前言:
本次实验是练习convolution和pooling的使用,更深一层的理解怎样对大的图片采用convolution得到每个特征的输出结果,然后采用pooling方法对这些结果进行计算,使之具有平移不变等特性。实验参考的是斯坦福网页教程:Exercise:Convolution and Pooling。也可以参考前面的博客:Deep learning:十七(Linear Decoders,Convolution和Pooling),且本次试验是在前面博文Deep learning:二十二(linear decoder练习)的学习到的特征提取网络上进行的。
实验基础:
首先来看看整个训练和测试过程的大概流程:从本文可以更清楚的看到,在训练阶段,是对小的patches进行whitening的。由于输入的数据是大的图片,所以每次进行convolution时都需要进行whitening和网络的权值计算,这样每一个学习到的隐含层节点的特征对每一张图片都可以得到一张稍小的特征图片,接着对这张特征图片进行均值pooling(在这之前,程序中有一些代码来测试convolution和pooling代码的正确性)。有了这些特征值以及标注值,就可以用softmax来训练多分类器了。
在测试阶段是对大图片采取convolution的,每次convolution的图像块也同样需要用训练时的whitening参数进行预处理,分别经过convolution和pooling提取特征,这和前面的训练过程一样。然后用训练好的softmax分类器就可进行预测了。
训练特征提取的网络参数用的时间比较多,而训练比如说softmax分类器则用的时间比较短。
在matlab中当有n维数组时,一般是从右向左进行剥皮计算,因为matlab输出都是按照这种方法进行的。当然了,如果要理解的话,从左向右和从右向左都是可以的,只要是方便理解就行。
程序中进行convolution测试的理由是:先用cnnConvolve函数计算出所给样本的convolution值,然后随机选取多个patch,用直接代数运算的方法得出网络的输出值,如果对于所有(比如说这里选的1000个)的patch,这两者之间的差都非常小的话,说明convution计算是正确的。
程序中进行pooling测试的理由是:采用函数cnnPool来计算,而该函数的参数为polling的维数以及需要pooling的数据。因此程序中先随便给一组数据,然后用手动的方法计算出均值pooling的结果,最后用cnnPool函数也计算出一个结果,如果两者的结果相同,则说明pooling函数是正确的。
程序中颜色特征的学习体现在:每次只对RGB中的一个通道进行convolution,分别计算3次,然后把三个通道得到的convolution结果矩阵对应元素相加即可。这样的话,后面的Pooling操作只需在一个图像上进行即可。
Convolution后得到的形式如下:
convolvedFeatures(featureNum, imageNum, imageRow, imageCol)
pooling后得到的形式如下:
pooledFeatures(featureNum, imageNum, poolRow, poolCol)
图片的保存形式如下:
convImages(imageRow, imageCol, imageChannel, imageNum)
由于只需训练4个类别的softmax分类器,所以其速度非常快,1分钟都不到。
一些matlab函数:
squeeze:
B = squeeze(A),B与A有相同的元素,但所有只有一行或只有一列的那个维度(a singleton dimension)被去除掉了。A singleton dimension的特征是size(A,dim) = 1。二维阵列不受squeeze影响; 如果 A 是一个row or column矢量或a scalar (1-by-1) value, then B = A。比如,rand(4,1,3)产生一个均匀分布的阵列,共3页,每页4行1列,经过squeeze后,1列的那个维度就没有了,只剩下4行3列的一个二维阵列。而rand(4,2,3)因为没有1列或1行的维度,所有squeeze后没有变化。
size:
size(A,n),如果A是一个多维矩阵,那么size(A,n)表示第n维的大小,返回值为一个实数。
实验结果:
训练出来的特征图像为:
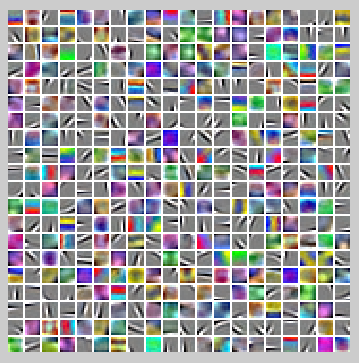
最终的预测准确度为:Accuracy: 80.406%
实验主要部分代码:
CnnExercise.m:
%% CS294A/CS294W Convolutional Neural Networks Exercise % Instructions % ------------ % % This file contains code that helps you get started on the % convolutional neural networks exercise. In this exercise, you will only % need to modify cnnConvolve.m and cnnPool.m. You will not need to modify % this file. %%====================================================================== %% STEP 0: Initialization % Here we initialize some parameters used for the exercise. imageDim = 64; % image dimension imageChannels = 3; % number of channels (rgb, so 3) patchDim = 8; % patch dimension numPatches = 50000; % number of patches visibleSize = patchDim * patchDim * imageChannels; % number of input units ,8*8*3=192 outputSize = visibleSize; % number of output units hiddenSize = 400; % number of hidden units epsilon = 0.1; % epsilon for ZCA whitening poolDim = 19; % dimension of pooling region %%====================================================================== %% STEP 1: Train a sparse autoencoder (with a linear decoder) to learn % features from color patches. If you have completed the linear decoder % execise, use the features that you have obtained from that exercise, % loading them into optTheta. Recall that we have to keep around the % parameters used in whitening (i.e., the ZCA whitening matrix and the % meanPatch) % --------------------------- YOUR CODE HERE -------------------------- % Train the sparse autoencoder and fill the following variables with % the optimal parameters: optTheta = zeros(2*hiddenSize*visibleSize+hiddenSize+visibleSize, 1);%对patch网络作用的所有参数个数 ZCAWhite = zeros(visibleSize, visibleSize); meanPatch = zeros(visibleSize, 1); load STL10Features.mat; % -------------------------------------------------------------------- % Display and check to see that the features look good W = reshape(optTheta(1:visibleSize * hiddenSize), hiddenSize, visibleSize); b = optTheta(2*hiddenSize*visibleSize+1:2*hiddenSize*visibleSize+hiddenSize); displayColorNetwork( (W*ZCAWhite)');%以前的博客中有解释 %%====================================================================== %% STEP 2: Implement and test convolution and pooling % In this step, you will implement convolution and pooling, and test