2018-07-07






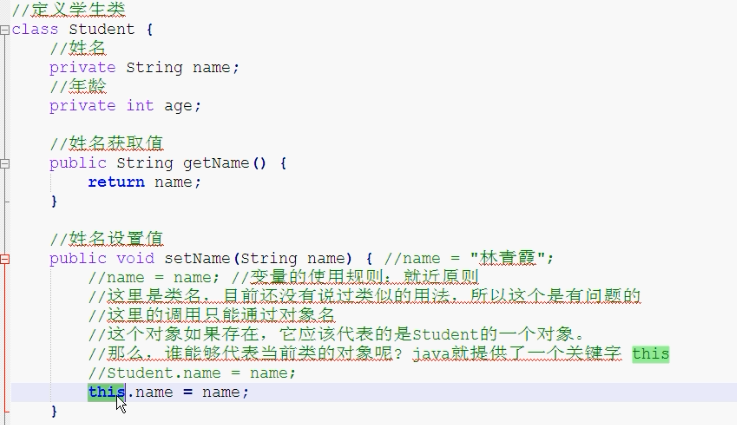
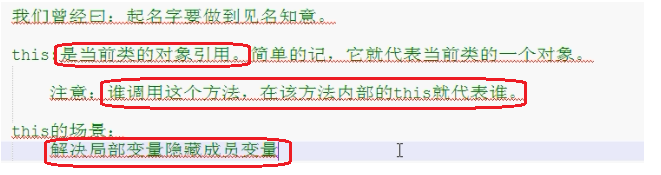
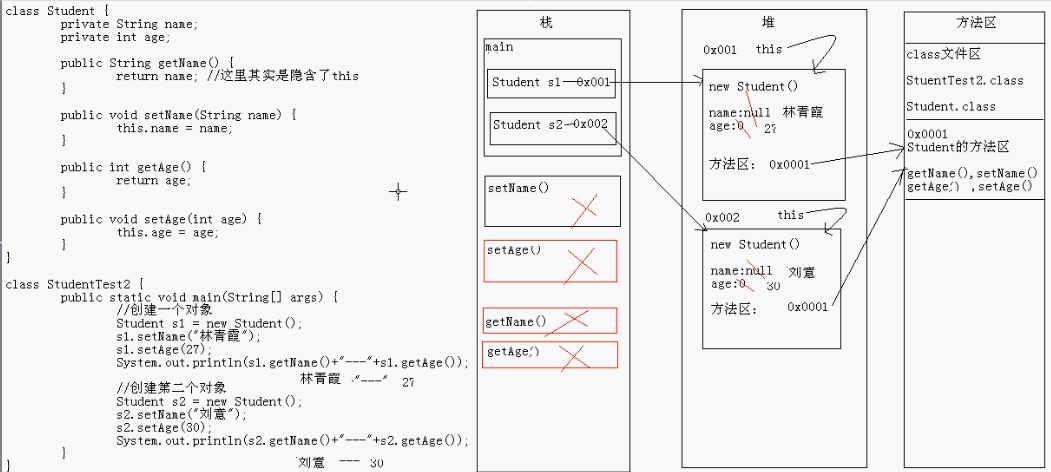
this关键字
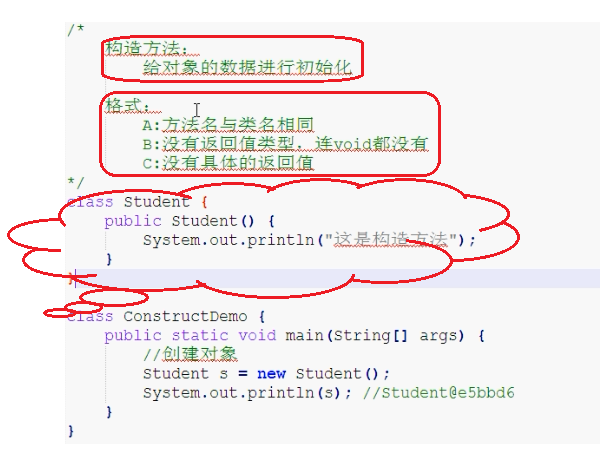
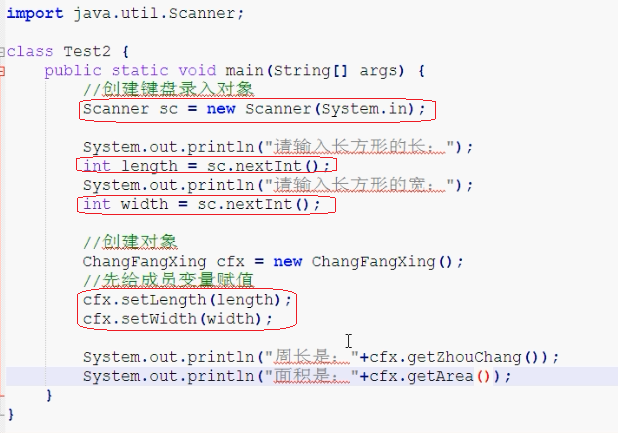
构造方法
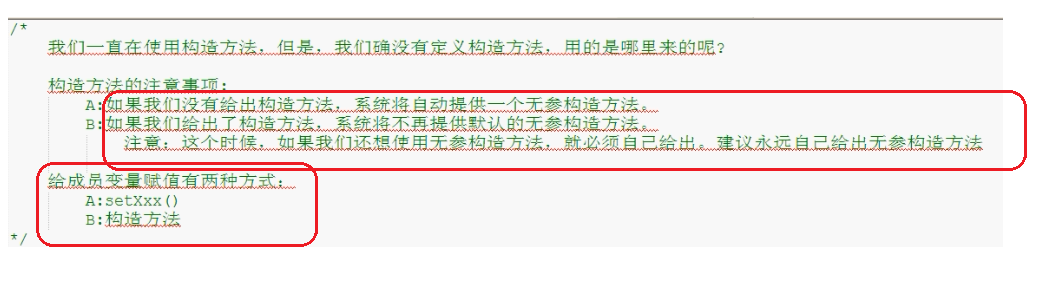
1 /* 2 我们一直在使用构造方法,但是,我们确没有定义构造方法,用的是哪里来的呢? 3 4 构造方法的注意事项: 5 A:如果我们没有给出构造方法,系统将自动提供一个无参构造方法。 6 B:如果我们给出了构造方法,系统将不再提供默认的无参构造方法。 7 注意:这个时候,如果我们还想使用无参构造方法,就必须自己给出。建议永远自己给出无参构造方法 8 9 给成员变量赋值有两种方式: 10 A:setXxx() 11 B:构造方法 12 */ 13 14 class Student { 15 private String name; 16 private int age; 17 18 public Student() { 19 //System.out.println("我给了,你还给不"); 20 System.out.println("这是无参构造方法"); 21 } 22 23 //构造方法的重载格式 24 public Student(String name) { 25 System.out.println("这是带一个String类型的构造方法"); 26 this.name = name; 27 } 28 29 public Student(int age) { 30 System.out.println("这是带一个int类型的构造方法"); 31 this.age = age; 32 } 33 34 public Student(String name,int age) { 35 System.out.println("这是一个带多个参数的构造方法"); 36 this.name = name; 37 this.age = age; 38 } 39 40 public void show() { 41 System.out.println(name+"---"+age); 42 } 43 } 44 45 class ConstructDemo2 { 46 public static void main(String[] args) { 47 //创建对象 48 Student s = new Student(); 49 s.show(); 