UDP
- unreliable, just add de-multiplexing and error checking on data than IP.
- Best effort datagram(数据报) service
- Multiplexing enables sharing of IP datagram service
- Simple transmitter & receiver
- Connectionless: no handshaking & no connection state
- Low header overhead
- No flow control, no error control, no congestion control
- UDP datagrams can be lost or out-of-order
- Applications
- multimedia (e.g. RTP)
- network services (e.g. DNS, RIP, SNMP)
UDP Datagram
-
0-255
- Well-known ports
-
256-1023
- Less well-known ports
-
1024-65536
- Ephemeral(短暂的) client ports
-
Source and destination port numbers
- Client ports are ephemeral(短暂的)
- Server ports are well-known
- Max number is 65,535
-
UDP length
- Total number of bytes in datagram (including header)
- 8 bytes ≤ length ≤ 65,535
-
UDP Checksum
- Optionally detects errors in UDP datagram(Because the error packet will be discard)

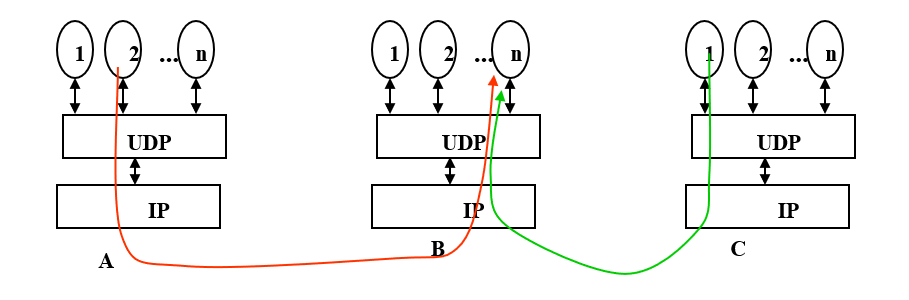
UDP De-Multiplexing(解复用)
- All UDP datagrams arriving to IP address B and destination port number n are delivered to the same process
- Source port number is not used in demultiplexing
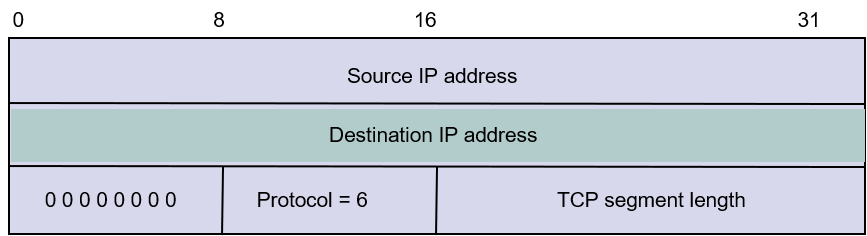
UDP Checksum Calculation

- UDP checksum detects for end-to-end errors
- Covers pseudoheader(伪报头) followed by UDP datagram
- IP addresses included to detect against** misdelivery(错误传输)**
- The use of UDP checksums is optional
- But hosts are required to have checksums enabled
TCP
- Reliable byte-stream service
- More complex transmitter & receiver
