import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.image as mpimg import seaborn as sns %matplotlib inline np.random.seed(2) from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix import itertools from keras.utils.np_utils import to_categorical # convert to one-hot-encoding from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Flatten, Conv2D, MaxPool2D from keras.optimizers import RMSprop from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator from keras.callbacks import ReduceLROnPlateau sns.set(style='white', context='notebook', palette='deep')
# Load the data train = pd.read_csv("F:\kaggleDataSetMNSI\train.csv") test = pd.read_csv("F:\kaggleDataSetMNSI\test.csv")
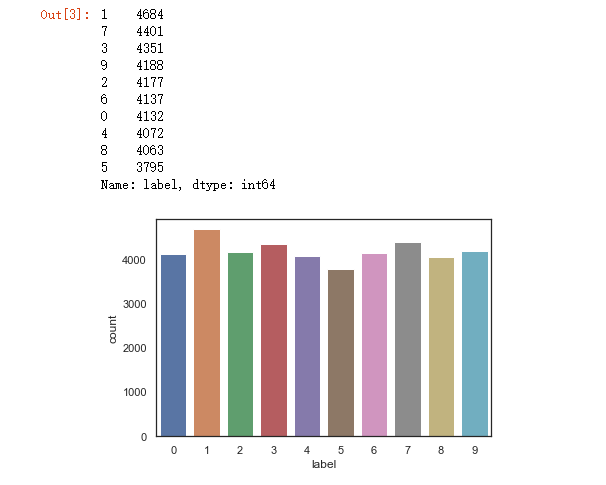
Y_train = train["label"] # Drop 'label' column X_train = train.drop(labels = ["label"],axis = 1) # free some space del train g = sns.countplot(Y_train) Y_train.value_counts()
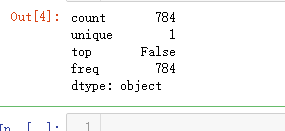
# Check the data X_train.isnull().any().describe()
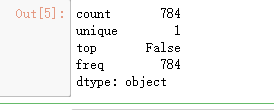
test.isnull().any().describe()
# Normalize the data X_train = X_train / 255.0 test = test / 255.0
# Reshape image in 3 dimensions (height = 28px, width = 28px , canal = 1) X_train = X_train.values.reshape(-1,28,28,1) test = test.values.reshape(-1,28,28,1)
# Encode labels to one hot vectors (ex : 2 -> [0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]) Y_train = to_categorical(Y_train, num_classes = 10)
# Set the random seed random_seed = 2
# Split the train and the validation set for the fitting X_train, X_val, Y_train, Y_val = train_test_split(X_train, Y_train, test_size = 0.1, random_state=random_seed)
# Some examples g = plt.imshow(X_train[0][:,:,0])
# Set the CNN model # my CNN architechture is In -> [[Conv2D->relu]*2 -> MaxPool2D -> Dropout]*2 -> Flatten -> Dense -> Dropout -> Out model = Sequential() model.add(Conv2D(filters = 32, kernel_size = (5,5),padding = 'Same', activation ='relu', input_shape = (28,28,1))) model.add(Conv2D(filters = 32, kernel_size = (5,5),padding = 'Same', activation ='relu')) model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2))) model.add(Dropout(0.25)) model.add(Conv2D(filters = 64, kernel_size = (3,3),padding = 'Same', activation ='relu')) model.add(Conv2D(filters = 64, kernel_size = (3,3),padding = 'Same', activation ='relu')) model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2,2))) model.add(Dropout(0.25)) model.add(Flatten()) model.add(Dense(256, activation = "relu")) model.add(Dropout(0.5)) model.add(Dense(10, activation = "softmax"))
# Define the optimizer optimizer = RMSprop(lr=0.001, rho=0.9, epsilon=1e-08, decay=0.0)
# Compile the model model.compile(optimizer = optimizer , loss = "categorical_crossentropy", metrics=["accuracy"])
# Set a learning rate annealer learning_rate_reduction = ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor='val_acc', patience=3, verbose=1, factor=0.5, min_lr=0.00001)
epochs = 1 # Turn epochs to 30 to get 0.9967 accuracy batch_size = 86
# Without data augmentation i obtained an accuracy of 0.98114 history = model.fit(X_train, Y_train, batch_size = batch_size, epochs = epochs, validation_data = (X_val, Y_val), verbose = 2)
# With data augmentation to prevent overfitting (accuracy 0.99286) datagen = ImageDataGenerator( featurewise_center=False, # set input mean to 0 over the dataset samplewise_center=False, # set each sample mean to 0 featurewise_std_normalization=False, # divide inputs by std of the dataset samplewise_std_normalization=False, # divide each input by its std zca_whitening=False, # apply ZCA whitening rotation_range=10, # randomly rotate images in the range (degrees, 0 to 180) zoom_range = 0.1, # Randomly zoom image width_shift_range=0.1, # randomly shift images horizontally (fraction of total width) height_shift_range=0.1, # randomly shift images vertically (fraction of total height) horizontal_flip=False, # randomly