partition算法作用为对指定范围内元素重新排序,使用输入的函数,把结果为true的元素放在结果为false的元素之前
stable_partition算法:与partition类似,不过不保证保留容器中的相对顺序
C++ partition()函数
partition() 和stable_partition函数定义于<algorithm>头文件中,因此需要引入头文件#include <algorithm>
格式:
ForwardIterator partition (ForwardIterator first,
ForwardIterator last,
UnaryPredicate pred);
其中,first 和 last 为正向迭代器,其组合 [first, last) 用于指定该函数的作用范围;pred 用于指定筛选规则。(筛选规则,其本质就是一个可接收 1 个参数且返回值类型为 bool 的函数,可以是普通函数,也可以是一个函数对象。)
同时,partition() 函数还会返回一个正向迭代器,其指向的是两部分数据的分界位置,更确切地说,指向的是第二组数据中的第 1 个元素。
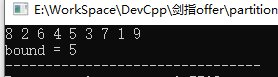
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> using namespace std; //以普通函数的方式定义partition()函数的筛选规则 bool cmp(int i) { return (i % 2) == 0; } //以函数对象的形式定义筛选规则 class cmp2{ public: bool operator()(const int& i) { return (i%2 == 0); } }; int main() { vector<int> myvector; for(int i=1;i<10;i++){ myvector.push_back(i); } vector<int>::iterator bound; //以 mycomp2 规则,对 myvector 容器中的数据进行分组 bound = std::partition(myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), cmp2()); for (vector<int>::iterator it = myvector.begin(); it != myvector.end(); ++it) { cout << *it << " "; } cout << " bound = " << *bound; return 0; }
运行结果:
C++ stable_partition()函数
partition() 函数只负责对指定区域内的数据进行分组,并不保证各组中元素的相对位置不发生改变。而如果想在分组的同时保证不改变各组中元素的相对位置,可以使用 stable_partition() 函数。
stable_partition() 函数可以保证对指定区域内数据完成分组的同时,不改变各组内元素的相对位置。
格式:
BidirectionalIterator stable_partition (BidirectionalIterator first,
BidirectionalIterator last,
UnaryPredicate pred);
举例:
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> using namespace std; //以普通函数的方式定义partition()函数的筛选规则 bool cmp(int i) { return (i % 2) == 0; } //以函数对象的形式定义筛选规则 class cmp2{ public: bool operator()(const int& i) { return (i%2 == 0); } }; int main() { vector<int> myvector; for(int i=1;i<10;i++){ myvector.push_back(i); } vector<int>::iterator bound; //以 mycomp2 规则,对 myvector 容器中的数据进行分组 bound = std::stable_partition(myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), cmp2()); for (vector<int>::iterator it = myvector.begin(); it != myvector.end(); ++it) { cout << *it << " "; } cout << " bound = " << *bound; return 0; }
