写一个简单的C词法分析器
在写本文过程中,我参考了《词法分析器的实现》中的一些内容。这里我们主要讨论写一个C语言的词法分析器。
一、关键字
首先,C语言中关键字有:
auto、break、case、char、const、continue、default、do、double、else、enum、extern、float、for、goto、if、int、long、register、return、short、signed、sizeof、static、struct、switch、typedef、unsigned、union、void、volatile、while等共32个关键字。
二、运算符
C语言中的运算符有:
(、)、[、]、->、.、!、~、++、--、-、()、*、&、*、/、%、+、-、<<、>>、<、<=、>、>=、==、!=、&、^、|、&&、||、?:、=、+=、-=、*=、/=、%=、&=、^=、|=、<<=、>>=、,、等共45个运算符。
说明:-减号与-负号在词法阶段无法判别,需要在语法或予以阶段判别;同理*乘号与*指针操作符也是这样的。
三、界符
另外C语言还有以下界符:
;、{、}、:
四、标示符
C语言中标示符的定义为:开头可以是下划线或字母,后面可以是下划线、字母或数字。
五、常数
整形数和浮点数
六、空白符
C语言中的空白符有:空格符、制表符、换行符,这些空白符在词法分析阶段可以被忽略。
七、注释
C语言中的注释形式为:/*…*/,可以多行注释。
下面我们给出C程序中token和其对应的种别码:
|
单词符号 |
种别码 |
单词符号 |
种别码 |
单词符号 |
种别码 |
|
auto |
1 |
union |
28 |
[ |
55 |
|
break |
2 |
unsigned |
29 |
] |
56 |
|
case |
3 |
void |
30 |
^ |
57 |
|
char |
4 |
volatile |
31 |
^= |
58 |
|
const |
5 |
while |
32 |
{ |
59 |
|
continue |
6 |
- |
33 |
| |
60 |
|
default |
7 |
-- |
34 |
|| |
61 |
|
do |
8 |
-= |
35 |
|= |
62 |
|
double |
9 |
-> |
36 |
} |
63 |
|
else |
10 |
! |
37 |
~ |
64 |
|
enum |
11 |
!= |
38 |
+ |
65 |
|
extern |
12 |
% |
39 |
++ |
66 |
|
float |
13 |
%= |
40 |
+= |
67 |
|
for |
14 |
& |
41 |
< |
68 |
|
goto |
15 |
&& |
42 |
<< |
69 |
|
if |
16 |
&= |
43 |
<<= |
70 |
|
int |
17 |
( |
44 |
<= |
71 |
|
long |
18 |
) |
45 |
= |
72 |
|
register |
19 |
* |
46 |
== |
73 |
|
return |
20 |
*= |
47 |
> |
74 |
|
short |
21 |
, |
48 |
>= |
75 |
|
signed |
22 |
. |
49 |
>> |
76 |
|
sizeof |
23 |
/ |
50 |
>>= |
77 |
|
static |
24 |
/= |
51 |
" |
78 |
|
struct |
25 |
: |
52 |
/*注释*/ |
79 |
|
switch |
26 |
; |
53 |
常数 |
80 |
|
typedef |
27 |
? |
54 |
标识符 |
81 |
我们的词法分析程序根据所给的源代码程序,输出的是二元组:<单词符号, 种别码>。对于常数的形式,我们也是直接以字符串的形式表达。
以上token存放在c_keys.txt文件中
// token auto 1 break 2 case 3 char 4 const 5 continue 6 default 7 do 8 double 9 else 10 enum 11 extern 12 float 13 for 14 goto 15 if 16 int 17 long 18 register 19 return 20 short 21 signed 22 sizeof 23 static 24 struct 25 switch 26 typedef 27 union 28 unsigned 29 void 30 volatile 31 while 32 - 33 -- 34 -= 35 -> 36 ! 37 != 38 % 39 %= 40 & 41 && 42 &= 43 ( 44 ) 45 * 46 *= 47 , 48 . 49 / 50 /= 51 : 52 ; 53 ? 54 [ 55 ] 56 ^ 57 ^= 58 { 59 | 60 || 61 |= 62 } 63 ~ 64 + 65 ++ 66 += 67 < 68 << 69 <<= 70 <= 71 = 72 == 73 > 74 >= 75 >> 76 >>= 77 " 78 /*注释*/ 79 常数 80 标识符 81
C 词法分析器程序如下:
