1.继承View组件,比如,LabelView继承了View
2.重写两个构造方法,比如,对于自定义View LabelView
LabelView(Context context),如果该自定义View是通过代码来实例化的,那么,就需要该构造方法;
LabelView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs),通过布局文件XML来使用该自定义View,那么,就需要该构造方法。
/**
* Constructor. This version is only needed if you will be instantiating
* the object manually (not from a layout XML file).
* @param context
*/
public LabelView(Context context) {
super(context);
initLabelView();
}
/**
* Construct object, initializing with any attributes we understand from a
* layout file. These attributes are defined in
* SDK/assets/res/any/classes.xml.
*
* @see android.view.View#View(android.content.Context, android.util.AttributeSet)
*/
public LabelView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
....
}
3.重写onDraw(Canvas canvas)和onMeasure(int measureWidth, int measureHeight)
onDraw(Canvas canvas),在实现自定义View的时候,你自己要创建一个Paint对象,用来设置自定义View的外观,尺寸,颜色。
然后,再在onDraw方法中,将图形绘制在系统传递过来的画布对象Canvas。
也就是说,系统回调onDraw来实现自定义View的渲染。
onMeasure(int measureWidth, int measureHeight),系统回调该方法,告诉你现在自定义View的宽度和高度是怎样设置的。
通过MeasureSpec.getMode(measureWidth),MeasureSpec.getSize(measureWidth)可以得到当前宽度的模式和大小。通过模式,可以知道用户设置的是wrap,match_parent,还是设置一个具体值,还说没有任何限制;通过大小,可以知道,当前系统检测到的当前View组件的宽度。
在得到这些信息后,你可以自己自定义,设置你想要的View组件的宽度和高度。
上面三个,就是自定义View的关键步骤。
-----------------------------------------------------------
其它方面:
1.Paint对象和Canvas的使用
要绘制一个自定义View,首先,你自己要确定出,图形的最终样式。按照最终样式,使用Paint对象,绘制出最终样式。Canvas对象的使用也需要关注。所以,在绘制图形的时候,要知道怎么使用Paint对象和Canvas绘制出最终的图形。
这方面的知识,需要补充。
2.属性设置
用户在使用你实现的自定义View的时候,它想自己定义View的属性,它想通过View提供的属性控制View的外观,尺寸,颜色等特征。那么,你实现的自定义View,就要提供给用户设置属性,并且要接收到用户传递过来的属性值,根据这些属性值构造出Paint对象。
这个的实现步骤:
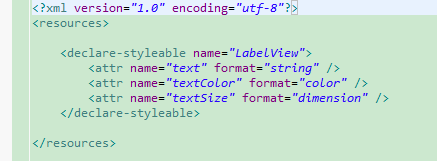
1).在res目录下的values目录,创建一个attrs.xml,然后,在里面添加属性描述。如下:声明了三个属性。
2).然后,在自定义View的类中,声明setter方法,如下:
根据用户传递过来的属性,重新绘制自定义VIew。requestLayout()的调用,会触发系统回调onMeasure(int measureWidth, int measureHeight)方法;invalidate()的调用,会触发系统回调onDraw()方法。
/**
* Sets the text to display in this label
*
* @param text
* The text to display. This will be drawn as one line.
