Vue.js 混入
混入 (mixins)定义了一部分可复用的方法或者计算属性。混入对象可以包含任意组件选项。当组件使用混入对象时,所有混入对象的选项将被混入该组件本身的选项。
来看一个简单的实例:
<div id = "databinding"></div>
<script type = "text/javascript">
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#databinding',
data: {
},
methods : {
},
});
// 定义一个混入对象
var myMixin = {
created: function () {
this.startmixin()
},
methods: {
startmixin: function () {
document.write("欢迎来到混入实例");
}
}
};
var Component = Vue.extend({
mixins: [myMixin]
})
var component = new Component();
</script>
选项合并
当组件和混入对象含有同名选项时,这些选项将以恰当的方式混合。
比如,数据对象在内部会进行浅合并 (一层属性深度),在和组件的数据发生冲突时以组件数据优先。
以下实例中,Vue 实例与混入对象包含了相同的方法。从输出结果可以看出两个选项合并了。
var mixin = {
created: function () {
document.write('混入调用' + '<br>')
}
}
new Vue({
mixins: [mixin],
created: function () {
document.write('组件调用' + '<br>')
}
});
输出结果为:
混入调用
组件调用
如果 methods 选项中有相同的函数名,则 Vue 实例优先级会较高。如下实例,Vue 实例与混入对象的 methods 选项都包含了相同的函数:
var mixin = {
methods: {
hellworld: function () {
document.write('HelloWorld 方法' + '<br>');
},
samemethod: function () {
document.write('Mixin:相同方法名' + '<br>');
}
}
};
var vm = new Vue({
mixins: [mixin],
methods: {
start: function () {
document.write('start 方法' + '<br>');
},
samemethod: function () {
document.write('Main:相同方法名' + '<br>');
}
}
});
vm.hellworld();
vm.start();
vm.samemethod();
输出结果为:
HelloWorld 方法
start 方法
Main:相同方法名
全局混入
也可以全局注册混入对象。注意使用! 一旦使用全局混入对象,将会影响到 所有 之后创建的 Vue 实例。使用恰当时,可以为自定义对象注入处理逻辑。
<script type = "text/javascript">
// 为自定义的选项 'myOption' 注入一个处理器。
Vue.mixin({
created: function () {
var myOption = this.$options.myOption
if (myOption) {
document.write(myOption)
}
}
})
new Vue({
myOption: 'hello!'
})
// => "hello!"
</script>
PS:谨慎使用全局混入对象,因为会影响到每个单独创建的 Vue 实例 (包括第三方模板)。
Vue.js Ajax(axios)
Vue.js 2.0 版本推荐使用 axios 来完成 ajax 请求。
Axios 是一个基于 Promise 的 HTTP 库,可以用在浏览器和 node.js 中。
Github开源地址: https://github.com/axios/axios
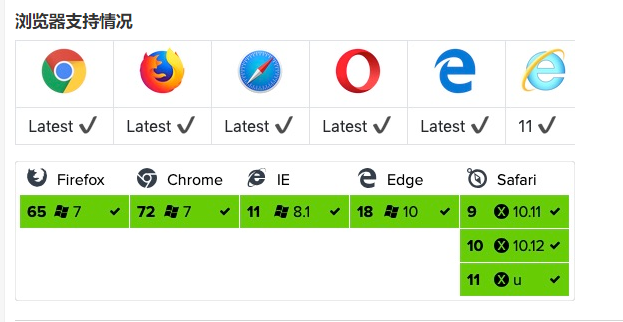
GET 方法
我们可以简单的读取 JSON 数据:
<div id="app">
{{ info }}
</div>
<script type = "text/javascript">
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data () {
return {
info: null
}
},
mounted () {
axios
.get('https://www.runoob.com/try/ajax/json_demo.json')
.then(response => (this.info = response))
.catch(function (error) { // 请求失败处理
console.log(error);
});
}
})
</script>
使用 response.data 读取 JSON 数据:
<div id="app">
<h1>网站列表</h1>
<div
v-for="site in info"
>
{{ site.name }}
</div>
</div>
<script type = "text/javascript">
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data () {
return {
info: null
}
},
mounted () {
axios
.get('https://www.runoob.com/try/ajax/json_demo.json')
.then(response => (this.info = response.data.sites))
.catch(function (error) { // 请求失败处理
console.log(error);
});
}
})
</script>
GET 方法传递参数格式如下:
// 直接在 URL 上添加参数 ID=12345
axios.get('/user?ID=12345')
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log(error);
});
// 也可以通过 params 设置参数:
axios.get('/user', {
params: {
ID: 12345
}
})
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log(error);
});
POST 方法
<div id="app">
{{ info }}
</div>
<script type = "text/javascript">
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data () {
return {
info: null
}
},
mounted () {
axios
.post('https://www.runoob.com/try/ajax/demo_axios_post.php')
.then(response => (this.info = response))