50 System.out.println("-------------"); 51 52 //创建对象2 53 Student s2 = new Student("林青霞"); 54 s2.show(); 55 System.out.println("-------------"); 56 57 //创建对象3 58 Student s3 = new Student(27); 59 s3.show(); 60 System.out.println("-------------"); 61 62 //创建对象4 63 Student s4 = new Student("林青霞",27); 64 s4.show(); 65 } 66 }



一个标准代码的终极版
1 /* 2 一个标准代码的最终版。 3 4 学生类: 5 成员变量: 6 name,age 7 构造方法: 8 无参,带两个参 9 成员方法: 10 getXxx()/setXxx() 11 show():输出该类的所有成员变量值 12 13 给成员变量赋值: 14 A:setXxx()方法 15 B:构造方法 16 17 输出成员变量值的方式: 18 A:通过getXxx()分别获取然后拼接 19 B:通过调用show()方法搞定 20 */ 21 class Student { 22 //姓名 23 private String name; 24 //年龄 25 private int age; 26 27 //构造方法 28 public Student() { 29 } 30 31 public Student(String name,int age) { 32 this.name = name; 33 this.age = age; 34 } 35 36 public String getName() { 37 return name; 38 } 39 40 public void setName(String name) { 41 this.name = name; 42 } 43 44 public int getAge() { 45 return age; 46 } 47 48 public void setAge(int age) { 49 this.age = age; 50 } 51 52 //输出所有的成员变量值 53 public void show() { 54 System.out.println(name+"---"+age); 55 } 56 } 57 58 //测试类 59 class StudentTest { 60 public static void main(String[] args) { 61 //方式1给成员变量赋值 62 //无参构造+setXxx() 63 