分类器有时会产生错误结果,这时可以要求分类器给出一个最优的类别猜测结果,同
时给出这个猜测的概率估计值。
概率论是许多机器学习算法的基础
在计算
特征值取某个值的概率时涉及了一些概率知识,在那里我们先统计特征在数据集中取某个特定值
的次数,然后除以数据集的实例总数,就得到了特征取该值的概率。
首先从一个最简单的概率分类器开始,然后给
出一些假设来学习朴素贝叶斯分类器。我们称之为“朴素”,是因为整个形式化过程只做最原始、
最简单的假设。
基于贝叶斯决策理论的分类方法

朴素贝叶斯是贝叶斯决策理论的一部分,所以讲述朴素负叶斯之前有必要快速了解一下贝叶
斯决策理论。
假设现在我们有一个数据集,它由两类数据组成
import matplotlib import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from numpy import * n = 1000 #number of points to create xcord0 = [] ycord0 = [] xcord1 = [] ycord1 = [] markers =[] colors =[] fw = open('E:\testSet.txt','w') for i in range(n): [r0,r1] = random.standard_normal(2) myClass = random.uniform(0,1) if (myClass <= 0.5): fFlyer = r0 + 9.0 tats = 1.0*r1 + fFlyer - 9.0 xcord0.append(fFlyer) ycord0.append(tats) else: fFlyer = r0 + 2.0 tats = r1+fFlyer - 2.0 xcord1.append(fFlyer) ycord1.append(tats) #fw.write("%f %f %d " % (fFlyer, tats, classLabel)) fw.close() fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(111) #ax.scatter(xcord,ycord, c=colors, s=markers) ax.scatter(xcord0,ycord0, marker='^', s=90) ax.scatter(xcord1,ycord1, marker='o', s=50, c='red') plt.plot([0,1], label='going up') plt.show()
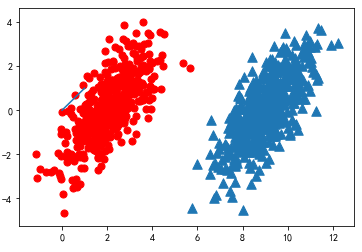

也就是说,我们会选择高概率对应的类别。这就是贝叶斯决策理论的核心思想,即选择具有
最高概率的决策。
条件概率



使用条件概率来分类


使用朴素贝叶斯进行文档分类
机器学习的一个重要应用就是文档的自动分类。在文档分类中,整 个 文 档 (如一封电子邮件)
是实例,而电子邮件中的某些元素则构成特征。虽然电子邮件是一种会不断增加的文本,但我们同
样也可以对新闻报道、用户留言、政府公文等其他任意类型的文本进行分类。我们可以观察文档中
出现的词,并把每个词的出现或者不出现作为一个特征,这样得到的特征数目就会跟词汇表中的词
目一样多。




使用Python进行文本分类

准备数据:从文本中构建词向量
将把文本看成单词向量或者词条向量,也就是说将句子转换为向量。考虑出现在所有文
档中的所有单词,再决定将哪些词纳人词汇表或者说所要的词汇集合,然后必须要将每一篇文档
转换为词汇表上的向量。
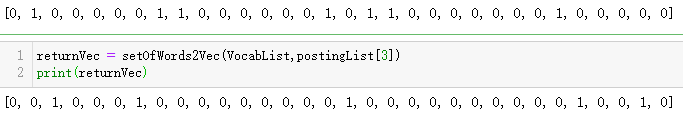
from numpy import * def loadDataSet(): postingList=[['my', 'dog', 'has', 'flea', 'problems', 'help', 'please'], ['maybe', 'not', 'take', 'him', 'to', 'dog', 'park', 'stupid'], ['my', 'dalmation', 'is', 'so', 'cute', 'I', 'love', 'him'], ['stop', 'posting', 'stupid', 'worthless', 'garbage'], ['mr', 'licks', 'ate', 'my', 'steak', 'how', 'to', 'stop', 'him'], ['quit', 'buying', 'worthless', 'dog', 'food', 'stupid']] classVec = [0,1,0,1,0,1] #1 is abusive, 0 not return postingList,classVec def createVocabList(dataSet): vocabSet = set([]) #create empty set for document in dataSet: vocabSet = vocabSet | set(document) #union of the two sets return list(vocabSet) def setOfWords2Vec(vocabList, inputSet): returnVec = [0]*len(vocabList) for word in inputSet: if word in vocabList: returnVec[vocabList.index(word)] = 1 else: print("the word: %s is not in my Vocabulary!" % word) return returnVec postingList,classVec = loadDataSet() VocabList = createVocabList(postingList) print(VocabList)

