Ansible安装部署
Ansible是一种集成IT系统的配置管理, 应用部署, 执行特定任务的开源平台. 它基于Python语言实现, 部署只需在主控端部署Ansible环境, 被控端无需安装代理工具, 只需打开SSH, 让主控端通过SSH秘钥认证对其进行所有的管理监控操作.它有一个很庞大的用户群体以及丰富的API, 相对适合部署到数量比较大且对系统软件安装要求比较严格的集群中.
安装环境:
System: Centos 6.7 x64
Master: master.example.com
Minion: client01.example.com
Minion: client02.example.com
一. 环境部署及安装
1. 关闭iptables和SELINUX
2. Master端安装EPEL第三方yum源
# rpm -Uvh http://ftp.linux.ncsu.edu/pub/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
3.安装Ansible
# yum install ansible -y
4.添加环境变量以便vi能正常显示中文注释.
# vi /etc/profile 添加: export LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8 export LANG=en_US.UTF-8 export LANGUAGE=en_US.UTF-8
# source /etc/profile
二. 初始配置
1. 修改主机及组配置
# cd /etc/ansible # cp hosts hosts.bak # cat /dev/null > hosts # vi /etc/ansible/hosts [webservers] client01.example.com client02.example.com [nginx01] client01.example.com [nginx02] client02.example.com
2.配置SSH秘钥认证
# yum install ssh* -y # ssh-keygen -t rsa Generating public/private rsa key pair. Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa): Created directory '/root/.ssh'. Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Enter same passphrase again: Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa. Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub. The key fingerprint is: 24:13:34:e9:71:2b:20:0b:48:a6:86:9a:1d:1b:1d:26 root@master.example.comThe key's randomart p_w_picpath is: +--[ RSA 2048]----+ |ooE o.+. | |* .+..oo. | |oooo.ooo.. | |oo.+ o+. | |o o .S | | | | | | | | | +-----------------+
同步公钥文件id_rsa.pub到目标主机
# ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@client01.example.com # ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@client02.example.com
校验SSH免密码配置是否成功.
# ssh root@client02.example.com
如直接进入则配置完成.
3.定义主机与组
(一个组就是一个标签,标签内的主机配置一样,在使用时调用标签执行写好的脚本或命令)
所有定义的主机与组规则都在/etc/Ansible/hosts下.
常见的写法:
192.168.1.21:2135 定义一个IP为192.168.1.21, SSH端口为2135的主机.
jumper ansible_ssh_port=22 ansible_ssh_host=192.168.1.50 定义一个别名为jumper, SSH端口为22, IP为192.168.1.50的主机.
组成员主机名称范例:
[webservers] www[001:006].example.com [dbservers] db-[a:f].example.com
4.定义主机变量
主机可以指定变量, 后面可以供Playbooks调用
[atlanta] host1 http_port=80 maxRequestsPerChild=808 host2 http_port=8080 maxRequestsPerChild=909
5.定义组变量
[atlanta] host1 host2 [atlanta:vars] ntp_server=ntp.atlanta.example.com proxy=proxy.atlanta.example.com
6.匹配目标
重启webservers组所有SSH服务.
# ansible webservers -m service -a "name=sshd state=restarted"
client01.example.com | success >> {
"changed": true,
"name": "sshd",
"state": "started"
}
client02.example.com | success >> {
"changed": true,
"name": "sshd",
"state": "started"
}三. Ansible常用模块及API
1.远程命令模块
command: 执行远程主机SHELL命令:
# ansible webservers -m command -a "free -m" client01.example.com | success | rc=0 >> total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 996 108 887 0 7 41 -/+ buffers/cache: 58 937 Swap: 1023 0 1023 client02.example.com | success | rc=0 >> total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 996 108 888 0 7 41 -/+ buffers/cache: 58 937 Swap: 1023 0 1023
script: 远程执行MASTER本地SHELL脚本.(类似scp+shell)
# echo "df -h" > ~/test.sh
# ansible webservers -m script -a "~/test.sh"
client01.example.com | success >> {
"changed": true,
"rc": 0,
"stderr": "OpenSSH_5.3p1, OpenSSL 1.0.1e-fips 11 Feb 2013
debug1: Reading configuration data /etc/ssh/ssh_config
debug1: Applying options for *
debug1: auto-mux: Trying existing master
debug1: mux_client_request_session: master session id: 2
debug1: mux_client_request_session: master session id: 2
Shared connection to client01.example.com closed.