- Connection-oriented: full-duplex(全双工) unicast connection between client & server processes
- Connection setup, connection state, connection release
- Higher header overhead
- Error control, flow control, and congestion(拥塞) control
- Higher delay than UDP
- Most applications use TCP
- HTTP, SMTP, FTP, TELNET, POP3, …
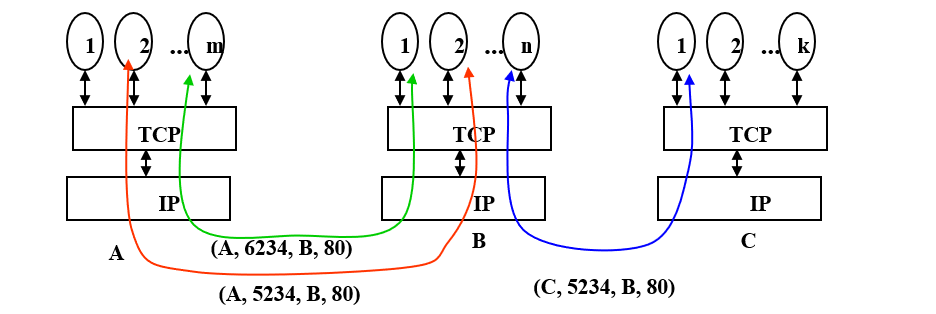
TCP Multiplexing
- A TCP connection is specified by a 4-tuple(数组)
- (source IP address, source port, destination IP address, destination port)
- TCP allows multiplexing of multiple connections between end systems to support multiple applications simultaneously
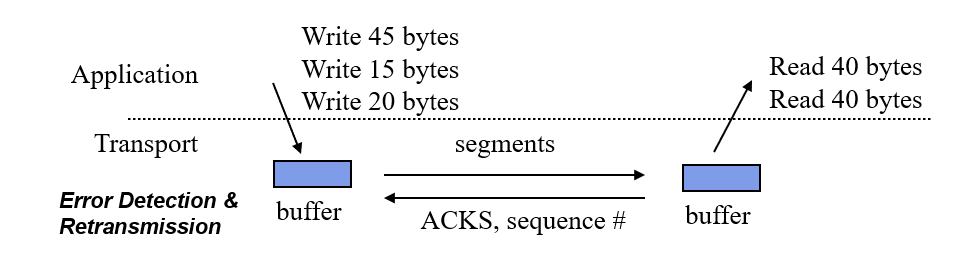
Reliable Byte-Stream Service
- Stream Data Transfer:transfers a contiguous stream of bytes across the network, with no indication of boundaries
- groups bytes into segments(部分)
- transmits segments as convenient (Push function defined)
Reliability: error control to deal with IP transfer impairments(损害)
TCP Segment Format
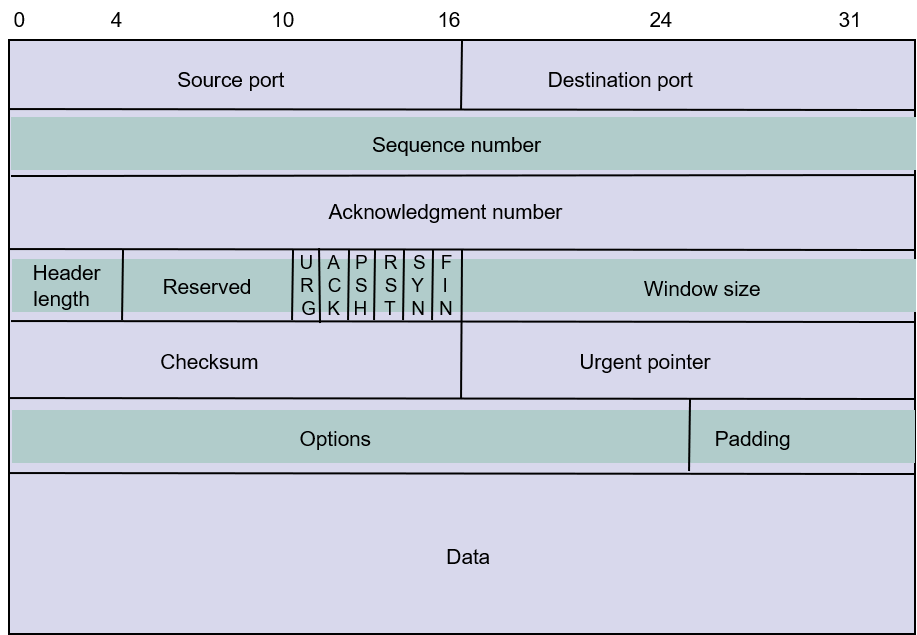
TCP Header
Window Size:TCP protocol need ACK to ensure the packet be transported, if we receive ACK after every packet arriving, it will waste a lot of time.So we need the Window Size to tell us how many packet we can send one time.
- 16 bits to advertise window size
- Used for flow control
- Sender will accept bytes with SN from ACK to ACK + window
- Maximum win size 65535 bytes
- TCP Checksum
- Internet checksum method
- TCP pseudoheader + TCP segment