import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import metrics from sklearn import datasets from sklearn.semi_supervised import LabelPropagation def load_data(): ''' 加载数据集 ''' digits = datasets.load_digits() ###### 混洗样本 ######## rng = np.random.RandomState(0) indices = np.arange(len(digits.data)) # 样本下标集合 rng.shuffle(indices) # 混洗样本下标集合 X = digits.data[indices] y = digits.target[indices] ###### 生成未标记样本的下标集合 #### # 只有 10% 的样本有标记 n_labeled_points = int(len(y)/10) # 后面 90% 的样本未标记 unlabeled_indices = np.arange(len(y))[n_labeled_points:] return X,y,unlabeled_indices #半监督学习标准迭代式标记传播算法LabelPropagation模型 def test_LabelPropagation(*data): ''' 测试 LabelPropagation 的用法 ''' X,y,unlabeled_indices=data # 必须拷贝,后面要用到 y y_train=np.copy(y) # 未标记样本的标记设定为 -1 y_train[unlabeled_indices]=-1 clf=LabelPropagation(max_iter=100,kernel='rbf',gamma=0.1) clf.fit(X,y_train) ### 获取预测准确率 # 预测标记 predicted_labels = clf.transduction_[unlabeled_indices] # 真实标记 true_labels = y[unlabeled_indices] print("Accuracy:%f"%metrics.accuracy_score(true_labels,predicted_labels)) # 或者 print("Accuracy:%f"%clf.score(X[unlabeled_indices],true_labels)) # 获取半监督分类数据集 data=load_data() # 调用 test_LabelPropagation test_LabelPropagation(*data)

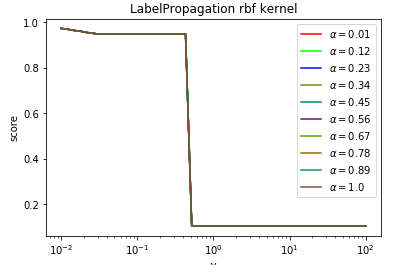
def test_LabelPropagation_rbf(*data): ''' 测试 LabelPropagation 的 rbf 核时,预测性能随 alpha 和 gamma 的变化 ''' X,y,unlabeled_indices=data # 必须拷贝,后面要用到 y y_train=np.copy(y) # 未标记样本的标记设定为 -1 y_train[unlabeled_indices]=-1 fig=plt.figure() ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1) alphas=np.linspace(0.01,1,num=10,endpoint=True) gammas=np.logspace(-2,2,num=50) # 颜色集合,不同曲线用不同颜色 colors=((1,0,0),(0,1,0),(0,0,1),(0.5,0.5,0),(0,0.5,0.5),(0.5,0,0.5),(0.4,0.6,0),(0.6,0.4,0),(0,0.6,0.4),(0.5,0.3,0.2)) ## 训练并绘图 for alpha,color in zip(alphas,colors): scores=[] for gamma in gammas: clf=LabelPropagation(max_iter=100,gamma=gamma,alpha=alpha,kernel='rbf') clf.fit(X,y_train) scores.append(clf.score(X[unlabeled_indices],y[unlabeled_indices])) ax.plot(gammas,scores,label=r"$alpha=%s$"%alpha,color=color) ### 设置图形 ax.set_xlabel(r"$gamma$") ax.set_ylabel("score") ax.set_xscale("log") ax.legend(loc="best") ax.set_title("LabelPropagation rbf kernel") plt.show() # 调用 test_LabelPropagation_rbf test_LabelPropagation_rbf(*data)
def test_LabelPropagation_knn(*data): ''' 测试 LabelPropagation 的 knn 核时,预测性能随 alpha 和 n_neighbors 的变化 ''' X,y,unlabeled_indices=data y_train=np.copy(y) # 必须拷贝,后面要用到 y y_train[unlabeled_indices]=-1 # 未标记样本的标记设定为 -1 fig=plt.figure() ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1) alphas=np.linspace(0.01,1,num=10,endpoint=True) Ks=[1,2,3,4,5,8,10,15,20,25,30,35,40,50] # 颜色集合,不同曲线用不同颜色 colors=((1,0,0),(0,1,0),(0,0,1),(0.5,0.5,0),(0,0.5,0.5),(0.5,0,0.5),(0.4,0.6,0),(0.6,0.4,0),(0,0.6,0.4),(0.5,0.3,0.2)) ## 训练并绘图 for alpha,color in zip(alphas,colors): scores=[] for K in Ks: clf=LabelPropagation(max_iter=100,n_neighbors=K,alpha=alpha,kernel='knn') clf.fit(X,y_train) scores.append(clf.score(X[unlabeled_indices],y[unlabeled_indices])) ax.plot(Ks,scores,label=r"$alpha=%s$"%alpha,color=color) ### 设置图形 ax.set_xlabel(r"$k$") ax.set_ylabel("score") ax.legend(loc="best") ax.set_title("LabelPropagation knn kernel") plt.show() # 调用 test_LabelPropagation_knn test_LabelPropagation_knn(*data)
