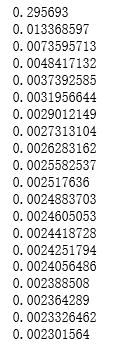
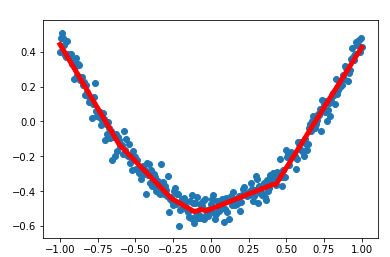
import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function = None): #构建权重: in_sizeXout_size大小的矩阵 weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]))#生成随机数 #构建偏置: 1Xout_size 的矩阵 biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1) #矩阵相乘 Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, weights) + biases if activation_function is None: outputs = Wx_plus_b else: outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b) #得到输出数据 return outputs #构造满足一元二次方程的函数 #为了使点更密一些,构建了分布在-1到1区间的300个点,直接采用np生成等差数列 #的方法,并将结果为300个点的一维数组转换为300X1的二维数组 x_data = np.linspace(-1,1,300)[:, np.newaxis] #加入一些噪声点,使它与x_data的维度一致,并且拟合为均值为0、方差0.05的正态分布 noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.05, x_data.shape) #y=x^2-0.5+噪声 y_data = np.square(x_data) - 0.5 + noise #以x和y的占位符来作为将要输入神经网络的变量: xs=tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1]) ys=tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1]) #构建隐藏层,假设隐藏层有10个神经元 h1 = add_layer(xs, 1,10, activation_function=tf.nn.relu) #构建输出层,假设输出层和输入层一样,有一个神经元 prediction = add_layer(h1, 10, 1, activation_function=None) #计算预测值和真实值间的误差 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys-prediction),reduction_indices=[1])) # 这一行定义了用什么方式去减少 loss,学习率是 0.1 train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss) #训练模型 # important step 对所有变量进行初始化 init = tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.Session() as sess: # 上面定义的都没有运算,直到 sess.run 才会开始运算 sess.run(init) # plot the real data fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1) ax.scatter(x_data, y_data) plt.ion() #训练1000次 for i in range(1000): # training train_step 和 loss 都是由 placeholder 定义的运算,所以这里要用 feed 传入参数 sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data}) #每50次打印出一次损失值 if(i % 50 == 0): print(sess.run(loss, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data})) prediction_value = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={xs: x_data}) # plot the prediction lines = ax.plot(x_data, prediction_value, 'r-', lw=5) plt.pause(0.9)