Spring概述
spring是什么:Spring是分层的JavaSE/EE应用full-stack轻量级开源框架以IOC(Inverse Of Control:反转控制)和AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming:面向切面编程)为内核,提供了展现SpringMVC和持久层Spring JDBC以及业务层事务管理等众多的企业级应用技术,还能整合开源世界众多著名的第三方框架和类库,逐渐成为使用最多的Java EE企业应用开源框架
spring体系结构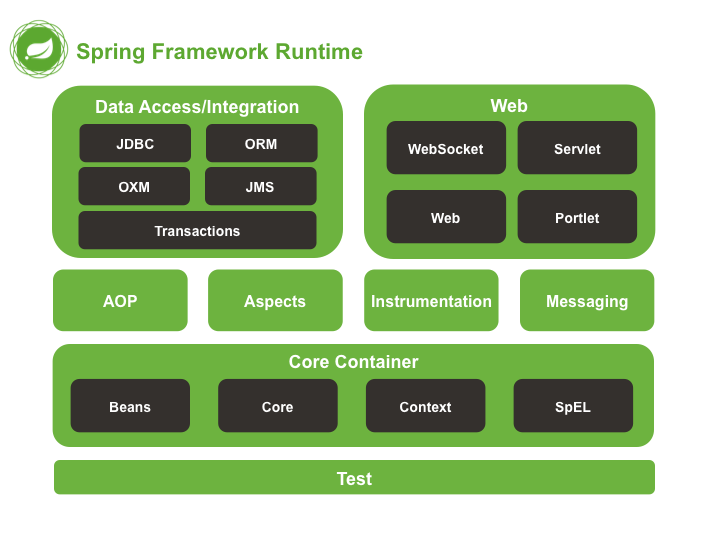
编写JDBC代码分析程序的耦合
//程序的耦合
public class JdbcDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
//1.注册驱动
DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver());
//2.获取连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy","root","12345");
//3.获取操作数据库的㔘对象
PreparedStatement pstm = conn.prepareStatement("select * from account");
//4.执行SQL,得到结果集
ResultSet rs = pstm.executeQuery();
//5.遍历结果集
while(rs.next()){
System.out.println(rs.getString("name"));
}
//6.释放资源
rs.close();
pstm.close();
conn.close();
}
}
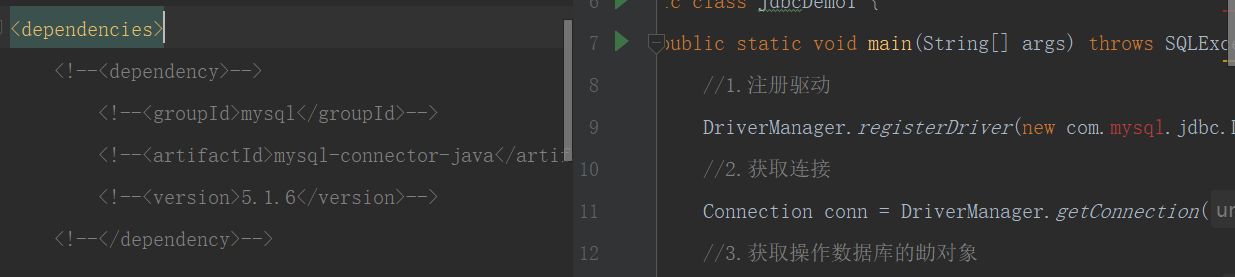
导入依赖jar包-MySQL
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
现在如果把依赖jar包去掉,则会发生编译期异常
耦合:程序间的依赖关系。包括类之间的依赖,方法之间的依赖
解耦:降低程序间的依赖关系
在实际开发中,应该做到编译期不依赖,运行时才依赖
解耦思路:第一步,使用反射来创建对象,而避免使用new关键字,第二步:通过读取配置文件来获取要创建的对象全限定类名
控制反转(Inversion of Control)把创建对象的权利交给框架,是框架的重要特征,并非面向对象编程的专用术语。他包括依赖注入(Dependency Injection简称DI)和依赖查找
明确sping的IOC的作用:
削减计算机程序的耦合(解除我们代码中的依赖关系),并不做增删改查操作,
spring基于XML的IOC环境搭建和入门
1.导入jar包
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.xml文件导入约束
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
</beans>
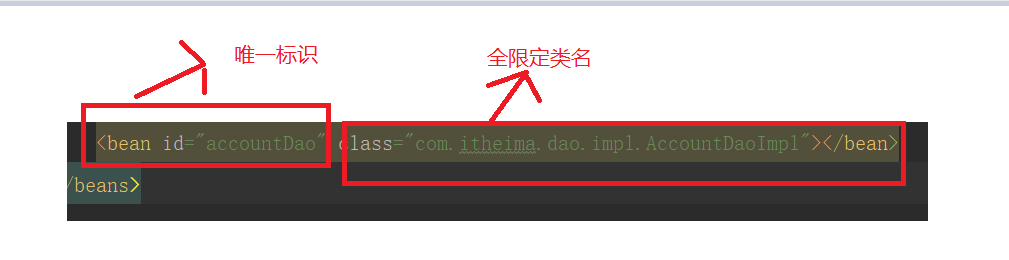
3.把对象的创建交给spring来管理
<!--把对象的创建交给spring来管理-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl"></bean>
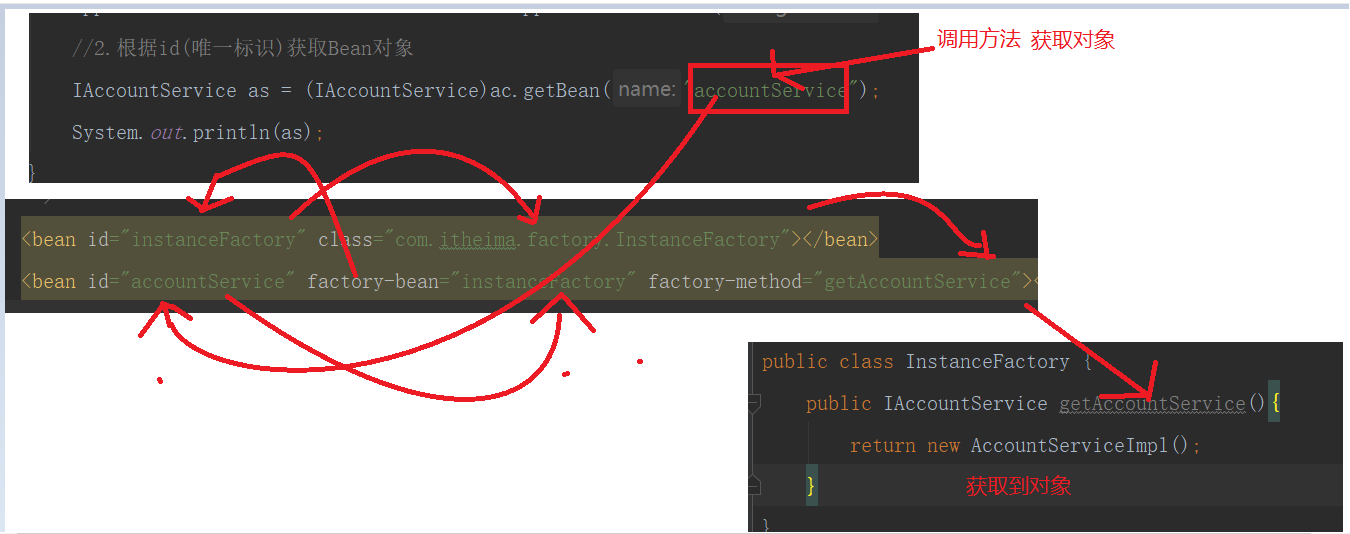
4.获取spring的Ioc核心容器,并根据id获取对象
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取核心容器对象
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根据id(唯一标识)获取Bean对象
