传统方法:
1万台服务器
ssh循环登陆节点列表并执行一堆命令
容易出错,效率低下,网络安全,ssh密钥和命令执行权限
2. 来源
作者住在,salt盐湖城
各种stack很火,openstack
3. 四大功能
(1)远程执行 Remote Execution 1w台机器同时执行命令 (2)配置(状态)管理 Configuration Managemet 修改配置文件,重新load,怎么干,装什么服务 (3)事件驱动 Event-Driven Infrastructure epoll 被动的,监听描述符,我centos挂了,事件发到队列,salt执行某些操作 (4)云管理 Salt Cloud 管理所有的公有云和私有云,不用学习各种云的API,salt已经封装好了
4.所有东西可以定制
描述语言,模板语言,web,所有centos执行命令,自己写状态写脚本,官方东西太多了,api
5. 组件 SaltStack Components
Salt Master
Salt Minions
为什么叫奴才?
认证的机制: 地主同意,奴才才能来地主家干活
奴才认你为地主,你才是地主
Execution Modules 执行模块
Formulas (States) 状态
.....
2.saltstack安装
安装官网:https://repo.saltstack.com
master端 192.168.194.131
minion端 192.168.194.132
2.1 安装centos,初始化
1.关闭SELinux,iptables。
关闭Linux中的iptables,firewalld,SELINUX https://blog.csdn.net/zha6476003/article/details/89425811
注:生成环境需要iptables开启 master端4505、4506端口,
#关闭firewalld,禁止开机启动 [root@VM_0_13_centos var]# systemctl stop firewalld [root@VM_0_13_centos var]# systemctl disable firewalld.service #关闭iptables [root@VM_0_13_centos var]# systemctl stop iptables
2.修改网卡配置,去掉UUID MAC等(克隆机器问题)
解决CentOS克隆虚拟机无法上网问题(UUID、MAC、IP)https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35428201/article/details/81435679
重新生成网卡
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42291597/article/details/83690681
[root@linux-node1 network-scripts]# cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 [root@linux-node2 ~]# vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 删除或注释HWADDR和UUID两行内容,修改IP
3.配置hostname,配置hosts
为什么需要修改hostname?
其实需要在hosts里面配置,然后根据dns服务器查找 minion,可以更快的找到
根据域名链接,更快更好
[root@localhost ~]# hostname linux-node1.example.com [root@localhost ~]# hostname linux-node2.example.com [root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/network # 重启后生效 # Created by anaconda NETWORKING=yes HOSTNAME=linux-node1.example.com [root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/network # 重启后生效 # Created by anaconda NETWORKING=yes HOSTNAME=linux-node2.example.com
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 192.168.194.131 linux-node1.example.com linux-node1 192.168.194.132 linux-node2.example.com linux-node2
2.2、安装不同版本
https://repo.saltstack.com/2018.3.html#rhel
测试环境 python3+ centos7 + salt 2019.2.1
https://mirrors.aliyun.com/saltstack/2019.2.html#rhel
具体直接下载,该版本对应的repo
2.2 安装Repo,salt
why?
redhat Python 3 support requires that EPEL be previously installed
1、安装repo (SaltStack repository and key) (有待商榷,请看上面)
方法1:
[root@localhost ~]# yum install https://repo.saltstack.com/py3/redhat/salt-ppy3-repo-latest.el7.noarch.rpm
方法2:aliyun镜像 https://mirrors.aliyun.com
[root@localhost ~]# cd /etc/yum.repos.d/ [root@localhost yum.repos.d]# wget https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo
方法3:安装2019版本
[root@host-192-168-23-22 yum-root-MoFHI0]# cat /etc/yum.repos.d/saltstack.repo [saltstack-repo] name=SaltStack repo for RHEL/CentOS $releasever baseurl=https://repo.saltstack.com/yum/redhat/$releasever/$basearch/latest enabled=1 gpgcheck=0
作业:
cobbler同步它们的yum仓库到自己的电脑?