*/
public void setText(String text) {
mText = text;
requestLayout();
invalidate();
}
3).在使用该自定义View的布局文件中,要声明该自定义View的命名空间,如下:
声明了一个命名空间
xmlns:app = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.example.customview"
红色部分,是该自定义View所在的包。
然后,你就可以使用app:text,这样命名空间加属性名的方式来设置属性。属性名,与attrs.xml中声明名字一样。
< RelativeLayout xmlns:android ="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools= "http://schemas.android.com/tools"
xmlns:app= "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.example.customview"
android:layout_width= "match_parent"
android:layout_height= "match_parent" >
<com.example.customview.LabelView
android:id ="@+id/oneLabelView"
android:layout_width ="wrap_content"
android:layout_height ="wrap_content"
app:text= "Somethine"
app:textColor ="#00868B"
app:textSize ="34sp" />
</ RelativeLayout>
---------------下面是实现例子--------------------------
import android.content.Context; import android.content.res.TypedArray; import android.graphics.Canvas; import android.graphics.Paint; import android.util.AttributeSet; import android.view.View; /** * Example of how to write a custom subclass of View. LabelView is used to draw * simple text views. Note that it does not handle styled text or right-to-left * writing systems. * */ public class LabelView extends View { private Paint mTextPaint; private String mText; private int mAscent; /** * Constructor. This version is only needed if you will be instantiating the * object manually (not from a layout XML file). * * @param context */ public LabelView(Context context) { super(context); initLabelView(); } /** * Construct object, initializing with any attributes we understand from a * layout file. These attributes are defined in * SDK/assets/res/any/classes.xml. * * @see android.view.View#View(android.content.Context, * android.util.AttributeSet) */ public LabelView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); initLabelView(); TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.LabelView); CharSequence s = a.getString(R.styleable.LabelView_text); if (s != null) { setText(s.toString()); } // Retrieve the color(s) to be used for this view and apply them. // Note, if you only care about supporting a single color, that you // can instead call a.getColor() and pass that to setTextColor(). setTextColor(a.getColor(R.styleable.LabelView_textColor, 0xFF000000)); int textSize = a.getDimensionPixelOffset( R.styleable.LabelView_textSize, 0); if (textSize > 0) { setTextSize(textSize); } a.recycle(); } private final void initLabelView() { mTextPaint = new Paint(); mTextPaint.setAntiAlias(true); // Must manually scale the desired text size to match screen density mTextPaint.setTextSize(16 * getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density); mTextPaint.setColor(0xFF000000); setPadding(3, 3, 3, 3); } /** * Sets the text to display in this label * * @param text * The text to display. This will be drawn as one line. */ public void setText(String text) { mText = text; requestLayout(); invalidate(); } /** * Sets the text size for this label * * @param size * Font size */ public void setTextSize(int size) { // This text size has been pre-scaled by the getDimensionPixelOffset // method mTextPaint.setTextSize(size); requestLayout(); invalidate(); } /** * Sets the text color for this label. * * @param color * ARGB value for the text */ public void setTextColor(int color) { mTextPaint.setColor(color); invalidate(); } /** * @see android.view.View#measure(int, int) */ @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { setMeasuredDimension(measureWidth(widthMeasureSpec), measureHeight(heightMeasureSpec)); } /** * Determines the width of this view * * @param measureSpec * A measureSpec packed into an int * @return The width of the view, honoring constraints from measureSpec */ private int measureWidth(int measureSpec) { int result = 0; int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec); int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec); if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) { // We were told how big to be result = specSize; } else { // Measure the text result = (int) mTextPaint.measureText(mText) + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight(); if (specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { // Respect AT_MOST value if that was what is called for by // measureSpec result = Math.min(result, specSize); } } return result; } /** * Determines the height of this view * * @param measureSpec * A measureSpec packed into an int * @return The height of the view, honoring constraints from measureSpec */ private int measureHeight(int measureSpec) { int result = 0; int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec); int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec); mAscent = (int) mTextPaint.ascent(); if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) { // We were told how big to be result = specSize; } else { // Measure the text (beware: ascent is a negative number) result = (int) (-mAscent + mTextPaint.descent()) + getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom(); if (specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { // Respect AT_MOST value if that was what is called for by // measureSpec result = Math.min(result, specSize); } } return result; } /** * Render the text * * @see android.view.View#onDraw(android.graphics.Canvas) */ @Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); canvas.drawText(mText, getPaddingLeft(), getPaddingTop() - mAscent, mTextPaint); } }