1、FFT算法概要:
FFT(Fast Fourier Transformation)是离散傅氏变换(DFT)的快速算法。即为快速傅氏变换。它是根据离散傅氏变换的奇、偶、虚、实等特性,对离散傅立叶变换的算法进行改进获得的。
2、FFT算法原理:
离散傅里叶变换DFT公式:
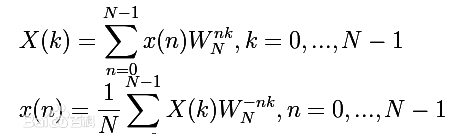
FFT算法(Butterfly算法)
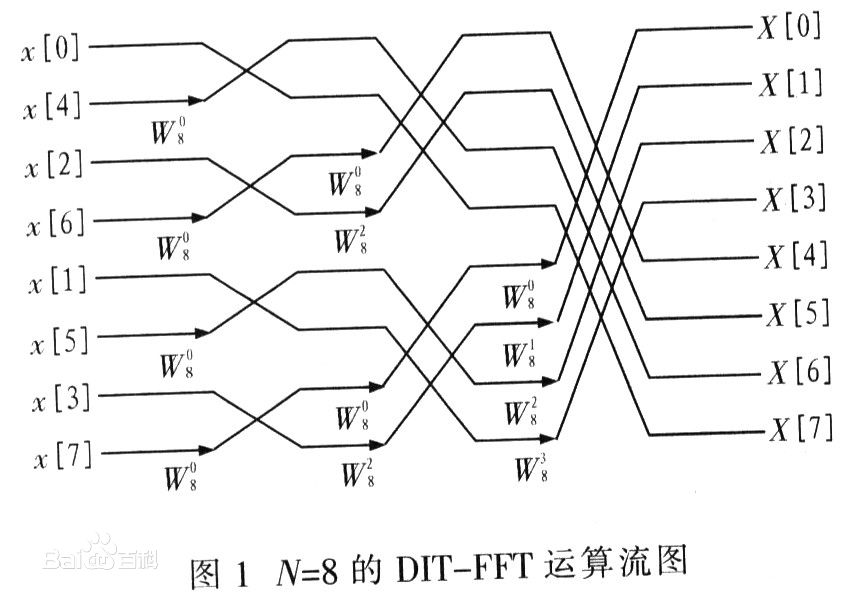
设x(n)为N项的复数序列,由DFT变换,任一X(m)的计算都需要N次复数乘法和N-1次复数加法,而一次复数乘法等于四次实数乘法和两次实数加法,一次复数加法等于两次实数加法,即使把一次复数乘法和一次复数加法定义成一次“运算”(四次实数乘法和四次实数加法),那么求出N项复数序列的X(m),即N点DFT变换大约就需要N^2次运算。当N=1024点甚至更多的时候,需要N2=1048576次运算,在FFT中,利用WN的周期性和对称性,把一个N项序列(设N=2k,k为正整数),分为两个N/2项的子序列,每个N/2点DFT变换需要(N/2)2次运算,再用N次运算把两个N/2点的DFT变换组合成一个N点的DFT变换。这样变换以后,总的运算次数就变成N+2*(N/2)^2=N+(N^2)/2。继续上面的例子,N=1024时,总的运算次数就变成了525312次,节省了大约50%的运算量。而如果我们将这种“一分为二”的思想不断进行下去,直到分成两两一组的DFT运算单元,那么N点的DFT变换就只需要N/2log2N次的运算,N在1024点时,运算量仅有5120次,是先前的直接算法的近1/200,点数越多,运算量的节约就越大,这就是FFT的优越性。
3、FFT算法官方实现:
![]()
搭建FFTW库并生成所需要的lib文件:
Step1:从官网下载对应的.zip文件,例如我是win10_x86的操作系统,下载64bit的安装包:

Step2:下载完成之后解压到你希望安装的FFTW库的位置
Step3:打开CMD命令操作行,切换到Step2中的安装目录下,执行下面的指令代码生成.lib文件(需要安装Visual Studio,用VC++中的lib命令生成系统能够使用的.lib文件)
 打开的方式为,按下window键,输入vs,小娜会自动帮你查找对应的File。
打开的方式为,按下window键,输入vs,小娜会自动帮你查找对应的File。
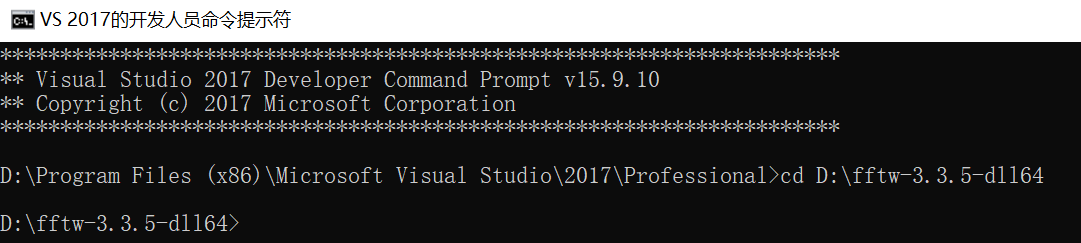 切换到对应的路径之后就可以使用lib命令来生成.lib文件了:
切换到对应的路径之后就可以使用lib命令来生成.lib文件了:
1 lib /def:libfftw3-3.def 2 lib /def:libfftw3f-3.def 3 lib /def:libfftw3l-3.def
查看对应的目录,我们就能看到生成的.lib文件:

在工程中使用FFTW库
首先在VS2017中创建一个工程命名为FFTW_Test
FFTW_Test.cpp文件内容如下:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 #include "fftw3.h" 5 #pragma comment(lib, "libfftw3-3.lib") 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 int main(void) 10 { 11 /* 12 *fftw_complex 是FFTW自定义的复数类 13 *引入<complex>则会使用STL的复数类 14 */ 15 fftw_complex x[5]; 16 fftw_complex y[5]; 17 18 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 19 x[i][REAL] = i; 20 x[i][IMAG] = 0; 21 } 22 23 //定义plan,包含序列长度、输入序列、输出序列、变换方向、变换模式 24 fftw_plan plan = fftw_plan_dft_1d(5, x, y, FFTW_FORWARD, FFTW_ESTIMATE); 25 26 //对于每个plan,应当"一次定义 多次使用",同一plan的运算速度极快 27 fftw_execute(plan); 28 29 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 30 cout << y[i][REAL] << " " << y[i][IMAG] << endl; 31 } 32 33 //销毁plan 34 fftw_destroy_plan(plan); 35 }
将FFTW相关的库文件拷贝到FFTW_Test工程目录下,拷贝的位置需要和FFTW_Test.cpp在同一个目录当中!
拷贝的文件如下图所示(只需要将FFTW安装目录下的这三个文件拷贝过去即可):

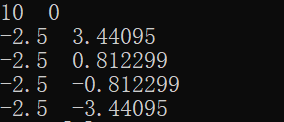
程序运行结果:
参考资料
- 官方网址:http://www.fftw.org/
- 官方下载:http://www.fftw.org/download.html
- 其他参考:https://blog.csdn.net/cyh706510441/article/details/46676123
4、FFT算法C/C++/Python代码:
Code1(DFT):
1 char DFT_Alg(float *Signal, float *Fre, int L) 2 { 3 long long i,j; 4 float real, imag, coff1, coff2; 5 coff1 = -2*pi/L; 6 for(i=0;i<L;i++){ 7 for(j=0;j<L;j++){ 8 coff2 = coff1*i*j; 9 real += Signal[j]*cos(coff2); 10 imag += Signal[j]*sin(coff2); 11 } 12 printf("Processing:%d ",i); 13 Fre[i] = real*real + imag*imag; 14 } 15 return 1; 16 }
Code2(FFT):

1 typedef float FFT_TYPE; 2 3 #ifndef PI 4 #define PI (3.14159265f) 5 #endif 6 7 typedef struct complex_st { 8 FFT_TYPE real; 9 FFT_TYPE img; 10 } complex; 11 12 static void BitReverse(complex *x, complex *r, int n, int l) 13 { 14 int i = 0; 15 int j = 0; 16 short stk = 0; 17 static complex *temp = 0; 18 19 temp = (complex *)malloc(sizeof(complex) * n); 20 if (!temp) { 21 return; 22 } 23 24 for(i=0; i<n; i++) { 25 stk = 0; 26 j = 0; 27 do { 28 stk |= (i>>(j++)) & 0x01; 29 if(j<l) 30 { 31 stk <<= 1; 32 } 33 }while(j<l); 34 35 if(stk < n) { /* 满足倒位序输出 */ 36 temp[stk] = x[i]; 37 } 38 } 39 /* copy @temp to @r */ 40 for (i=0; i<n; i++) { 41 r[i] = temp[i]; 42 } 43 free(temp); 44 } 45 46 int fft(complex *x, int N) 47 { 48 int i,j,l,ip; 49 static int M = 0; 50 static int le,le2; 51 static FFT_TYPE sR,sI,tR,tI,uR,uI; 52 53 M = (int)(log(N) / log(2)); 