saltstack有自己的yum源 https://repo.saltstack.com
zabbix有自己的yum源 https://repo.zabbix.com
2.更新缓存
[root@localhost ~]# yum clean expire-cache
3.安装salt
master端
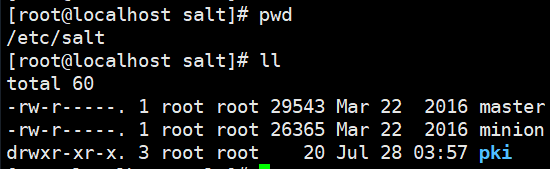
[root@localhost ~]# yum install salt-master -y
[root@localhost ~]# yum install salt-minion -y
minion端
[root@localhost ~]# yum install salt-minion -y
4.启动salt-master
只在,master端
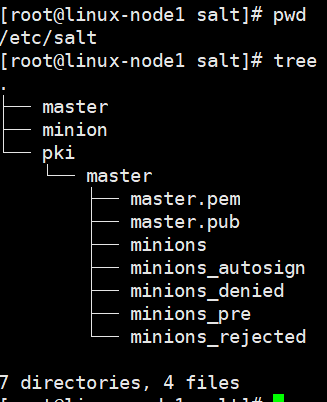
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart salt-master
3. 运行Salt
1.启动minion
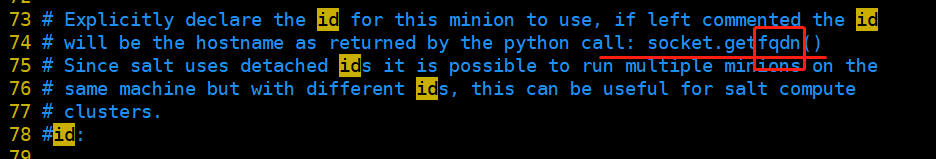
(1)minion配置文件
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/salt/minion
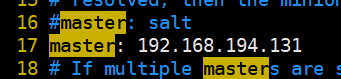
配置master的ip
配置id
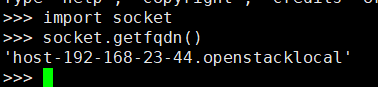
id:默认通过python的方法socket.getfqdn()去获取fqdn名。所以要求设置好主机名并能解析。也可以使用IP地址,看业务需求。
冒号有空格
多一个空格都报错
(2)启动minion
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart salt-minion
2. 公钥管理
可以直接在master配置文件,打开auto_accept开关,如果minion比较多的话
1. 如何认证的?
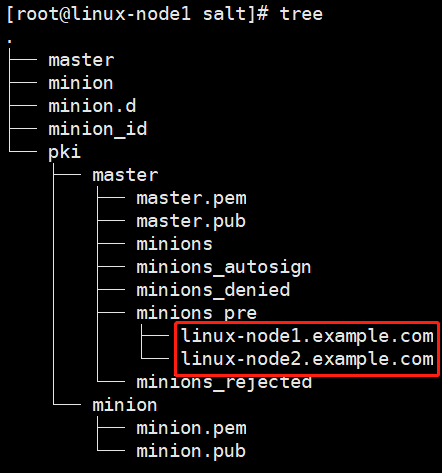
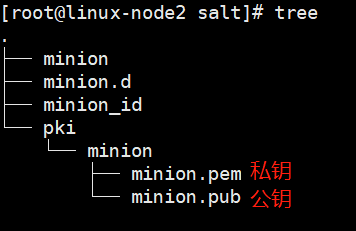
认证机制
已经告诉minion了,master是谁
现在需要master同意接受minion
安全问题
通信之前进行认证,公钥私钥(类同与ssh认证)
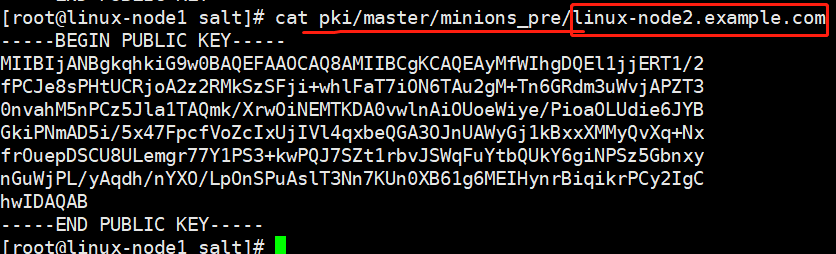
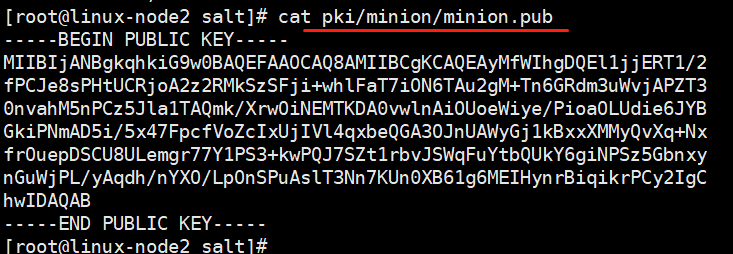
(1)查看状态
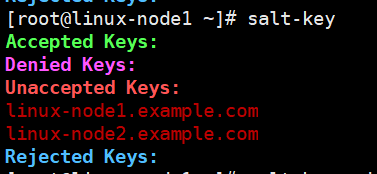
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt-key --help -a ACCEPT # 支持通配符 -A --accept-all
(2)接受minion
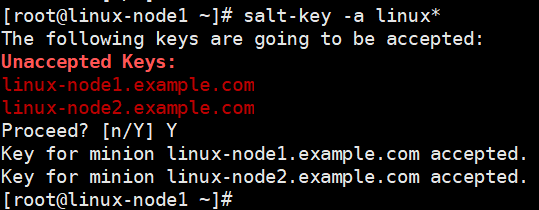
(3)公钥交互的过程
master端,把能控制的主机放在minion
minion端,得到master的公钥
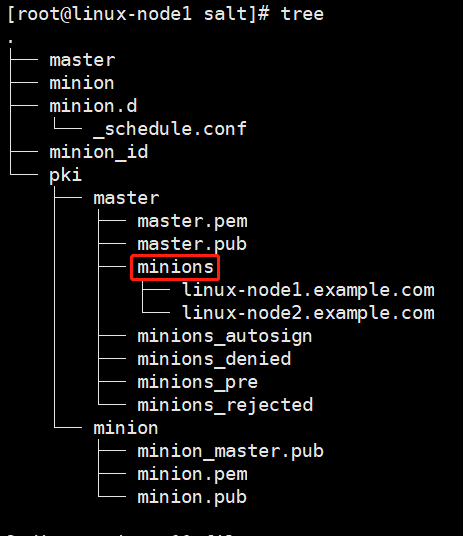
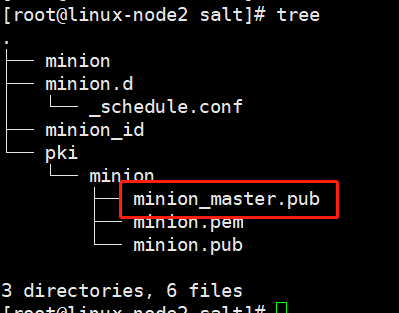
AES加密的
高级加密标准(英语:Advanced Encryption Standard,缩写:AES),在密码学中又称Rijndael加密法,是美国联邦政府采用的一种区块加密标准。
2.1 minion_id的生成过程
https://my.oschina.net/u/877567/blog/199136
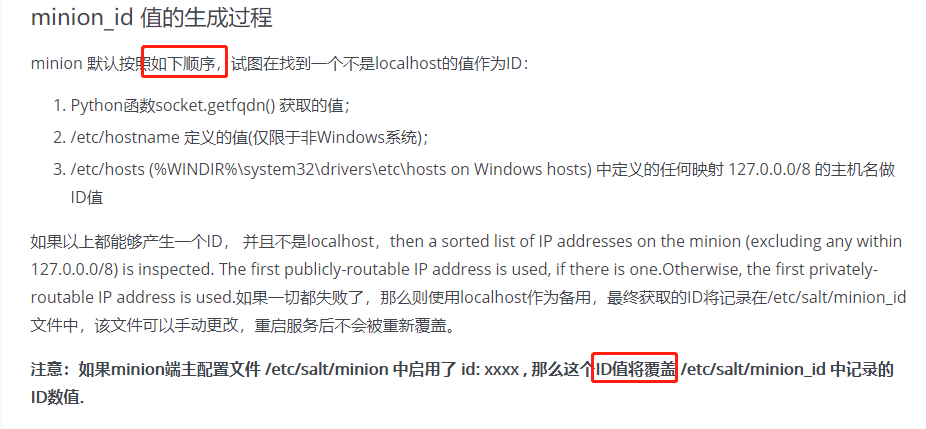
2.2 如何修改id
1.停止minion
2.master端 salt-key -d 删除id
3.minion删除pki (实质删除 rm -rf pki/minion)
4. 删除minion_id
5. 修改minion的id,再启动,再在salt-master操作
需求:
多个匹配时候,如何以ip进行匹配,执行salt命令
根据的是 id 进行匹配的
现在将id的值由hostname改为ip地址
操作