",
"stdout": "Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda3 6.6G 815M 5.5G 13% /
tmpfs 499M 0 499M 0% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 190M 27M 154M 15% /boot
"
}
client02.example.com | success >> {
"changed": true,
"rc": 0,
"stderr": "OpenSSH_5.3p1, OpenSSL 1.0.1e-fips 11 Feb 2013
debug1: Reading configuration data /etc/ssh/ssh_config
debug1: Applying options for *
debug1: auto-mux: Trying existing master
debug1: mux_client_request_session: master session id: 2
debug1: mux_client_request_session: master session id: 2
Shared connection to client02.example.com closed.
",
"stdout": "Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda3 6.6G 815M 5.5G 13% /
tmpfs 499M 0 499M 0% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 190M 27M 154M 15% /boot
"
}2. copy模块
实现主控端向目标主机拷贝文件, 类似scp功能.
该实例实现~/test.sh文件至webservers组目标主机/tmp下, 并更新文件owner和group
# ansible webservers -m copy -a "src=~/test.sh dest=/tmp/ owner=root group=root mode=0755"
client01.example.com | success >> {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "c989bd551bfa8c755f6cacacb90c5c509432110e",
"dest": "/tmp/test.sh",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "69a238d8cb3c5f979252010b3299e524",
"mode": "0755",
"owner": "root",
"size": 6,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1445322165.21-234077402845688/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
client02.example.com | success >> {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "c989bd551bfa8c755f6cacacb90c5c509432110e",
"dest": "/tmp/test.sh",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "69a238d8cb3c5f979252010b3299e524",
"mode": "0755",
"owner": "root",
"size": 6,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1445322165.2-164402895387597/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}3.stat模块
获取远程文件状态信息, 包括atime, ctime, mtime, md5, uid, gid等信息.
# ansible webservers -m stat -a "path=/etc/sysctl.conf"
client02.example.com | success >> {
"changed": false,
"stat": {
、
、
、
}
}
client01.example.com | success >> {
"changed": false,
"stat": {
、
、
、
}
}4.get_url模块
实现在远程主机下载指定URL到本地.
# ansible webservers -m get_url -a "url=http://www.showerlee.com dest=/tmp/index.html mode=0400 force=yes"
client02.example.com | success >> {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "470d6ab960810153bb8149c3754b0e8a2d89209d",
"dest": "/tmp/index.html",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "009949f770f35a4ea82105e5e923abcb",
"mode": "0400",
"msg": "OK (unknown bytes)",
"owner": "root",
