


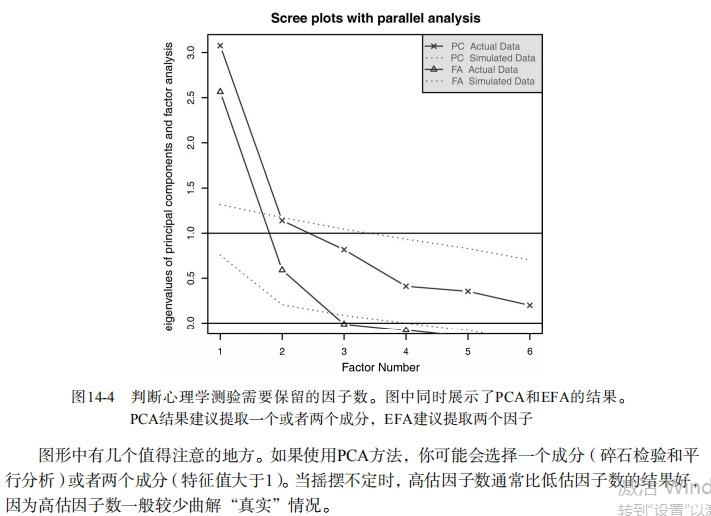







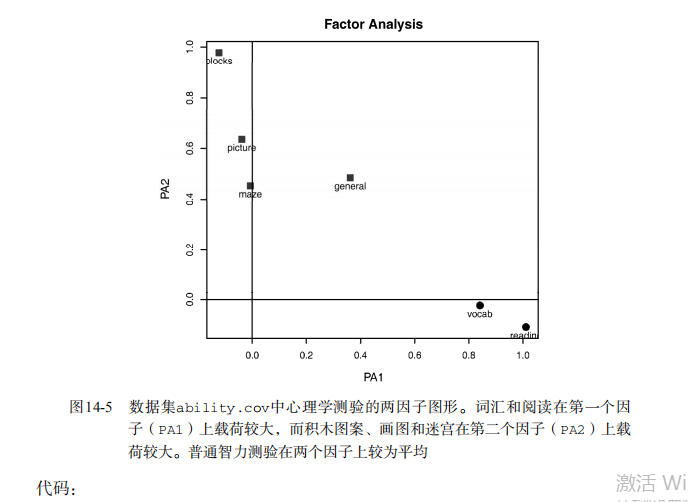
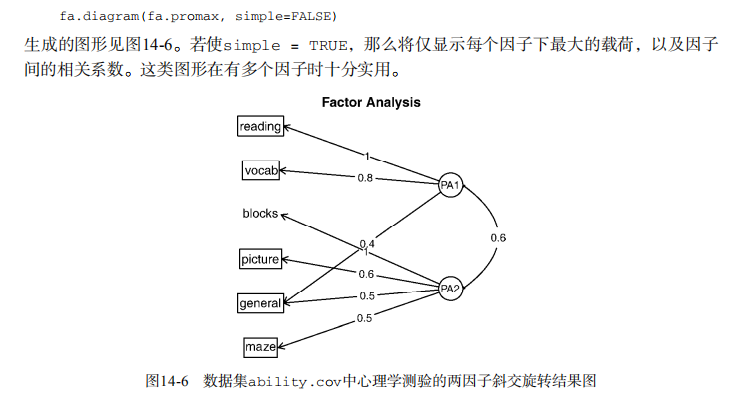




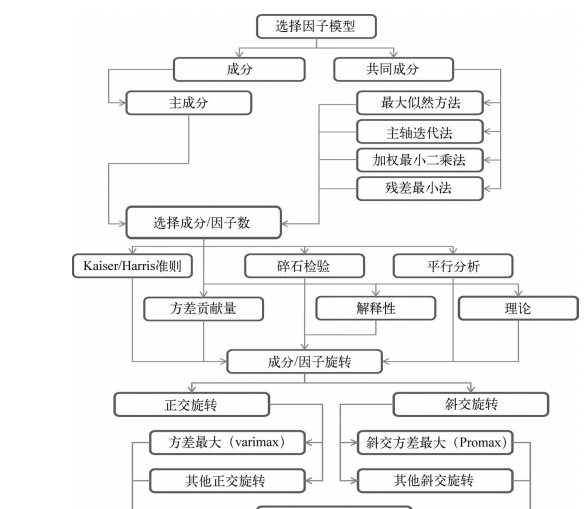
#--------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 14 # # Principal components and factor analysis # # requires package psych # # install.packages("psych") # #--------------------------------------------# par(ask=TRUE) set.seed(1234) # make results reproducible # Listing 14.1 - Principal components analysis of US Judge Ratings library(psych) pc <- principal(USJudgeRatings[,-1], nfactors=1) pc # Principal components analysis Harman23.cor data library(psych) fa.parallel(Harman23.cor$cov, n.obs=302, fa="pc", n.iter=100, show.legend=FALSE, main="Scree plot with parallel analysis") # Listing 14.2 - Principal components analysis of body measurements library(psych) PC <- principal(Harman23.cor$cov, nfactors=2, rotate="none") PC # Listing 14.3 - Principal components analysis with varimax rotation rc <- principal(Harman23.cor$cov, nfactors=2, rotate="varimax") rc # Listing 14.4 - Obtaining componenet scores from raw data library(psych) pc <- principal(USJudgeRatings[,-1], nfactors=1, score=TRUE) head(pc$scores) cor(USJudgeRatings$CONT, pc$score) # Listing 14.5 - Obtaining principal component scoring coefficients library(psych) rc <- principal(Harman23.cor$cov, nfactors=2, rotate="varimax") round(unclass(rc$weights), 2) ## Exploratory factor analysis of ability.cov data options(digits=2) library(psych) covariances <- ability.cov$cov # convert covariances to correlations correlations <- cov2cor(covariances) correlations # determine number of factors to extract fa.parallel(correlations, n.obs=112, fa="both", n.iter=100, main="Scree plots with parallel analysis") # Listing 14.6 - Principal axis factoring without rotation fa <- fa(correlations, nfactors=2, rotate="none", fm="pa") fa # Listing 14.7 - Factor extraction with orthogonal rotation fa.varimax <- fa(correlations, nfactors=2, rotate="varimax", fm="pa") fa.varimax # Listing 14.8 - Factor extraction with oblique rotation fa.promax <- fa(correlations, nfactors=2, rotate="promax", fm="pa") fa.promax # calculate factor loading matrix fsm <- function(oblique) { if (class(oblique)[2]=="fa" & is.null(oblique$Phi)) { warning("Object doesn't look like oblique EFA") } else { P <- unclass(oblique$loading) F <- P %*% oblique$Phi colnames(F) <- c("PA1", "PA2") return(F) } } fsm(fa.promax) # plot factor solution factor.plot(fa.promax, labels=rownames(fa.promax$loadings)) fa.diagram(fa.promax, simple=FALSE) # factor scores fa.promax$weights