.catch(function (error) { // 请求失败处理
console.log(error);
});
}
})
</script>
POST 方法传递参数格式如下:
axios.post('/user', {
firstName: 'Fred', // 参数 firstName
lastName: 'Flintstone' // 参数 lastName
})
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log(error);
});
执行多个并发请求
function getUserAccount() {
return axios.get('/user/12345');
}
function getUserPermissions() {
return axios.get('/user/12345/permissions');
}
axios.all([getUserAccount(), getUserPermissions()])
.then(axios.spread(function (acct, perms) {
// 两个请求现在都执行完成
}));
axios API
可以通过向 axios 传递相关配置来创建请求。
axios(config)
// 发送 POST 请求
axios({
method: 'post',
url: '/user/12345',
data: {
firstName: 'Fred',
lastName: 'Flintstone'
}
});
// GET 请求远程图片
axios({
method:'get',
url:'http://bit.ly/2mTM3nY',
responseType:'stream'
})
.then(function(response) {
response.data.pipe(fs.createWriteStream('ada_lovelace.jpg'))
});
axios(url[, config])
// 发送 GET 请求(默认的方法)
axios('/user/12345');
请求方法的别名
为方便使用,官方为所有支持的请求方法提供了别名,可以直接使用别名来发起请求:
axios.request(config)
axios.get(url[, config])
axios.delete(url[, config])
axios.head(url[, config])
axios.post(url[, data[, config]])
axios.put(url[, data[, config]])
axios.patch(url[, data[, config]])
注意:在使用别名方法时, url、method、data 这些属性都不必在配置中指定。
并发
处理并发请求的助手函数:
axios.all(iterable)
axios.spread(callback)
创建实例
可以使用自定义配置新建一个 axios 实例:
axios.create([config])
const instance = axios.create({
baseURL: 'https://some-domain.com/api/',
timeout: 1000,
headers: {'X-Custom-Header': 'foobar'}
});
实例方法
以下是可用的实例方法。指定的配置将与实例的配置合并:
axios#request(config)
axios#get(url[, config])
axios#delete(url[, config])
axios#head(url[, config])
axios#post(url[, data[, config]])
axios#put(url[, data[, config]])
axios#patch(url[, data[, config]])
请求配置项
下面是创建请求时可用的配置选项,注意只有 url 是必需的。如果没有指定 method,请求将默认使用 get 方法。
{
// `url` 是用于请求的服务器 URL
url: "/user",
// `method` 是创建请求时使用的方法
method: "get", // 默认是 get
// `baseURL` 将自动加在 `url` 前面,除非 `url` 是一个绝对 URL。
// 它可以通过设置一个 `baseURL` 便于为 axios 实例的方法传递相对 URL
baseURL: "https://some-domain.com/api/",
// `transformRequest` 允许在向服务器发送前,修改请求数据
// 只能用在 "PUT", "POST" 和 "PATCH" 这几个请求方法
// 后面数组中的函数必须返回一个字符串,或 ArrayBuffer,或 Stream
transformRequest: [function (data) {
// 对 data 进行任意转换处理
return data;
}],
// `transformResponse` 在传递给 then/catch 前,允许修改响应数据
transformResponse: [function (data) {
// 对 data 进行任意转换处理
return data;
}],
// `headers` 是即将被发送的自定义请求头
headers: {"X-Requested-With": "XMLHttpRequest"},
// `params` 是即将与请求一起发送的 URL 参数
// 必须是一个无格式对象(plain object)或 URLSearchParams 对象
params: {
ID: 12345
},
// `paramsSerializer` 是一个负责 `params` 序列化的函数
// (e.g. https://www.npmjs.com/package/qs, http://api.jquery.com/jquery.param/)
paramsSerializer: function(params) {
return Qs.stringify(params, {arrayFormat: "brackets"})
},
// `data` 是作为请求主体被发送的数据
// 只适用于这些请求方法 "PUT", "POST", 和 "PATCH"
// 在没有设置 `transformRequest` 时,必须是以下类型之一:
// - string, plain object, ArrayBuffer, ArrayBufferView, URLSearchParams
// - 浏览器专属:FormData, File, Blob
// - Node 专属: Stream
data: {
firstName: "Fred"
},
// `timeout` 指定请求超时的毫秒数(0 表示无超时时间)
// 如果请求花费了超过 `timeout` 的时间,请求将被中断
timeout: 1000,
// `withCredentials` 表示跨域请求时是否需要使用凭证
withCredentials: false, // 默认的
// `adapter` 允许自定义处理请求,以使测试更轻松
// 返回一个 promise 并应用一个有效的响应 (查阅 [response docs](#response-api)).