"sha256sum": "",
"size": 81635,
"src": "/tmp/tmpa44PoE",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0,
"url": "http://www.showerlee.com"
}
client01.example.com | success >> {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "9b1afd16f97c07638965ba0c5cf01037af00a38a",
"dest": "/tmp/index.html",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "5a935e77927286dfcb7a0190e8af461b",
"mode": "0400",
"msg": "OK (unknown bytes)",
"owner": "root",
"sha256sum": "",
"size": 81679,
"src": "/tmp/tmp5WHuj0",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0,
"url": "http://www.showerlee.com"
}5.yum模块
Linux包管理平台操作, 常见都会有yum和apt, 此处会调用yum管理模式
# ansible webservers -m yum -a "name=curl state=latest"
client01.example.com | success >> {
"changed": false,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"All packages providing curl are up to date"
]
}
client02.example.com | success >> {
"changed": false,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"All packages providing curl are up to date"
]
}6. cron模块
远程主机crontab配置
# ansible webservers -m cron -a "name='check dir' hour='5,2' job='ls -alh > /dev/null'"
client02.example.com | success >> {
"changed": true,
"jobs": [
"check dir"
]
}
client01.example.com | success >> {
"changed": true,
"jobs": [
"check dir"
]
}7.service模块
远程主机系统服务管理
# ansible webservers -m service -a "name=crond state=stopped" # ansible webservers -m service -a "name=crond state=restarted" # ansible webservers -m service -a "name=crond state=reloaded"
8.user服务模块
远程主机系统用户管理
添加用户: # ansible webservers -m user -a "name=johnd comment='John Doe'" 删除用户: # ansible webservers -m user -a "name=johnd state=absent remove=yes"
四. playbook介绍(http://www.jianshu.com/p/41c4ed3ce779)
1、playbook简介
像很多其它配置文件管理方法一样,Ansible使用一种比较直白的方法来描述自己的任务配置文件。
Ansible 的任务配置文件被称之为“playbook”,我们可以称之为“剧本”。
每一出剧本(playbook)中都包含一系列的任务,这每个任务在ansible中又被称为一出“戏剧”(play)。一个剧本(playbook)中包含多出戏剧(play)。
2、playbook语法简介
YAML语法编写
格式如下所示: house: family: name: Doe parents: - John - Jane children: - Paul - Mark - Simone address: number: 34 street: Main Street city: Nowheretown zipcode: 12345
3、playbook实战
之前我们分享的Ansbile基础模块使用时,那种Ad-hoc点对点的,一次执行一个模块的操作方式已经使得Andsible一种非常强大的管理工具;但playbook将会使Ansible成为超一流的管理工具。
现在越来越多的DevOPS也开始将目光移向了Ansible,因为Ansible可以轻松的将shell脚本或简单的shell命令转换为Ansible plays.
:
#!/bin/bash # 安装Apache yum install --quiet -y httpd httpd-devel # 复制配置文件 cp /path/to/config/httpd.conf /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf cp /path/to/httpd-vhosts.conf /etc/httpd/conf/httpd-vhosts.conf # 启动Apache,并设置开机启动 service httpd start chkconfig httpd on