flip images vertical_flip=False) # randomly flip images datagen.fit(X_train)
# Fit the model history = model.fit_generator(datagen.flow(X_train,Y_train, batch_size=batch_size), epochs = epochs, validation_data = (X_val,Y_val), verbose = 2, steps_per_epoch=X_train.shape[0] // batch_size , callbacks=[learning_rate_reduction])

# Plot the loss and accuracy curves for training and validation fig, ax = plt.subplots(2,1) ax[0].plot(history.history['loss'], color='b', label="Training loss") ax[0].plot(history.history['val_loss'], color='r', label="validation loss",axes =ax[0]) legend = ax[0].legend(loc='best', shadow=True) ax[1].plot(history.history['acc'], color='b', label="Training accuracy") ax[1].plot(history.history['val_acc'], color='r',label="Validation accuracy") legend = ax[1].legend(loc='best', shadow=True)
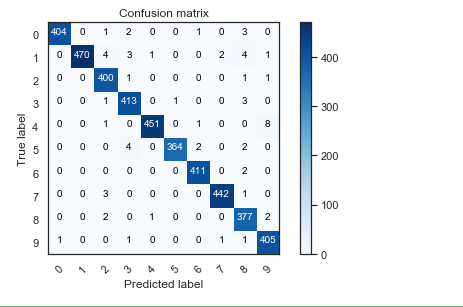
# Look at confusion matrix def plot_confusion_matrix(cm, classes, normalize=False, title='Confusion matrix', cmap=plt.cm.Blues): """ This function prints and plots the confusion matrix. Normalization can be applied by setting `normalize=True`. """ plt.imshow(cm, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap) plt.title(title) plt.colorbar() tick_marks = np.arange(len(classes)) plt.xticks(tick_marks, classes, rotation=45) plt.yticks(tick_marks, classes) if normalize: cm = cm.astype('float') / cm.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis] thresh = cm.max() / 2. for i, j in itertools.product(range(cm.shape[0]), range(cm.shape[1])): plt.text(j, i, cm[i, j], horizontalalignment="center", color="white" if cm[i, j] > thresh else "black") plt.tight_layout() plt.ylabel('True label') plt.xlabel('Predicted label') # Predict the values from the validation dataset Y_pred = model.predict(X_val) # Convert predictions classes to one hot vectors Y_pred_classes = np.argmax(Y_pred,axis = 1) # Convert validation observations to one hot vectors Y_true = np.argmax(Y_val,axis = 1) # compute the confusion matrix confusion_mtx = confusion_matrix(Y_true, Y_pred_classes) # plot the confusion matrix plot_confusion_matrix(confusion_mtx, classes = range(10))
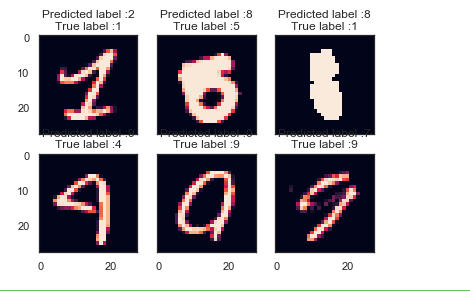
# Display some error results # Errors are difference between predicted labels and true labels errors = (Y_pred_classes - Y_true != 0) Y_pred_classes_errors = Y_pred_classes[errors] Y_pred_errors = Y_pred[errors] Y_true_errors = Y_true[errors] X_val_errors = X_val[errors] def display_errors(errors_index,img_errors,pred_errors, obs_errors): """ This function shows 6 images with their predicted and real labels""" n = 0 nrows = 2 ncols = 3 fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows,ncols,sharex=True,sharey=True) for row in range(nrows): for col in range(ncols): error = errors_index[n] ax[row,col].imshow((img_errors[error]).reshape((28,28))) ax[row,col].set_title("Predicted label :{} True label :{}".format(pred_errors[error],obs_errors[error])) n += 1 # Probabilities of the wrong predicted numbers Y_pred_errors_prob = np.max(Y_pred_errors,axis = 1) # Predicted probabilities of the true values in the error set true_prob_errors = np.diagonal(np.take(Y_pred_errors, Y_true_errors, axis=1)) # Difference between the probability of the predicted label and the true label delta_pred_true_errors = Y_pred_errors_prob - true_prob_errors # Sorted list of the delta prob errors sorted_dela_errors = np.argsort(delta_pred_true_errors) # Top 6 errors most_important_errors = sorted_dela_errors[-6:] # Show the top 6 errors display_errors(most_important_errors, X_val_errors, Y_pred_classes_errors, Y_true_errors)
# predict results results = model.predict(test) # select the indix with the maximum probability results = np.argmax(results,axis = 1) results = pd.Series(results,name="Label")
submission = pd.concat([pd.Series(range(1,28001),name = "ImageId"),results],axis = 1) submission.to_csv("cnn_mnist_datagen.csv",index=False)