Student s1 = new Student(); 64 s1.setName("林青霞"); 65 s1.setAge(27); 66 //输出值 67 System.out.println(s1.getName()+"---"+s1.getAge()); 68 s1.show(); 69 System.out.println("----------------------------"); 70 71 //方式2给成员变量赋值 72 Student s2 = new Student("刘意",30); 73 System.out.println(s2.getName()+"---"+s2.getAge()); 74 s2.show(); 75 } 76 }

注意:import必须放在所有的class文件前面
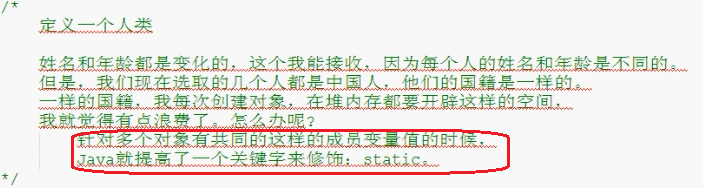
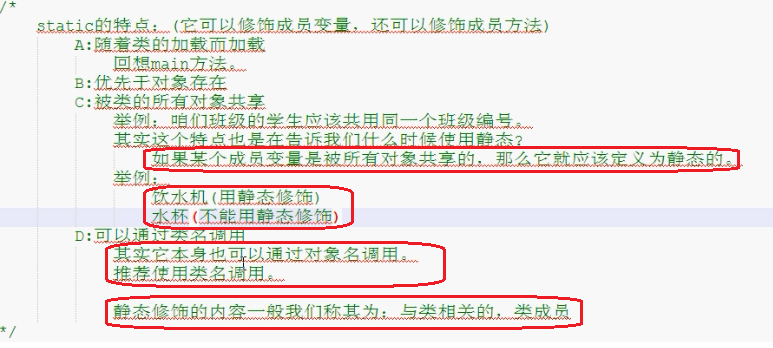
Static关键字
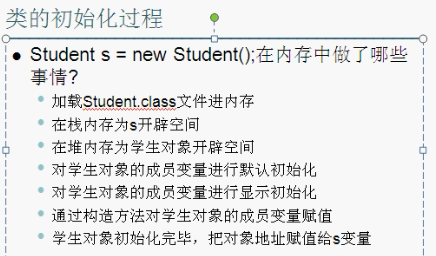
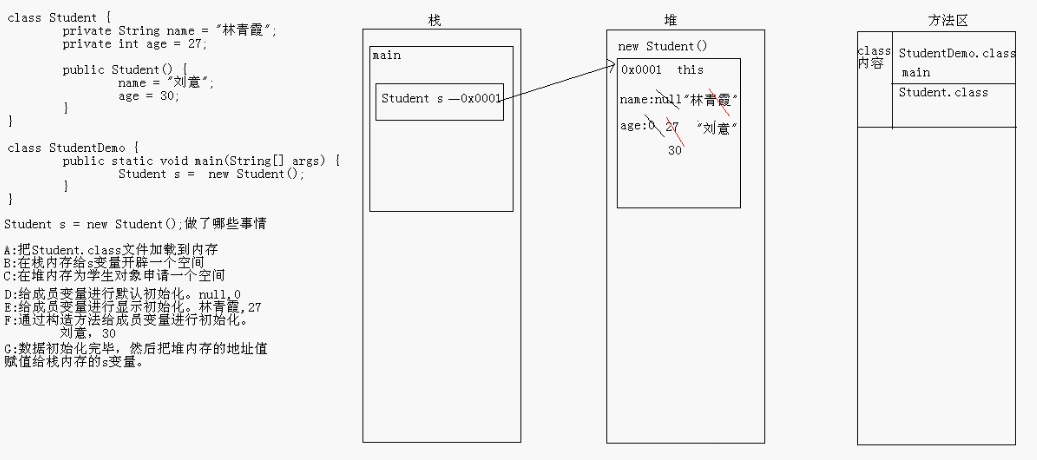
内存图

1 /* 2 static关键字注意事项 3 A:在静态方法中是没有this关键字的 4 如何理解呢? 5 静态是随着类的加载而加载,this是随着对象的创建而存在。 6 静态比对象先存在。 7 B:静态方法只能访问静态的成员变量和静态的成员方法 8 静态方法: 9 成员变量:只能访问静态变量 10 成员方法:只能访问静态成员方法 11 非静态方法: 12 成员变量:可以是静态的,也可以是非静态的 13 成员方法:可是是静态的成员方法,也可以是非静态的成员方法。 14 简单记: 15 静态只能访问静态。 16 */ 17 class Teacher { 18 public int num = 10; 19 public static int num2 = 20; 20 21 public void show() { 22 System.out.println(num); //隐含的告诉你访问的是成员变量 23 System.out.println(this.num); //明确的告诉你访问的是成员变量 24 System.out.println(num2); 25 26 //function(); 27 //function2(); 28 } 29 30 public static void method() { 31 //无法从静态上下文中引用非静态 变量 num 32 //System.out.println(num); 33 System.out.println(num2); 34 35 //无法从静态上下文中引用非静态 