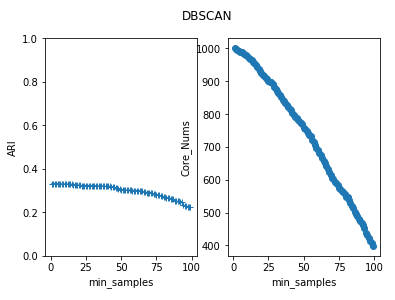
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import cluster from sklearn.metrics import adjusted_rand_score from sklearn.datasets.samples_generator import make_blobs def create_data(centers,num=100,std=0.7): X, labels_true = make_blobs(n_samples=num, centers=centers, cluster_std=std) return X,labels_true #密度聚类DBSCAN模型 def test_DBSCAN(*data): X,labels_true=data clst=cluster.DBSCAN() predicted_labels=clst.fit_predict(X) print("ARI:%s"% adjusted_rand_score(labels_true,predicted_labels)) print("Core sample num:%d"%len(clst.core_sample_indices_)) # 用于产生聚类的中心点 centers=[[1,1],[2,2],[1,2],[10,20]] # 产生用于聚类的数据集 X,labels_true=create_data(centers,1000,0.5) # 调用 test_DBSCAN 函数 test_DBSCAN(X,labels_true)
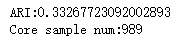
def test_DBSCAN_epsilon(*data): ''' 测试 DBSCAN 的聚类结果随 eps 参数的影响 ''' X,labels_true=data epsilons=np.logspace(-1,1.5) ARIs=[] Core_nums=[] for epsilon in epsilons: clst=cluster.DBSCAN(eps=epsilon) predicted_labels=clst.fit_predict(X) ARIs.append( adjusted_rand_score(labels_true,predicted_labels)) Core_nums.append(len(clst.core_sample_indices_)) ## 绘图 fig=plt.figure() ax=fig.add_subplot(1,2,1) ax.plot(epsilons,ARIs,marker='+') ax.set_xscale('log') ax.set_xlabel(r"$epsilon$") ax.set_ylim(0,1) ax.set_ylabel('ARI') ax=fig.add_subplot(1,2,2) ax.plot(epsilons,Core_nums,marker='o') ax.set_xscale('log') ax.set_xlabel(r"$epsilon$") ax.set_ylabel('Core_Nums') fig.suptitle("DBSCAN") plt.show() # 调用 test_DBSCAN_epsilon 函数 test_DBSCAN_epsilon(X,labels_true)

def test_DBSCAN_min_samples(*data): ''' 测试 DBSCAN 的聚类结果随 min_samples 参数的影响 ''' X,labels_true=data min_samples=range(1,100) ARIs=[] Core_nums=[] for num in min_samples: clst=cluster.DBSCAN(min_samples=num) predicted_labels=clst.fit_predict(X) ARIs.append( adjusted_rand_score(labels_true,predicted_labels)) Core_nums.append(len(clst.core_sample_indices_)) ## 绘图 fig=plt.figure() ax=fig.add_subplot(1,2,1) ax.plot(min_samples,ARIs,marker='+') ax.set_xlabel( "min_samples") ax.set_ylim(0,1) ax.set_ylabel('ARI') ax=fig.add_subplot(1,2,2) ax.plot(min_samples,Core_nums,marker='o') ax.set_xlabel( "min_samples") ax.set_ylabel('Core_Nums') fig.suptitle("DBSCAN") plt.show() # 调用 test_DBSCAN_min_samples 函数 test_DBSCAN_min_samples(X,labels_true)