# 1.停止minion [root@host-192-168-23-44 salt]# pwd /etc/salt [root@host-192-168-23-44 salt]# systemctl stop salt-minion # 2.master删除minion [root@host-192-168-23-39 ]# salt-key -d host-192-168-23-44* # 3.minion删除pki、缓存的minion_id [root@host-192-168-23-44 salt]# rm -rf pki/ # 实质删除 rm -rf pki/minion [root@host-192-168-23-44 salt]# rm -rf minion_id # 4.minion修改id
[root@host-192-168-23-44 salt]# vim /etc/salt/minion
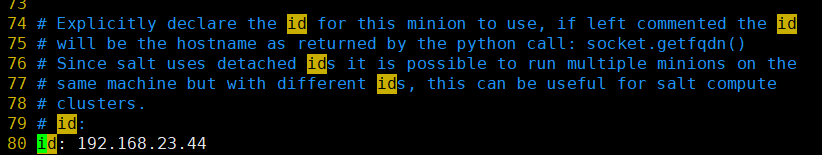
# 5.重启minion,在master重新操作 [root@host-192-168-23-44 salt]# systemctl restart salt-minion [root@host-192-168-23-44 salt]# systemctl status salt-minion -l
3.远程执行
salt 命令
*是通配符,转义了就行
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' test.ping [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt * test.ping [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt "*" test.ping
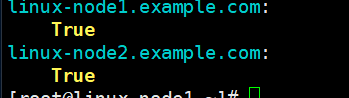
* 匹配了所有了目标
test 模块
ping 模块的方法
ssh中Ping是ICMP
这里的ping,是master给minion发了一个包,能收到返回True
‘uptime’ 方法的参数
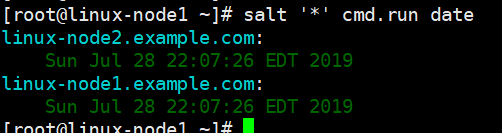