adapter: function (config) {
/* ... */
},
// `auth` 表示应该使用 HTTP 基础验证,并提供凭据
// 这将设置一个 `Authorization` 头,覆写掉现有的任意使用 `headers` 设置的自定义 `Authorization`头
auth: {
username: "janedoe",
password: "s00pers3cret"
},
// `responseType` 表示服务器响应的数据类型,可以是 "arraybuffer", "blob", "document", "json", "text", "stream"
responseType: "json", // 默认的
// `xsrfCookieName` 是用作 xsrf token 的值的cookie的名称
xsrfCookieName: "XSRF-TOKEN", // default
// `xsrfHeaderName` 是承载 xsrf token 的值的 HTTP 头的名称
xsrfHeaderName: "X-XSRF-TOKEN", // 默认的
// `onUploadProgress` 允许为上传处理进度事件
onUploadProgress: function (progressEvent) {
// 对原生进度事件的处理
},
// `onDownloadProgress` 允许为下载处理进度事件
onDownloadProgress: function (progressEvent) {
// 对原生进度事件的处理
},
// `maxContentLength` 定义允许的响应内容的最大尺寸
maxContentLength: 2000,
// `validateStatus` 定义对于给定的HTTP 响应状态码是 resolve 或 reject promise 。如果 `validateStatus` 返回 `true` (或者设置为 `null` 或 `undefined`),promise 将被 resolve; 否则,promise 将被 rejecte
validateStatus: function (status) {
return status >= 200 && status < 300; // 默认的
},
// `maxRedirects` 定义在 node.js 中 follow 的最大重定向数目
// 如果设置为0,将不会 follow 任何重定向
maxRedirects: 5, // 默认的
// `httpAgent` 和 `httpsAgent` 分别在 node.js 中用于定义在执行 http 和 https 时使用的自定义代理。允许像这样配置选项:
// `keepAlive` 默认没有启用
httpAgent: new http.Agent({ keepAlive: true }),
httpsAgent: new https.Agent({ keepAlive: true }),
// "proxy" 定义代理服务器的主机名称和端口
// `auth` 表示 HTTP 基础验证应当用于连接代理,并提供凭据
// 这将会设置一个 `Proxy-Authorization` 头,覆写掉已有的通过使用 `header` 设置的自定义 `Proxy-Authorization` 头。
proxy: {
host: "127.0.0.1",
port: 9000,
auth: : {
username: "mikeymike",
password: "rapunz3l"
}
},
// `cancelToken` 指定用于取消请求的 cancel token
// (查看后面的 Cancellation 这节了解更多)
cancelToken: new CancelToken(function (cancel) {
})
}
响应结构
axios请求的响应包含以下信息:
{
// `data` 由服务器提供的响应
data: {},
// `status` HTTP 状态码
status: 200,
// `statusText` 来自服务器响应的 HTTP 状态信息
statusText: "OK",
// `headers` 服务器响应的头
headers: {},
// `config` 是为请求提供的配置信息
config: {}
}
使用 then 时,会接收下面这样的响应:
axios.get("/user/12345")
.then(function(response) {
console.log(response.data);
console.log(response.status);
console.log(response.statusText);
console.log(response.headers);
console.log(response.config);
});
在使用 catch 时,或传递 rejection callback 作为 then 的第二个参数时,响应可以通过 error 对象可被使用。
配置的默认值
你可以指定将被用在各个请求的配置默认值。
全局的 axios 默认值:
axios.defaults.baseURL = 'https://api.example.com';
axios.defaults.headers.common['Authorization'] = AUTH_TOKEN;
axios.defaults.headers.post['Content-Type'] = 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded';
自定义实例默认值:
// 创建实例时设置配置的默认值
var instance = axios.create({
baseURL: 'https://api.example.com'
});
// 在实例已创建后修改默认值
instance.defaults.headers.common['Authorization'] = AUTH_TOKEN;
配置的优先顺序
配置会以一个优先顺序进行合并。这个顺序是:在 lib/defaults.js 找到的库的默认值,然后是实例的 defaults 属性,最后是请求的 config 参数。后者将优先于前者。这里是一个例子:
// 使用由库提供的配置的默认值来创建实例
// 此时超时配置的默认值是 `0`
var instance = axios.create();
// 覆写库的超时默认值
// 现在,在超时前,所有请求都会等待 2.5 秒
instance.defaults.timeout = 2500;
// 为已知需要花费很长时间的请求覆写超时设置
instance.get('/longRequest', {
timeout: 5000
});
拦截器
在请求或响应被 then 或 catch 处理前拦截它们。
// 添加请求拦截器
axios.interceptors.request.use(function (config) {