// C语言词法分析器 #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <map> #include <string> #include <fstream> #include <sstream> #include <vector> using namespace std; struct _2tup { string token; int id; }; bool is_blank(char ch) { return ch == ' ' || ch == ' '; } bool adv(string& token, char& ch, string::size_type& pos, const string& prog) { token += ch; ++pos; if (pos >= prog.size()) { return false; } else { ch = prog[pos]; return true; } } bool gofor(char& ch, string::size_type& pos, const string& prog) { ++pos; if (pos >= prog.size()) { return false; } else { ch = prog[pos]; return true; } } _2tup scanner(const string& prog, string::size_type& pos, const map<string, int>& keys, int& row) { /* if 标示符 else if 数字 else 符号 */ _2tup ret; string token; int id = 0; char ch; ch = prog[pos]; while(is_blank(ch)) { ++pos; ch = prog[pos]; } // 判断标示符、关键字 if ((ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') || (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z') || ch == '_') { while((ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') || (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') || (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z') || ch == '_') { token += ch; if (!gofor(ch, pos, prog)) { break; } //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; } // 这里先看做都是其他标示符 id = keys.size(); // 验证是否是关键字 map<string, int>::const_iterator cit = keys.find(token); if (cit != keys.end()) { id = cit->second; } } // 识别常数 else if ((ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') || ch == '.') { while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9' || ch == '.') { token += ch; if (!gofor(ch, pos, prog)) { break; } //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; } id = keys.size() - 1; int dot_num = 0; for (string::size_type i = 0; i != token.size(); ++i) { if (token[i] == '.') { ++dot_num; } } if (dot_num > 1) { id = -1; } } else { map<string, int>::const_iterator cit; switch (ch) { case '-': // - 操作符 token += ch; if (gofor(ch, pos, prog)) //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; { if (ch == '-' || ch == '=' || ch == '>') // -- 操作符 { token += ch; gofor(ch, pos, prog); //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; } } cit = keys.find(token); if (cit != keys.end()) { id = cit->second; } break; case '!': // ! 操作符 case '%': // % 操作符 case '*': case '^': case '=': token += ch; if (gofor(ch, pos, prog)) //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; { if (ch == '=') // !% %= 操作符 { token += ch; gofor(ch, pos, prog); //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; } } cit = keys.find(token); if (cit != keys.end()) { id = cit->second; } break; case '/': // / 操作符 token += ch; if (gofor(ch, pos, prog)) //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; { if (ch == '=') // /= 操作符 { token += ch; gofor(ch, pos, prog); //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; } else if (ch == '/') // 单行注释 { token += ch; ++pos; while (pos < prog.size()) { ch = prog[pos]; if (ch == ' ') { break; } token += ch; ++pos; } if (pos >= prog.size()) { ; } else { ; } id = keys.size() - 2; break; } else if (ch == '*') // 注释 { // 实现方式1 //string::size_type p1 = pos - 1; // //string::size_type p2 = prog.find("*/", p1); //if (p2 != string::npos) //{ // token = prog.substr(p1, p2 - p1 + 2); // pos = p2 + 2; // ch = prog[pos]; // id = keys.size() - 2; //} //else //{ // id = -1; //} //break; // 注释的另一种实现,为了得到出错行号 token += ch; //++pos; if (!gofor(ch, pos, prog)) { token += " !!!注释错误!!!"; id = -10; break; } //ch = prog[pos]; if (pos + 1 >= prog.size()) { token += ch; token += " !!!注释错误!!!"; id = -10; break; } char xh = prog[pos + 1]; while (ch != '*' || xh != '/') { token += ch; if (ch == ' ') { ++row; } //++pos; if (!gofor(ch, pos, prog)) { token += " !!!注释错误!!!"; id = -10; ret.token = token; ret.id = id; return ret; } //ch = prog[pos]; if (pos + 1 >= prog.size()) { token += ch; token += " !!!注释错误!!!"; id = -10; ret.token = token; ret.id = id; return ret; } xh = prog[pos + 1]; } token += ch; token += xh; pos += 2; ch = prog[pos]; id = keys.size() - 2; break; } } cit = keys.find(token); if (cit != keys.end()) { id = cit->second; } break; case '&': token += ch; if (gofor(ch, pos, prog)) //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; { if (ch == '&' || ch == '=') { token += ch; gofor(ch, pos, prog); //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; } } cit = keys.find(token); if (cit != keys.end()) { id = cit->second; } break; case '|': token += ch; if (gofor(ch, pos, prog)) //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; { if (ch == '|' || ch == '=') { token += ch; gofor(ch, pos, prog); //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; } } cit = keys.find(token); if (cit != keys.end()) { id = cit->second; } break; case '+': token += ch; if (gofor(ch, pos, prog)) //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; { if (ch == '+' || ch == '=') { token += ch; gofor(ch, pos, prog); //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; } } cit = keys.find(token); if (cit != keys.end()) { id = cit->second; } break; case '<': token += ch; if (gofor(ch, pos, prog)) //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; { if (ch == '<') { token += ch; if (gofor(ch, pos, prog)) //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; { if (ch == '=') { token += ch; gofor(ch, pos, prog); //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; } } } else if (ch == '=') { token += ch; gofor(ch, pos, prog); //++pos; //ch = prog[ch]; } } cit = keys.find(token); if (cit != keys.end()) { id = cit->second; } break; case '>': token += ch; if (gofor(ch, pos, prog)) //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; { if (ch == '>') { token += ch; if (gofor(ch, pos, prog)) //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; { if (ch == '=') { token += ch; gofor(ch, pos, prog); //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; } } } else if (ch == '=') { token += ch; gofor(ch, pos, prog); //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; } } cit = keys.find(token); if (cit != keys.end()) { id = cit->second; } break; case '(': case ')': case ',': case '.': case ':': case ';': case '?': case '[': case ']': case '{': case '}': case '~': case '"': token += ch; gofor(ch, pos, prog); //++pos; //ch = prog[pos]; cit = keys.find(token); if (cit != keys.end()) { id = cit->second; } break; //case '#': // id = 0; // token += ch; // break; case ' ': token += "换行"; ++pos; ch = prog[pos]; id = -2; break; default: token += "错误"; ++pos; ch = prog[pos]; id = -1; break; } } ret.token = token; ret.id = id; return ret; } void init_keys(const string& file, map<string, int>& keys) { ifstream fin(file.c_str()); if (!fin) { cerr << file << " doesn't exist!" << endl; exit(1); } keys.clear(); string line; string key; int id; while (getline(fin, line)) { istringstream sin(line); sin >> key >> id; keys[key] = id; } } void read_prog(const string& file, string& prog) { ifstream fin(file.c_str()); if (!fin) { cerr << file << " error!" << endl; exit(2); } prog.clear(); string line; while (getline(fin, line)) { prog += line + ' '; } } int main() { map<string, int> keys; init_keys("c_keys.txt", keys); string prog; read_prog("prog.txt", prog); vector< _2tup > tups; string token, id; string::size_type pos = 0; int row = 1; _2tup tu; cout << prog << endl << endl; // prog += "#"; // 标识充值,其实可以检测 pos 来判别是否终止 int no = 0; do { tu = scanner(prog, pos, keys, row); switch (tu.id) { case -1: ++no; cout << no << ": "; cout << "Error in row" << row << "!" << '<' << tu.token<< "," << tu.id << '>' << endl; tups.push_back(tu); break; case -2: ++row; // cout << '<' << tu.token<< "," << tu.id << '>' << endl; break; default: ++no; cout << no << ": "; cout << '<' << tu.token<< "," << tu.id << '>' << endl; tups.push_back(tu); break; } } while (/*tu.id != 0 && */pos < prog.size()); cout << endl << tups.size() << endl; return 0; }
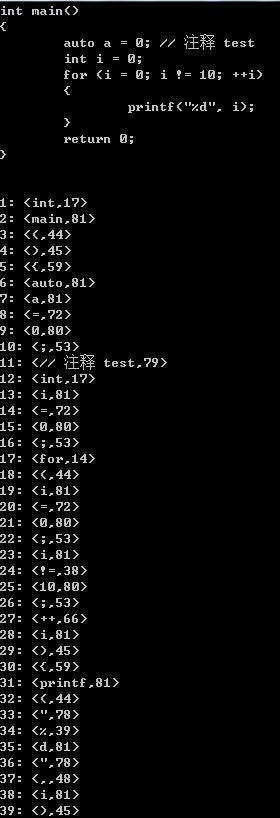
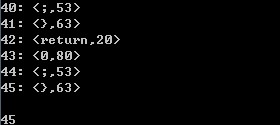
测试样例1:
int main() { auto a = 0; // 注释 test int i = 0; for (i = 0; i != 10; ++i) { printf("%d", i); } return 0; }
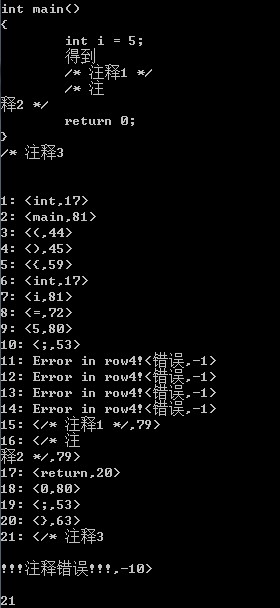
测试样例2
int main() { int i = 5; 得到 /* 注释1 */ /* 注 释2 */ return 0; } /* 注释3
总结
以上我们实现了一个C语言的词法分析器,其原理主要就是根据C语言中各个token的规则,逐位分析。
词法分析后续工作还有语法分析、语义分析等等。
另外还有制作一个过滤注释的程序、C预处理器等。
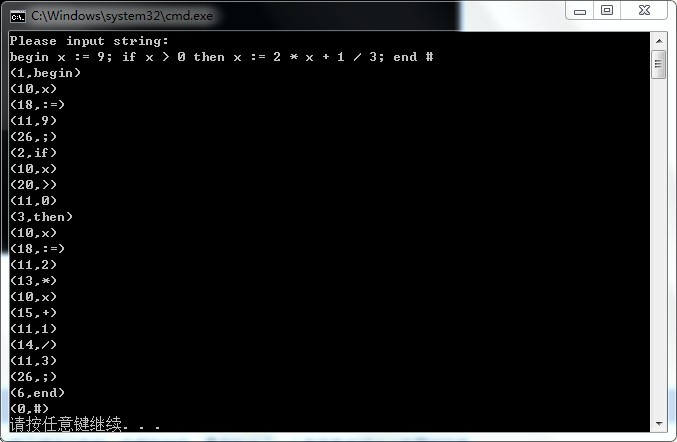
附:《词法分析器的实现》中的相关内容
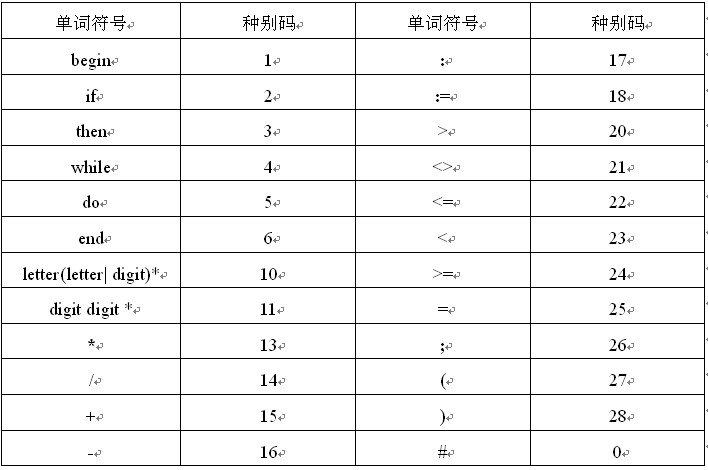
