A* /IDA* 算法(Astar/IDAstar)初步学习笔记
0x01 引入
看一道sb题
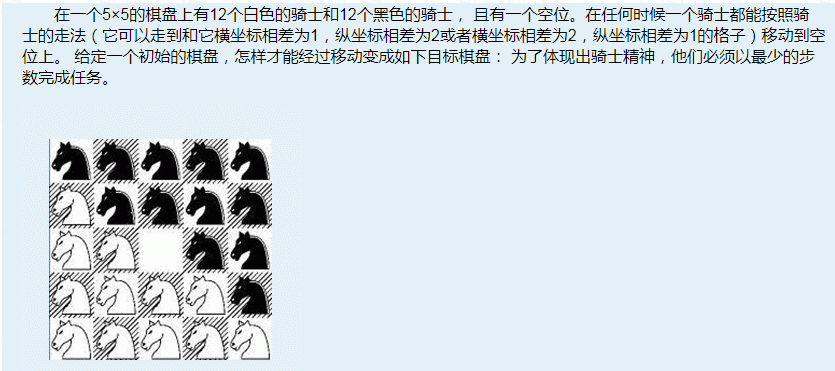

看完题的我:
我:省选题竟然还有爆搜题目!看我用BFS过了他
于是我满心欢喜地打完了朴素的不能再朴素的BFS,交了上去
恭喜!你TLE+MEL了此题!
W D N M D
显然,若使用BFS,到第十层的状态数将会是(8^{10})个,空间很快就会爆炸
那么……
我:限制层数为15!我要DFS!
这次没有爆空间!
AMDDFS,YES!恭喜!你TLE了此题!
我:……
DFS仍然不能解决状态数过多的情况(哪怕加上一些剪枝)
那么……
0x02 解决
考虑一个事实:
设还有x个骑士没有归位,则最好情况下要移动x次,每一次都让一个骑士归位
跟着这个事实,我们可以剪掉大量的无用状态
具体来讲,我们设到达当前状态用了(f(x))部,还有(g(x))个骑士未归位
根据上述事实,若(f(x)+g(x))大于限制步数,则无法在规定步数内全部归位,这个状态就可以剪掉
这似乎是个很玄学的剪枝,但事实证明它很有效
为什么呢,因为它交上去过了
0x03 总结
上一节的剪枝包含了A*的主要思想
细心的同学们应该发现了,我们刚刚使用了(f(x))和(g(x))来描述“来到当前状态所用的步数”和“至少需要的个数”
事实上,这不是个巧合
下面我们搬出来自己YY的A*定义
设起点到当前状态的距离(在例题中为步数)为(f(x)),估计当前状态到终点的距离为(g(x)),距离限制为(u(x))
则若(f(x)+g(x)>u(x)),当前状态无效
漂亮地下了个并不完整的定义,不过大部分情况可以这么理解
0x04 扩展——IDA*
我们可以看到,在上一题中,(u(x))是定值,为15
那么有没有不是定值的呢?
再看一道题

我知道可以双向BFS过不用再说了
看到这道题:
DFS:搜索的能力是有极限的,越是沉迷剪枝,就越会发现搜索是有极限的...除非成为超越搜索的存在。
BFS:你到底想说什么啊DFS?
DFS:BFS!我不做搜索了!
首先,这道题看上去和上一题并没有什么本质上的区别,所以无脑上A*
等等,(u(x))死哪去了?
当然没有……
经过手玩一些东西,我们发现最优答案的层数大概率不会很大
那我们……设定一个(u(x))?
感觉很难定下来的样子……
既然不会枚举很多,那我们干脆……枚举(u(x))!
似乎很不科学,但我也想不到什么更好的办法了
那就上吧
于是非常轻易地打出了按照这种思路的搜索
然后就过了……
后就过了……
就过了……
过了……
了……