// 在发送请求之前做些什么
return config;
}, function (error) {
// 对请求错误做些什么
return Promise.reject(error);
});
// 添加响应拦截器
axios.interceptors.response.use(function (response) {
// 对响应数据做点什么
return response;
}, function (error) {
// 对响应错误做点什么
return Promise.reject(error);
});
如果你想在稍后移除拦截器,可以这样:
var myInterceptor = axios.interceptors.request.use(function () {/*...*/});
axios.interceptors.request.eject(myInterceptor);
可以为自定义 axios 实例添加拦截器。
var instance = axios.create();
instance.interceptors.request.use(function () {/*...*/});
错误处理:
axios.get('/user/12345')
.catch(function (error) {
if (error.response) {
// 请求已发出,但服务器响应的状态码不在 2xx 范围内
console.log(error.response.data);
console.log(error.response.status);
console.log(error.response.headers);
} else {
// Something happened in setting up the request that triggered an Error
console.log('Error', error.message);
}
console.log(error.config);
});
可以使用 validateStatus 配置选项定义一个自定义 HTTP 状态码的错误范围。
axios.get('/user/12345', {
validateStatus: function (status) {
return status < 500; // 状态码在大于或等于500时才会 reject
}
})
取消
使用 cancel token 取消请求。
Axios 的 cancel token API 基于cancelable promises proposal
可以使用 CancelToken.source 工厂方法创建 cancel token,像这样:
var CancelToken = axios.CancelToken;
var source = CancelToken.source();
axios.get('/user/12345', {
cancelToken: source.token
}).catch(function(thrown) {
if (axios.isCancel(thrown)) {
console.log('Request canceled', thrown.message);
} else {
// 处理错误
}
});
// 取消请求(message 参数是可选的)
source.cancel('Operation canceled by the user.');
还可以通过传递一个 executor 函数到 CancelToken 的构造函数来创建 cancel token:
var CancelToken = axios.CancelToken;
var cancel;
axios.get('/user/12345', {
cancelToken: new CancelToken(function executor(c) {
// executor 函数接收一个 cancel 函数作为参数
cancel = c;
})
});
// 取消请求
cancel();
注意:可以使用同一个 cancel token 取消多个请求。
请求时使用 application/x-www-form-urlencoded
axios 会默认序列化 JavaScript 对象为 JSON。 如果想使用 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 格式,你可以使用下面的配置。
浏览器
在浏览器环境,你可以使用 URLSearchParams API:
const params = new URLSearchParams();
params.append('param1', 'value1');
params.append('param2', 'value2');
axios.post('/foo', params);
URLSearchParams 不是所有的浏览器均支持。
除此之外,你可以使用 qs 库来编码数据:
const qs = require('qs');
axios.post('/foo', qs.stringify({ 'bar': 123 }));
// Or in another way (ES6),
import qs from 'qs';
const data = { 'bar': 123 };
const options = {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'content-type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded' },
data: qs.stringify(data),
url,
};
axios(options);
Promises
axios 依赖原生的 ES6 Promise 实现而被支持。
如果你的环境不支持 ES6 Promise,你可以使用 polyfill。
TypeScript支持
axios 包含 TypeScript 的定义。
import axios from "axios";
axios.get("/user?ID=12345");
Vue.js Ajax(vue-resource)
Vue 要实现异步加载需要使用到 vue-resource 库。
Vue.js 2.0 版本推荐使用 axios 来完成 ajax 请求。
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/vue-resource/1.5.1/vue-resource.min.js"></script>
Get 请求
以下是一个简单的 Get 请求实例,请求地址是一个简单的 txt 文本:
<div id="box">
<input type="button" @click="get()" value="点我异步获取数据(Get)">
</div>
<script type = "text/javascript">
window.onload = function(){