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' cmd.run 'uptime' linux-node1.example.com: 11:07:37 up 1:01, 1 user, load average: 0.01, 0.04, 0.05 linux-node2.example.com: 11:07:37 up 1:01, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' cmd.run 'free -m' linux-node2.example.com: total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 972 129 453 7 389 651 Swap: 2047 0 2047 linux-node1.example.com: total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 972 288 289 7 394 488
4.通信机制
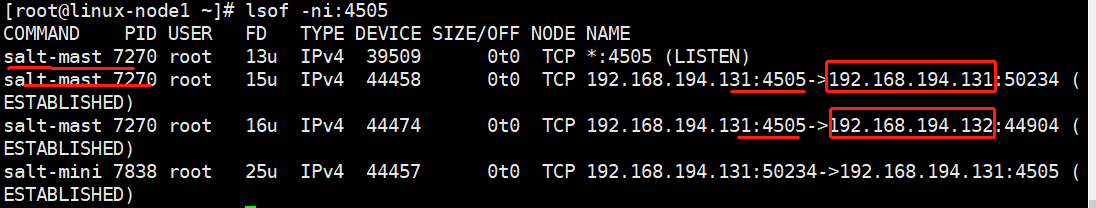
(1)端口开放
minion不需要监听端口,minion只需要连到master上。
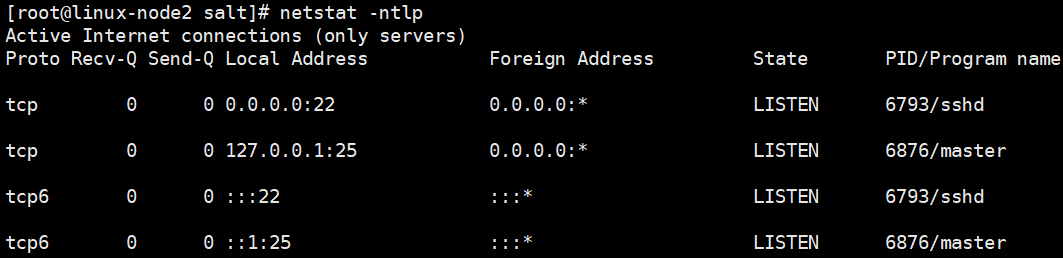
master端:4505,4506。
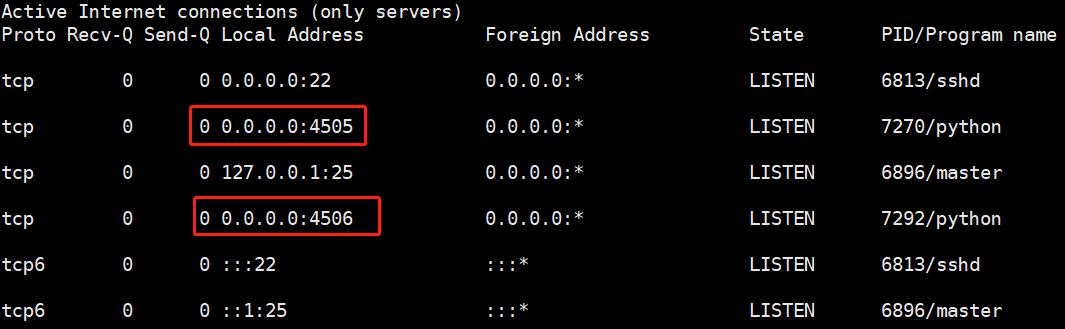
(2)ZeroMQ http://zeromq.org
官方文档:https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/topics/development/topology.html
底层通信利用了ZeroMQ
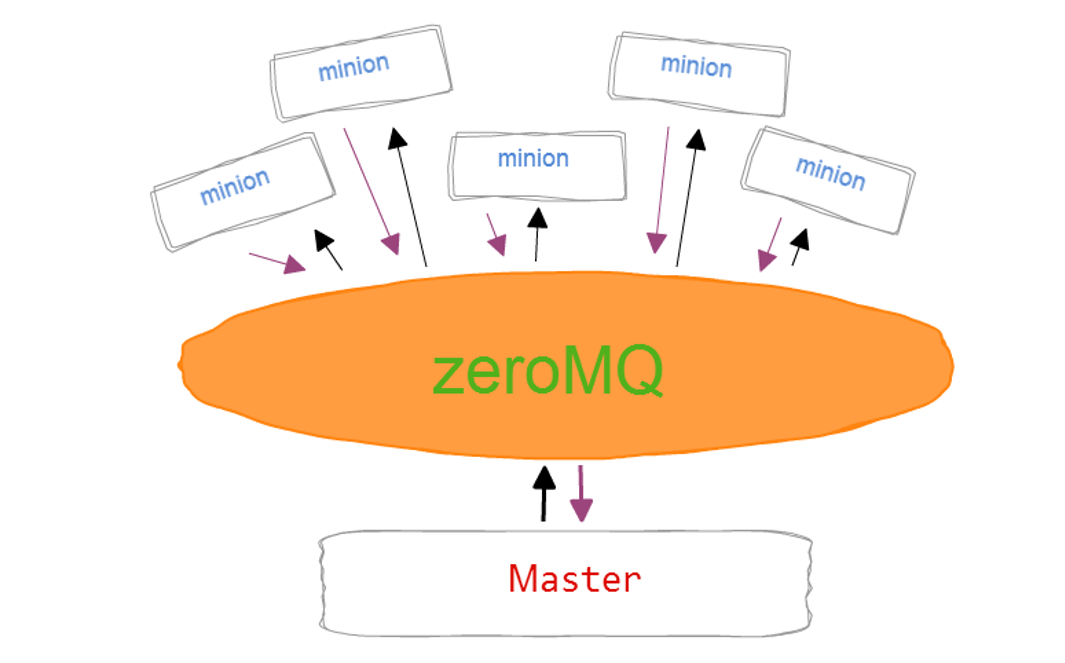
(1)发送与订阅 (订报纸,并行)
所有minion会连接到4505,发送命令。所有主机同时执行,同时返回
(2)4506接受返回,请求与相应。
5. 配置管理
https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/topics/yaml/index.html
1.YAML语法

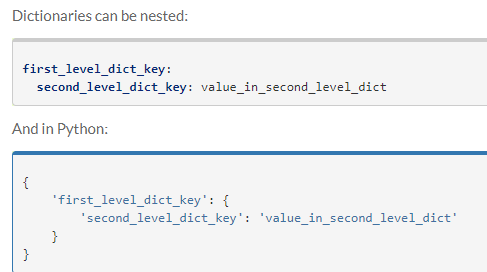
语法规则:3个基本规则
缩进2个空格
冒号后面必有空格:除了路径与结尾
短横线后1个空格



2. 状态配置文件放哪?
