一、MNIST实验内容
MNIST的实验比较简单,可以直接通过下面的程序加上程序上的部分注释就能很好的理解了,后面在完善具体的相关的数学理论知识,先记录在这里:
代码如下所示:
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np %matplotlib inline mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('/home/ubuntu-mm/TensorFlow/Learning/MNIST_data', one_hot=True) #下载MINIST数据集 #表示输入任意数量的MNIST图像,每一张图展平成784维的向量 #placeholder是占位符,在训练时指定 x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) #初始化W,b矩阵 W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10])) b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10])) #tf.matmul(X,W)表示x乘以W y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x, W) + b) #为了计算交叉熵,我们首先需要添加一个新的占位符用于输入正确值 y_ = tf.placeholder("float", [None,10]) #交叉熵损失函数 cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y)) #模型的训练,不断的降低成本函数 #要求TensorFlow用梯度下降算法(gradient descent algorithm)以0.01的学习速率最小化交叉熵 train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01).minimize(cross_entropy) #在运行计算之前,需要添加一个操作来初始化我们创建的变量 init = tf.global_variables_initializer() #在Session里面启动我模型,并且初始化变量 with tf.Session() as sess: # sess = tf.Session() # sess.run(init) sess.run(init) #开始训练模型,循环训练1000次 for i in range(50): #随机抓取训练数据中的100个批处理数据点 batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100) #然后我们用这些数据点作为参数替换之前的占位符来运行train_step sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys}) #检验真实标签与预测标签是否一致 correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1), tf.argmax(y_,1)) #计算精确度,将true和false转化成相应的浮点数,求和取平均 accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float")) #计算所学习到的模型在测试数据集上面的正确率 print(sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: mnist.test.images, y_: mnist.test.labels})) print 'W is:',W.eval()[10] print 'b is:',b.eval() batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100) # print 'batch_xs[1]=',batch_xs[1] print 'batch_ys[1]=',batch_ys[1] x_in = tf.reshape(batch_xs[1],[1,784]) Y_Predict = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x_in, W) + b) print 'Y_Predict is :',Y_Predict.eval() Ori_Pic = np.zeros([28,28]) for m in range(784): i = m%28 j = (m-i)/28 Ori_Pic[j][i] = batch_xs[1][m] plt.figure(1) plt.imshow(Ori_Pic)
实验运行的结果如下所示:
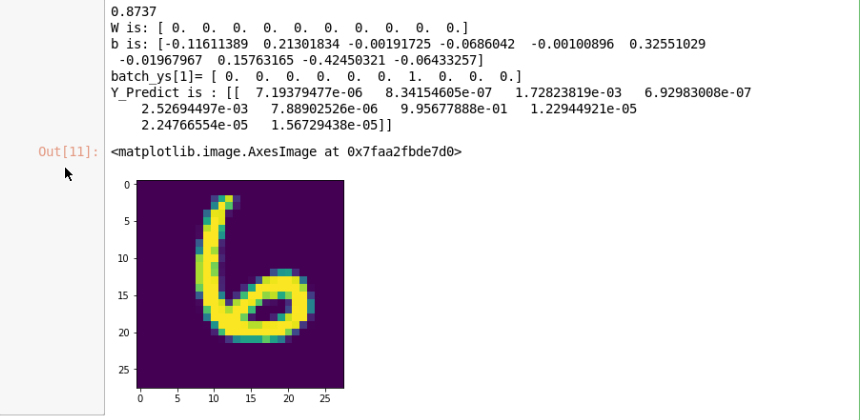 由结果显示的可知:图片对应为6的概率是99.56%
由结果显示的可知:图片对应为6的概率是99.56%
二、交叉熵损失函数的基本原理: