一、什么是爬虫
爬虫:一段自动抓取互联网信息的程序,从互联网上抓取对于我们有价值的信息。
二、Python爬虫架构
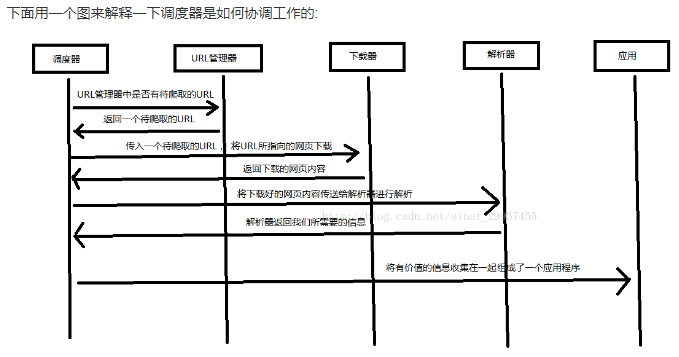
Python 爬虫架构主要由五个部分组成,分别是调度器、URL管理器、网页下载器、网页解析器、应用程序(爬取的有价值数据)。
调度器:相当于一台电脑的CPU,主要负责调度URL管理器、下载器、解析器之间的协调工作。
URL管理器:包括待爬取的URL地址和已爬取的URL地址,防止重复抓取URL和循环抓取URL,实现URL管理器主要用三种方式,通过内存、数据库、缓存数据库来实现。
网页下载器:通过传入一个URL地址来下载网页,将网页转换成一个字符串,网页下载器有urllib2(Python官方基础模块)包括需要登录、代理、和cookie,requests(第三方包)
网页解析器:将一个网页字符串进行解析,可以按照我们的要求来提取出我们有用的信息,也可以根据DOM树的解析方式来解析。网页解析器有正则表达式(直观,将网页转成字符串通过模糊匹配的方式来提取有价值的信息,当文档比较复杂的时候,该方法提取数据的时候就会非常的困难)、html.parser(Python自带的)、beautifulsoup(第三方插件,可以使用Python自带的html.parser进行解析,也可以使用lxml进行解析,相对于其他几种来说要强大一些)、lxml(第三方插件,可以解析 xml 和 HTML),html.parser 和 beautifulsoup 以及 lxml 都是以 DOM 树的方式进行解析的。
应用程序:就是从网页中提取的有用数据组成的一个应用。
import urllib.request
import http.cookiejar
url = "http://www.baidu.com"
response1 = urllib.request.urlopen(url)
print("第一种方法")
#获取状态码,200表示成功
print(response1.getcode())
#获取网页内容的长度
print(len(response1.read()))
第一种方法
200
156265
print("第二种方法")
request = urllib.request.Request(url)
#模拟Mozilla浏览器进行爬虫
request.add_header("user-agent","Mozilla/5.0")
response2 = urllib.request.urlopen(request)
print(response2.getcode())
print(len(response2.read()))
第二种方法
200
156328
print("第三种方法")
cookie = http.cookiejar.CookieJar()
#加入urllib.request处理cookie的能力
opener = urllib.request.build_opener(urllib.request.HTTPCookieProcessor(cookie))
urllib.request.install_opener(opener)
response3 = urllib.request.urlopen(url)
print(response3.getcode())
print(len(response3.read()))
print(cookie)
第三种方法
200
156488
<CookieJar[<Cookie BAIDUID=CA8C47A224EE898DC34E66D0182C70C3:FG=1 for .baidu.com/>, <Cookie BIDUPSID=CA8C47A224EE898D968EF5993499742B for .baidu.com/>, <Cookie H_PS_PSSID=1446_21123 for .baidu.com/>, <Cookie PSTM=1575029972 for .baidu.com/>, <Cookie delPer=0 for .baidu.com/>, <Cookie BDSVRTM=0 for www.baidu.com/>, <Cookie BD_HOME=0 for www.baidu.com/>]>
四、第三方库 Beautiful Soup 的安装
Beautiful Soup: Python 的第三方插件用来提取 xml 和 HTML 中的数据,官网地址 https://www.crummy.com/software/BeautifulSoup/
1、安装 Beautiful Soup
2、测试是否安装成功
编写一个 Python 文件,输入:
import bs4
print(bs4)
<module 'bs4' from 'e:\python\lib\site-packages\bs4\__init__.py'>
五、使用 Beautiful Soup 解析 html 文件
import re
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
#创建一个BeautifulSoup解析对象
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc,"html.parser",from_encoding="utf-8")
#获取所有的链接
links = soup.find_all('a')
print("所有的链接")
for link in links:
print(link.name,link['href'],link.get_text())
所有的链接
a http://example.com/elsie Elsie
a http://example.com/lacie Lacie
a http://example.com/tillie Tillie
print("获取特定的URL地址")
link_node = soup.find('a',href="http://example.com/elsie")
print(link_node.name,link_node['href'],link_node['class'],link_node.get_text())
print("正则表达式匹配")
link_node = soup.find('a',href=re.compile(r"ti"))
print(link_node.name,link_node['href'],link_node['class'],link_node.get_text())
print("获取P段落的文字")
p_node = soup.find('p',class_='story')
print(p_node.name,p_node['class'],p_node.get_text())
获取特定的URL地址
a http://example.com/elsie ['sister'] Elsie
正则表达式匹配
a http://example.com/tillie ['sister'] Tillie
获取P段落的文字
p ['story'] Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
Elsie,
Lacie and
Tillie;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.