方法 function() 36 //function(); 37 function2(); 38 } 39 40 public void function() { 41 42 } 43 44 public static void function2() { 45 46 } 47 } 48 49 class TeacherDemo { 50 public static void main(String[] args) { 51 //创建对象 52 Teacher t = new Teacher(); 53 t.show(); 54 System.out.println("------------"); 55 t.method(); 56 } 57 }
public static void main(String[] args){ ...}
详细解释
1 /* 2 main方法的格式讲解: 3 public static void main(String[] args) {...} 4 5 public:公共的,访问权限是最大的。由于main方法是被jvm调用,所以权限要够大。 6 static:静态的,不需要创建对象,通过类名就可以。方便jvm的调用。 7 void:因为我们曾经说过,方法的返回值是返回给调用者,而main方法是被jvm调用。你返回内容给jvm没有意义。 8 main:是一个常见的方法入口。我见过的语言都是以main作为入口。 9 String[] args:这是一个字符串数组。值去哪里了? 10 这个东西到底有什么用啊?怎么给值啊? 11 这个东西早期是为了接收键盘录入的数据的。 12 格式是: 13 java MainDemo hello world java 14 */ 15 class MainDemo { 16 public static void main(String[] args) { 17 //System.out.println(args); //[Ljava.lang.String;@175078b 18 //System.out.println(args.length); //0 19 //System.out.println(args[0]); //ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 20 21 //接收数据后 22 System.out.println(args); 23 System.out.println(args.length); 24 //System.out.println(args[0]); 25 for(int x=0; x<args.length; x++) { 26 System.out.println(args[x]); 27 } 28 } 29 }