将其转换为一个完整的playbook后:
--- - hosts: all tasks: - name: "安装Apache" command: yum install --quiet -y httpd httpd-devel - name: "复制配置文件" command: cp /tmp/httpd.conf /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf command: cp /tmp/httpd-vhosts.conf /etc/httpd/conf/httpd-vhosts.conf - name: "启动Apache,并设置开机启动" command: service httpd start command: chkconfig httpd on
将以上内容放在一个名为playbook.yml的文件中,直接调用ansible-playbook命令,即可运行,运行结果和脚本运行结果一致:
# ansible-playbook ./playbook.yml
在上述playbook中,我们使用了“command”模块来运行了标准的shell命令。我们还给了每一出play一个“name”,因此当我们运行playbook时,每一个play都会有非常易读的的信息输出:
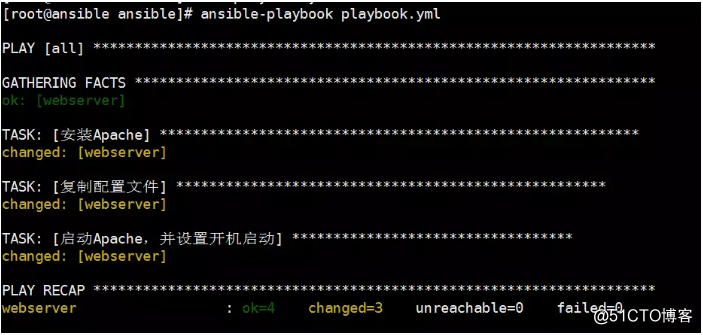
上面的playbook已经可以很好的运行shell脚本了,但是Ansible还有很多其他内置模块,可以大幅提升处理复杂配置的能力。
---
- hosts: all
sudo: yes
tasks:
- name: 安装Apache
yum: name={{ item }} state=present
with_items:
- httpd
- httpd-devel
- name: 复制配置文件 copy:
src: "{{ item.src }}"
dest: "{{ item.dest }}"
owner: root
group: root
mode: 0644
with_items:
- {
src: "/tmp/httpd.conf",
dest: "/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf" }
- {
src: "/tmp/httpd-vhosts.conf",
dest: "/etc/httpd/conf/httpd-vhosts.conf"
}
- name: 检查Apache运行状态,并设置开机启动
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes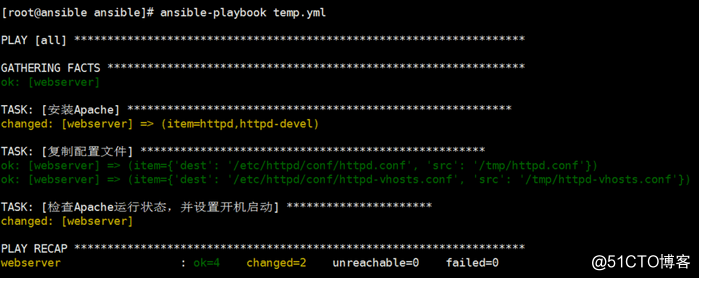
测试:
---
- hosts: test
#sudo: yes
vars:
bupath: "/home/ubuntu/ceshi1.sh"
sconf: "/etc/sysctl.conf"
tasks:
- name: "测试执行脚本"
shell: "{{ item }}"
with_items:
- "/home/ubuntu/ceshi1.sh"
- name: "测试获取信息"
stat: "path={{ item.dest }}"
with_items:
- {
dest: "/etc/sysctl.conf" }
- {
dest: "/etc/passwd" }
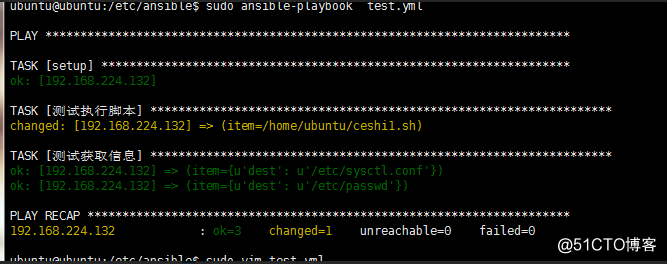
YAML语法
1 YAML使用可打印的Unicode字符,可使用UTF-8或UTF-16。
2 使用空白字符未文件缩排来表示结构;不过不能使用跳格字符。
3 注解由井字号( # )开始,可以出现在一行中的任何位置,而且范围只有一行(也就是一般所谓的单行注解)
4 每个清单成员以单行表示,并用短杠+空白( - )起始。或使用方括号( [ ] ),并用逗号+空白( , )分开成员。
5 每个杂凑表的成员用冒号+空白( : )分开键值和内容。或使用大括号( { } ),并用逗号+空白( , )分开。 杂凑表的键值可以用问号 ( ? )起始,用来明确的表示多个词汇组成的键值。
6 字串平常并不使用引号,但必要的时候可以用双引号 ( " )或单引号 ( ' )框住。使用双引号表示字串时,可用倒斜线( )开始的跳脱字符(这跟C语言类似)表示特殊字符。
7 区块的字串用缩排和修饰词(非必要)来和其他资料分隔,有新行保留(preserve)(使用符号 | )或新行折叠(flod)(使用符号 > )两种方式。
8 在单一档案中,可用连续三个连字号(——)区分多个档案。另外,还有选择性的连续三个点号( ... )用来表示档案结尾。
9 重复的内容可使从参考标记星号 ( * )复制到锚点标记( & )。
10 指定格式可以使用两个惊叹号 ( !! ),后面接上名称。
11 档案中的单一文件可以使用指导指令,使用方法是百分比符号( % )。有两个指导指令
如果在命令行上将-v标志传递给ansible-playbook,那么您将看到每个执行任务的stdout和stderr:
$ ansible-playbook -v playbook.yaml
Ansible还内置了对日志记录的支持。打开日志记录,修改ansible.ctl
[defaults] log_path = /var/log/ansible.log
本文转载自:
http://www.showerlee.com/archives/1649
http://www.jianshu.com/p/41c4ed3ce779
转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/hellvenus/1982079