考虑一个事情:
搜索树每增加一层,节点数增加固定倍数
大概是这样:
第一层:(x^0)
第二层:(x^1)
第三层:(x^2)
第四层:(x^3)
第五层:(x^4)
(cdots)
以此类推,第n层的节点数为(x^{n-1})
根据我们在小学二年级就学过的等比数列求和公式:
(q为公比)
可以得到
所以,大部分时间都耗在了最后一层上
因此,时间复杂度应该是科学的……
事实上,这种枚举上限的方法就叫做IDA*
全名迭代加深A*搜索……
这种方法使用的地方已经说过了,在这里强调一下:
整棵搜索树的状态总数非常大,且高度无法估计,但答案的深度很小(相对于整棵搜索树)
0x05 代码
骑士精神(IDA*)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int ans[5][5]={{1,1,1,1,1},
{0,1,1,1,1},
{0,0,-1,1,1},
{0,0,0,0,1},
{0,0,0,0,0}};
const int d[8][2]={{1,2},{1,-2},{-1,2},{-1,-2},{2,1},{2,-1},{-2,1},{-2,-1}};//same:x+y=3/x+y=11
inline void read(int &x) {
x=0;
int f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {
if (ch=='-') {
f=-1;
}
ch=getchar();
}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {
x=x*10+ch-'0';
ch=getchar();
}
x*=f;
}
int a[5][5];
int n;
inline int check() {
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<5;j++) {
if (a[i][j]!=ans[i][j]) {
return 0;
}
}
}
return 1;
}
int found;
inline int count() {
int cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<5;j++) {
if (a[i][j]!=ans[i][j]) {
cnt++;
}
}
}
return cnt;
}
void Astar(int step,int x,int y,int max_step,int pre) {
if (step==max_step) {
if (check()) {
found=1;
}
return;
}
if (found) {
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<8;i++) {
int x1=x+d[i][0];
int y1=y+d[i][1];
if (pre!=-1) {
if ((pre<4&&i+pre==3)||(pre>=4&&i+pre==11)) {
continue;
}
}
if (x1<0||x1>4||y1<0||y1>4) {
continue;
}
swap(a[x][y],a[x1][y1]);
if (count()+step<=max_step&&!found) {
Astar(step+1,x1,y1,max_step,i);
}
swap(a[x][y],a[x1][y1]);
}
}
int main() {
read(n);
while(n--) {
found=0;
int sx,sy;
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<5;j++) {
char ch;
cin>>ch;
a[i][j]=ch-'0';
if (ch=='*') {
a[i][j]=-1;
sx=i;
sy=j;
}
}
}
if (check()) {
printf("%d
",0);
continue;
}
int max_step=1;
for(;max_step<=15;max_step++) {
Astar(0,sx,sy,max_step,-1);
if (found) {
break;
}
}
if (found) {
printf("%d
",max_step);
} else {
printf("-1
");
}
}
return 0;
}
八数码难题(IDA*)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int d[4][2]={{0,1},{1,0},{-1,0},{0,-1}};
const int ans[3][3]={{1,2,3},
{8,0,4},
{7,6,5}};
inline void read(int &x) {
x=0;
int f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {
if (ch=='-') {
f=-1;
}
ch=getchar();
}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {
x=x*10+ch-'0';
ch=getchar();
}
x*=f;
}
int a[3][3];
inline int check() {
for(int i=0;i<3;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<3;j++) {
if (a[i][j]!=ans[i][j]) {
return 0;
}
}
}
return 1;
}
int found;
inline int count() {
int cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<3;j++) {
if (a[i][j]!=ans[i][j]) {
cnt++;
}
}
}
return cnt;
}
void Astar(int step,int x,int y,int max_step,int last_step) {
if (step==max_step) {
if (check()) {
found=1;
}
return;
}
if (found) {
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<4;i++) {
int x1=x+d[i][0];
int y1=y+d[i][1];
if (i+last_step==3) {
continue;
}
if (x1<0||x1>2||y1<0||y1>2) {
continue;
}
swap(a[x][y],a[x1][y1]);
if (!(count()+step>max_step)&&!found) {
Astar(step+1,x1,y1,max_step,i);
}
swap(a[x][y],a[x1][y1]);
}
}
int main() {
int sx,sy;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<3;j++) {
char ch=getchar();
a[i][j]=ch-'0';
if (!a[i][j]) {
sx=i;
sy=j;
}
}
}
if (check()) {
printf("%d
",0);
return 0;
}
int max_step=0;
for(;;) {
max_step++;
Astar(0,sx,sy,max_step,-1);
if (found) {
break;
}
}
printf("%d
",max_step);
return 0;
}