54 55 BitReverse(x,x,N,M); 56 57 for (l=1; l<=M; l++) { 58 le = (int)pow(2,l); 59 le2 = (int)(le / 2); 60 uR = 1; 61 uI = 0; 62 sR = cos(PI / le2); 63 sI = -sin(PI / le2); 64 for (j=1; j<=le2; j++) { 65 //jm1 = j - 1; 66 for (i=j-1; i<=N-1; i+=le) { 67 ip = i + le2; 68 tR = x[ip].real * uR - x[ip].img * uI; 69 tI = x[ip].real * uI + x[ip].img * uR; 70 x[ip].real = x[i].real - tR; 71 x[ip].img = x[i].img - tI; 72 x[i].real += tR; 73 x[i].img += tI; 74 } 75 tR = uR; 76 uR = tR * sR - uI * sI; 77 uI = tR * sI + uI *sR; 78 } 79 } 80 return 0; 81 } 82 int ifft(complex *x, int N) 83 { 84 int k = 0; 85 for (k=0; k<=N-1; k++) { 86 x[k].img = -x[k].img; 87 } 88 fft(x, N); /* using FFT */ 89 for (k=0; k<=N-1; k++) { 90 x[k].real = x[k].real / N; 91 x[k].img = -x[k].img / N; 92 } 93 return 0; 94 }
Code3(DFT-Python):
1 def DFT(x): 2 """ 3 Input: 4 x (numpy array) = input sequence of length N 5 Output: 6 The function should return a numpy array of length N 7 X (numpy array) = The N point DFT of the input sequence x 8 """ 9 N = len(x) 10 real = np.zeros(N) 11 imag = np.zeros(N) 12 for i in range(N): 13 for j in range(N): 14 real[i] += x[j]*np.cos(-2*np.pi*i*j/N) 15 imag[i] += x[j]*np.sin(-2*np.pi*i*j/N) 16 Res = 1j*imag + real 17 return Res 18 def IDFT(X): 19 """ 20 Input: 21 X (numpy array) = frequency spectrum (length N) 22 Output: 23 The function should return a numpy array of length N 24 x (numpy array) = The N point IDFT of the frequency spectrum X 25 """ 26 N = len(X) 27 real = np.zeros(N) 28 imag = np.zeros(N) 29 for i in range(N): 30 for k in range(N): 31 param1 = X[k].real 32 param2 = X[k].imag 33 sin = np.sin(2*np.pi*i*k/N) 34 cos = np.cos(2*np.pi*i*k/N) 35 real[i] += param1*cos-param2*sin 36 imag[i] += param1*sin+param2*cos 37 Res = 1j*imag/N + real/N 38 return Res
5、多种平台的FFT算法移植:
未完待续