该文中关键字有:
begin、if、then、while、do、end
运算符有:
:=、+、-、*、/、<、<=、<>、>、>=、=、;、(、)、#
标示符ID和整形常熟的定义为:
ID = letter(letter|digit)*
NUM = digit digit*
空白符由空格、制表符、换行符组成,空格用来分割ID、NUM、运算符、界符、关键字等。词法分析阶段通常将其忽略。
各种token及对应的种别码
程序输出二元组(syn, token或sum),其中syn为单词种别码,token为存放的单词自身字符串,sum为整形常数。
程序如下(有些改动):
#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> using namespace std; char prog[80], token[8]; char ch; int syn, p, m = 0, n, row, sum = 0; char* rwtab[6] = {"begin", "if", "then", "while", "do", "end"}; void scanner() { /* if 标示符 else if 数字 else 符号 */ for (n = 0; n < 8; ++n) { token[n] = NULL; } ch = prog[p++]; while(ch == ' ') { ch = prog[p]; ++p; } if ((ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') || (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z')) { m = 0; while((ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') || (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') || (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z')) { token[m++] = ch; ch = prog[p++]; } token[m++] = '�'; --p; syn = 10; for (n = 0; n < 6; ++n) { if (strcmp(token, rwtab[n]) == 0) { syn = n + 1; break; } } } else if ((ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')) { sum = 0; while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') { sum = sum * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = prog[p++]; } --p; syn = 11; if (sum > 32767) { syn = -1; } } else switch (ch) { case '<': m = 0; token[m++] = ch; ch = prog[p++]; if (ch == '>') { syn = 21; token[m++] = ch; } else if (ch == '=') { syn = 22; token[m++] = ch; } else { syn = 23; --p; } break; case '>': m = 0; token[m++] = ch; ch = prog[p++]; if (ch == '=') { syn = 24; token[m++] = ch; } else { syn = 20; --p; } break; case ':': m = 0; token[m++] = ch; ch = prog[p++]; if (ch == '=') { syn = 18; token[m++] = ch; } else { syn = 17; --p; } break; case '*': syn = 13; token[0] = ch; break; case '/': syn = 14; token[0] = ch; break; case '+': syn = 15; token[0] = ch; break; case '-': syn = 16; token[0] = ch; break; case '=': syn = 25; token[0] = ch; break; case ';': syn = 26; token[0] = ch; break; case '(': syn = 27; token[0] = ch; break; case ')': syn = 28; token[0] = ch; break; case '#': syn = 0; token[0] = ch; break; case ' ': syn = -2; break; default: syn = -1; break; } } int main() { p = 0; row = 1; cout << "Please input string:" << endl; do { cin.get(ch); prog[p++] = ch; } while (ch != '#'); p = 0; do { scanner(); switch (syn) { case 11: cout << '(' << syn << "," << sum << ")" << endl; break; case -1: cout << "Error in row" << row << "!" << endl; break; case -2: ++row; break; default: cout << "(" << syn << "," << token << ")" << endl; break; } } while (syn != 0); }