[root@host-192-168-23-39 master]# vim /etc/salt/master
# base # test测试环境 # 开发环境

3. 配置master
[root@host-192-168-23-39 master]# vim /etc/salt/master
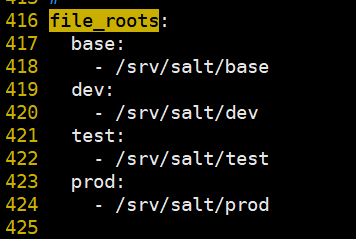
[root@linux-node1 ~]# mkdir -p /srv/salt/{base,dev,test,prod}
[root@linux-node1 ~]# tree /srv/salt/
/srv/salt/
├── base
├── dev
├── prod
└── test
# 每次修改master配置文件必须重启master
[root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl restart salt-master
4. 配置Apache的sls
[root@linux-node1 base]# tree . └── web └── apache.sls 1 directory, 1 file [root@linux-node1 base]# cd web/ [root@linux-node1 web]# cat apache.sls apache-install: pkg.installed: - name: httpd apache-service: service.running: - name: httpd - enable: True
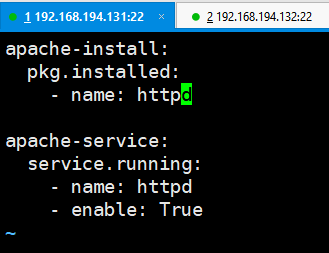
远程执行模块,配置管理模块
apache-install: pkg.installed: # 不同系统,包安装命令 - name: httpd apache-service: # id,不能重复 service.running: # 状态模块:方法 - name: httpd #参数 # name包的名称: - enable: True # enable 开机启动:
5. 执行命令
[root@linux-node1 web]# salt 'linux-node2.example.com' state.sls web.apache saltenv=prod [root@linux-node1 web]# salt 'linux-node2.example.com' state.sls web.apache # 默认在base环境下 # 对应 apache.sls中的各个参数
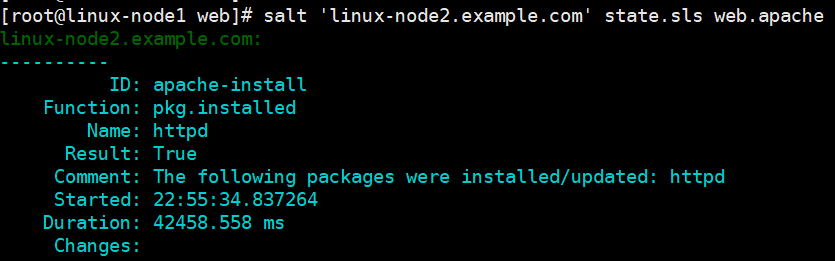