var vm = new Vue({
el:'#box',
data:{
msg:'Hello World!',
},
methods:{
get:function(){
//发送get请求
this.$http.get('/try/ajax/ajax_info.txt').then(function(res){
document.write(res.body);
},function(){
console.log('请求失败处理');
});
}
}
});
}
</script>
如果需要传递数据,可以使用 this.$http.get('get.php',{params : jsonData}) 格式,第二个参数 jsonData 就是传到后端的数据。
this.$http.get('get.php',{params : {a:1,b:2}}).then(function(res){
document.write(res.body);
},function(res){
console.log(res.status);
});
post 请求
post 发送数据到后端,需要第三个参数 {emulateJSON:true}。
emulateJSON 的作用: 如果Web服务器无法处理编码为 application/json 的请求,你可以启用 emulateJSON 选项。
<div id="box">
<input type="button" @click="post()" value="点我异步获取数据(Post)">
</div>
<script type = "text/javascript">
window.onload = function(){
var vm = new Vue({
el:'#box',
data:{
msg:'Hello World!',
},
methods:{
post:function(){
//发送 post 请求
this.$http.post('/try/ajax/demo_test_post.php',{name:"菜鸟教程",url:"http://www.runoob.com"},{emulateJSON:true}).then(function(res){
document.write(res.body);
},function(res){
console.log(res.status);
});
}
}
});
}
</script>
demo_test_post.php 代码如下:
<?php
$name = isset($_POST['name']) ? htmlspecialchars($_POST['name']) : '';
$city = isset($_POST['url']) ? htmlspecialchars($_POST['url']) : '';
echo '网站名: ' . $name;
echo "
";
echo 'URL 地址: ' .$city;
?>
语法 & API
你可以使用全局对象方式 Vue.http 或者在一个 Vue 实例的内部使用 this.$http来发起 HTTP 请求。
// 基于全局Vue对象使用http
Vue.http.get('/someUrl', [options]).then(successCallback, errorCallback);
Vue.http.post('/someUrl', [body], [options]).then(successCallback, errorCallback);
// 在一个Vue实例内使用$http
this.$http.get('/someUrl', [options]).then(successCallback, errorCallback);
this.$http.post('/someUrl', [body], [options]).then(successCallback, errorCallback);
vue-resource 提供了 7 种请求 API(REST 风格):
get(url, [options])
head(url, [options])
delete(url, [options])
jsonp(url, [options])
post(url, [body], [options])
put(url, [body], [options])
patch(url, [body], [options])
除了 jsonp 以外,另外 6 种的 API 名称是标准的 HTTP 方法。
options 参数说明:
| 参数 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| url | string | 请求的目标URL |
| body | Object, FormData, string | 作为请求体发送的数据 |
| headers | Object | 作为请求头部发送的头部对象 |
| params | Object | 作为URL参数的参数对象 |
| method | string | HTTP方法 (例如GET,POST,...) |
| timeout | number | 请求超时(单位:毫秒) (0表示永不超时) |
| before | function(request) | 在请求发送之前修改请求的回调函数 |
| progress | function(event) | 用于处理上传进度的回调函数 ProgressEvent |
| credentials | boolean | 是否需要出示用于跨站点请求的凭据 |
| emulateHTTP | boolean | 是否需要通过设置X-HTTP-Method-Override头部并且以传统POST方式发送PUT,PATCH和DELETE请求。 |
| emulateJSON | boolean | 设置请求体的类型为application/x-www-form-urlencoded |
通过如下属性和方法处理一个请求获取到的响应对象:
| 参数 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| url | string | 响应的 URL 源 |
| body | Object, Blob, string | 响应体数据 |
| headers | Header | 请求头部对象 |
| ok | boolean | 当 HTTP 响应码为 200 到 299 之间的数值时该值为 true |
| status | number | HTTP 响应码 |
| statusText | string | HTTP 响应状态 |
| 方法 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| text() | 约定值 | 以字符串方式返回响应体 |
| json() | 约定值 | 以格式化后的 json 对象方式返回响应体 |
| blob() | 约定值 | 以二进制 Blob 对象方式返回响应体 |