returnVec = setOfWords2Vec(VocabList,postingList[0]) print(returnVec)
训练算法:从词向量计算概率
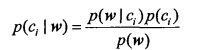


朴素贝叶斯分类器训练函数
def trainNB0(trainMatrix,trainCategory): numTrainDocs = len(trainMatrix) numWords = len(trainMatrix[0]) pAbusive = sum(trainCategory)/float(numTrainDocs) p0Num = ones(numWords) p1Num = ones(numWords) #change to ones() p0Denom = 2.0 p1Denom = 2.0 #change to 2.0 for i in range(numTrainDocs): if trainCategory[i] == 1: p1Num += trainMatrix[i] p1Denom += sum(trainMatrix[i]) else: p0Num += trainMatrix[i] p0Denom += sum(trainMatrix[i]) p1Vect = log(p1Num/p1Denom) #change to log() p0Vect = log(p0Num/p0Denom) #change to log() return p0Vect,p1Vect,pAbusive
import matplotlib import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from numpy import * t = arange(0.0, 0.5, 0.01) s = sin(2*pi*t) logS = log(s) fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(211) ax.plot(t,s) ax.set_ylabel('f(x)') ax.set_xlabel('x') ax = fig.add_subplot(212) ax.plot(t,logS) ax.set_ylabel('ln(f(x))') ax.set_xlabel('x') plt.show()


贝叶斯分类函数 def classifyNB(vec2Classify, p0Vec, p1Vec, pClass1): p1 = sum(vec2Classify * p1Vec) + log(pClass1) #element-wise mult p0 = sum(vec2Classify * p0Vec) + log(1.0 - pClass1) if p1 > p0: return 1 else: return 0
这里的相乘是指对应元素
相乘,即先将两个向量中的第1个元素相乘,然后将第2个元素相乘,以此类推。接下来将词汇表
中所有词的对应值相加,然后将该值加到类别的对数概率上。最后,比较类别的概率返回大概率
对应的类别标签。
def testingNB(): listOPosts,listClasses = loadDataSet() myVocabList = createVocabList(listOPosts) trainMat=[] for postinDoc in listOPosts: trainMat.append(setOfWords2Vec(myVocabList, postinDoc)) p0V,p1V,pAb = trainNB0(array(trainMat),array(listClasses)) testEntry = ['love', 'my', 'dalmation'] thisDoc = array(setOfWords2Vec(myVocabList, testEntry)) print(testEntry,'classified as: ',classifyNB(thisDoc,p0V,p1V,pAb)) testEntry = ['stupid', 'garbage'] thisDoc = array(setOfWords2Vec(myVocabList, testEntry)) print(testEntry,'classified as: ',classifyNB(thisDoc,p0V,p1V,pAb)) testingNB()

准备数据:文档词袋模型

朴素贝叶斯词袋模型
def classifyNB(vec2Classify, p0Vec, p1Vec, pClass1): p1 = sum(vec2Classify * p1Vec) + log(pClass1) #element-wise mult p0 = sum(vec2Classify * p0Vec) + log(1.0 - pClass1) if p1 > p0: return 1 else: return 0