test下,http服务已经安装,启动了
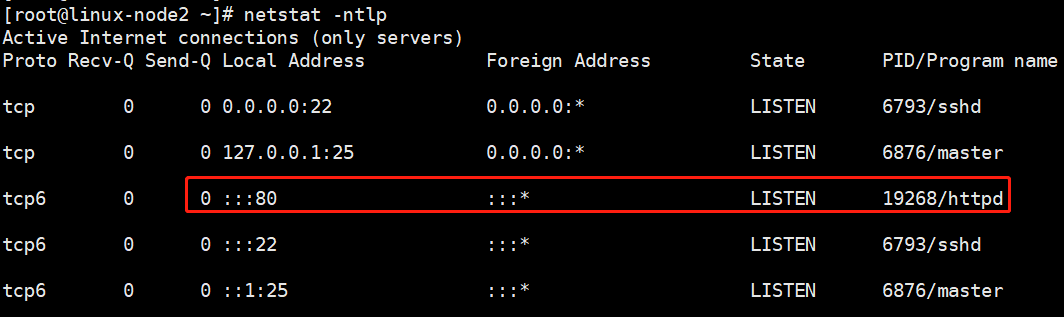
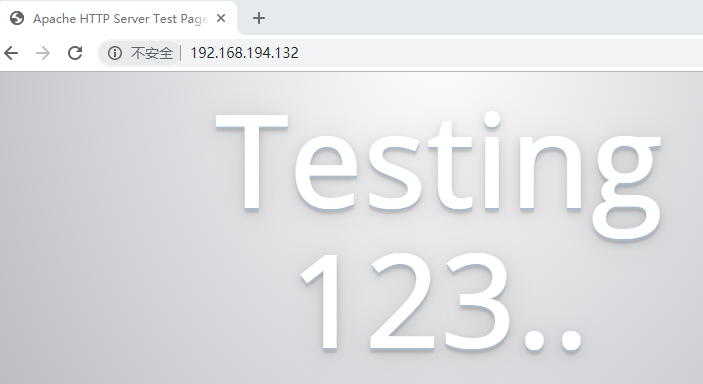
minion关闭httpd,在来一遍
[root@linux-node2 ~]# systemctl stop httpd
[root@linux-node1 web]# salt 'linux-node2.example.com' state.sls web.apache

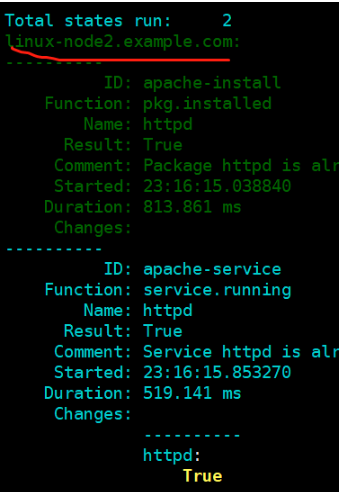
linux-node2.example.com: ---------- ID: apache-install Function: pkg.installed Name: httpd Result: True Comment: Package httpd is already installed. Started: 23:00:32.264555 Duration: 627.531 ms Changes: ---------- ID: apache-service Function: service.running Name: httpd Result: True Comment: Service httpd is already enabled, and is running Started: 23:00:32.892558 Duration: 413.061 ms Changes: ---------- httpd: True Summary ------------ Succeeded: 2 (changed=1) Failed: 0 ------------ Total states run: 2
6. 高级配置 top.sls
上述都是不自动化的,自动化是:我说干活,你们就干活
(1)top.file # 默认在base环境下
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master
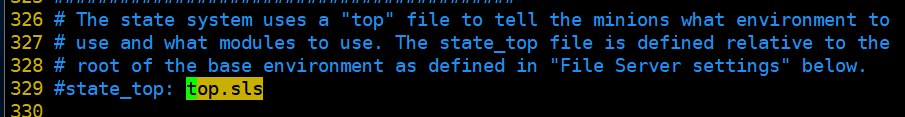
(2)编写top.sls
[root@linux-node1 base]# pwd /srv/salt/base [root@linux-node1 base]# cat top.sls base: '*': - web.apache
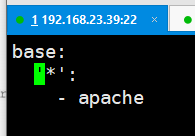
base: # 环境 '*': # 所有节点执行这个状态 - web.apache # 执行web目录下的apache.sls
(3)执行命令,高级状态 highstate