IAccountService as = (IAccountService)ac.getBean("accountService");
IAccountDao adao = ac.getBean("accountDao",IAccountDao.class);
System.out.println(as);
System.out.println(adao);
}
ApplicationCntext的常用三个实现类:
1.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:可以加载类路径下的配置文件,要求配置文件必须在类路径下
2.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:加载磁盘任意路劲下的配置文件(必须有访问权限)
3.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:用于读取注解创建容器的
ApplicationCntext和BeanFactory都是创建对象的,他们有什么区别
ApplicationCntext:他在创建核心容器是,创建对象策略是采用立即加载的方式。也就是说,只要一读取完配置文件就创建配置文件中配置的对象
BeanFactory:他在创建核心容器时,创建对象采取的策略是采用延迟加载的方式,也就是说,什么时候根据id获取对象,就什么时候创建对象
spring中bean的细节之三种创建Bean对象的方式
第一种方式
<!--第一种方式:使用默认构造函数创建
在spring额配置文件中使用bean标签,配以id和class属性之后,且没有其他属性和标签时
采用的就是默认构造函数创建bean对象,此时如果类中没有默认的构造函数,则对象创立失败
-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
第二种方式
模拟的工厂类
package com.itheima.factory;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService;
import com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl;
public class InstanceFactory {
public IAccountService getAccountService(){
return new AccountServiceImpl();
}
}
<!--第二种方式:
使用普通工厂中的方法创建对象(使用某个类中的方法创建,并存入spring容器)
-->
<bean id="instanceFactory" class="com.itheima.factory.InstanceFactory"></bean>
<bean id="accountService" factory-bean="instanceFactory" factory-method="getAccountService"></bean>
第三种方式
模拟的工厂类
package com.itheima.factory;
import com.itheima.service.IAccountService;
import com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl;
public class StaticFactory {
public static IAccountService getAccountService(){
return new AccountServiceImpl();
}
}
<!--第三种方式:
使用工厂中的静态方法创建对象(使用某个类的静态方法创建对象,并存入spring容器中)
-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.factory.StaticFactory" factory-method="getAccountService"></bean>