[root@linux-node1 base]# salt '*' state.highstate
* 通知谁,所有主机干活,在所有节点上执行这个highstate
topfile里面*是指定哪些主机节点干活。
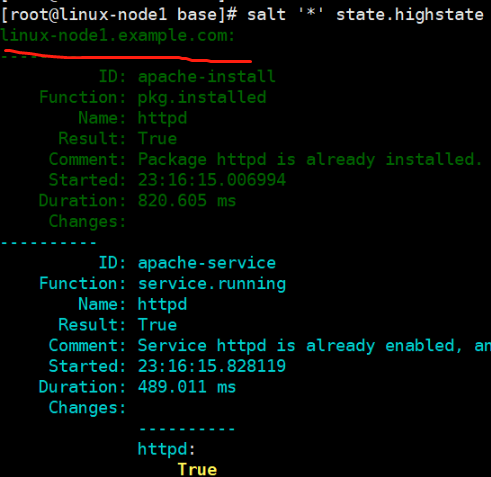
(4)test
100台机器,先在1个上面跑一下,再在其他上面跑
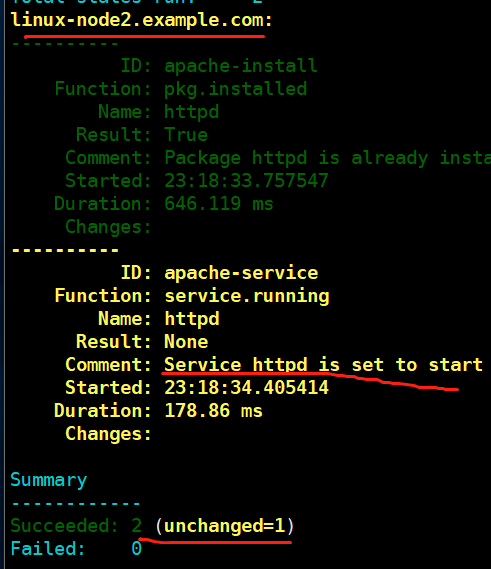
[root@linux-node1 base]# salt '*' state.highstate test=True # 不是真的执行,如何执行的话,会发生什么
先关闭node2的 httpd
4. 总结
1.出现问题
Question1:
只有一个秘钥
只出现一个主机
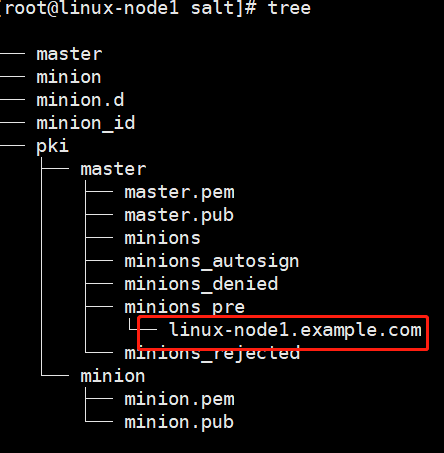
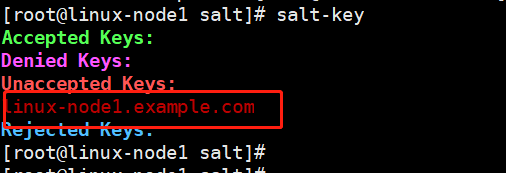
解决方法: 其他机器的minion配置文件有错误,注意空格,冒号
Question2:
[root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl status salt-minion Jul 28 05:52:10 linux-node1.example.com salt-minion[9702]: [ERROR ] The Salt Master has cached the public key for this node, this salt minion will wait for 10 seconds before attempting to re-authenticate salt master已缓存此节点的公钥,此salt minion将等待10秒,然后再尝试重新验证。
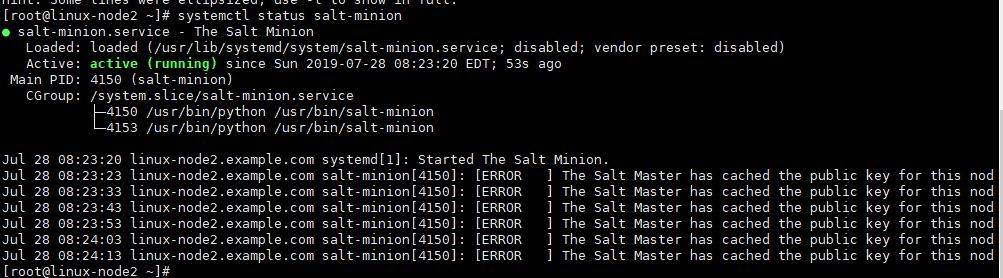
网上参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/phennry/p/5419451.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/phennry/p/5419451.html
https://blog.csdn.net/xiegh2014/article/details/53114257
https://blog.51cto.com/molewan/2060851
解决办法:
请务必关闭selinux和iptables
2. 小提醒
知识获取廉价,文档获取廉价,你抄我我抄你
我的时间很贵
培训的价值,用更短的时间学会这个东西