them % on a small part of the data set to ensure that you have implemented % these two functions correctly. In the next step, you will actually % convolve and pool the features with the STL10 images. %% STEP 2a: Implement convolution % Implement convolution in the function cnnConvolve in cnnConvolve.m % Note that we have to preprocess the images in the exact same way % we preprocessed the patches before we can obtain the feature activations. load stlTrainSubset.mat % loads numTrainImages, trainImages, trainLabels %% Use only the first 8 images for testing convImages = trainImages(:, :, :, 1:8); % NOTE: Implement cnnConvolve in cnnConvolve.m first!w和b已经是矩阵或向量的形式了 convolvedFeatures = cnnConvolve(patchDim, hiddenSize, convImages, W, b, ZCAWhite, meanPatch); %% STEP 2b: Checking your convolution % To ensure that you have convolved the features correctly, we have % provided some code to compare the results of your convolution with % activations from the sparse autoencoder % For 1000 random points for i = 1:1000 featureNum = randi([1, hiddenSize]);%随机选取一个特征 imageNum = randi([1, 8]);%随机选取一个样本 imageRow = randi([1, imageDim - patchDim + 1]);%随机选取一个点 imageCol = randi([1, imageDim - patchDim + 1]); %在那8张图片中随机选取1张图片,然后又根据随机选取的左上角点选取1个patch patch = convImages(imageRow:imageRow + patchDim - 1, imageCol:imageCol + patchDim - 1, :, imageNum); patch = patch(:); %这样是按照列的顺序来排列的 patch = patch - meanPatch; patch = ZCAWhite * patch;%用同样的参数对该patch进行白化处理 features = feedForwardAutoencoder(optTheta, hiddenSize, visibleSize, patch); %计算出该patch的输出值 if abs(features(featureNum, 1) - convolvedFeatures(featureNum, imageNum, imageRow, imageCol)) > 1e-9 fprintf('Convolved feature does not match activation from autoencoder\n'); fprintf('Feature Number : %d\n', featureNum); fprintf('Image Number : %d\n', imageNum); fprintf('Image Row : %d\n', imageRow); fprintf('Image Column : %d\n', imageCol); fprintf('Convolved feature : %0.5f\n', convolvedFeatures(featureNum, imageNum, imageRow, imageCol)); fprintf('Sparse AE feature : %0.5f\n', features(featureNum, 1)); error('Convolved feature does not match activation from autoencoder'); end end disp('Congratulations! Your convolution code passed the test.'); %% STEP 2c: Implement pooling % Implement pooling in the function cnnPool in cnnPool.m % NOTE: Implement cnnPool in cnnPool.m first! pooledFeatures = cnnPool(poolDim, convolvedFeatures); %% STEP 2d: Checking your pooling % To ensure that you have implemented pooling, we will use your pooling % function to pool over a test matrix and check the results. testMatrix = reshape(1:64, 8, 8);%将1~64这64个数字弄成一个矩阵,按列的方向依次递增 %直接计算均值pooling值 expectedMatrix = [mean(mean(testMatrix(1:4, 1:4))) mean(mean(testMatrix(1:4, 5:8))); ... mean(mean(testMatrix(5:8, 1:4))) mean(mean(testMatrix(5:8, 5:8))); ]; testMatrix = reshape(testMatrix, 1, 1, 8, 8); %squeeze去掉维度为1的那一维 pooledFeatures = squeeze(cnnPool(4, testMatrix));%参数值为4表明是对4*4的区域进行pooling if ~isequal(pooledFeatures, expectedMatrix) disp('Pooling incorrect'); disp('Expected'); disp(expectedMatrix); disp('Got'); disp(pooledFeatures); else disp('Congratulations! Your pooling code passed the test.'); end %%====================================================================== %% STEP 3: Convolve and pool with the dataset % In this step, you will convolve each of the features you learned with % the full large images to obtain the convolved features. You will then % pool the convolved features to obtain the pooled features for % classification. % % Because the convolved features matrix is very large, we will do the % convolution and pooling 50 features at a time to avoid running out of % memory. Reduce this number if necessary stepSize = 50; assert(mod(hiddenSize, stepSize) == 0, 'stepSize should divide hiddenSize');%hiddenSize/stepSize为整数,这里分8次进行 load stlTrainSubset.mat % loads numTrainImages, trainImages, trainLabels load stlTestSubset.mat % loads numTestImages, testImages, testLabels pooledFeaturesTrain = zeros(hiddenSize, numTrainImages, ...%image是大图片的尺寸,这里为64 floor((imageDim - patchDim + 1) / poolDim), ... %.poolDim为多大的区域pool一次,这里为19,即19*19大小pool一次. floor((imageDim - patchDim + 1) / poolDim) );%最后算出的pooledFeaturesTrain大小为400*2000*3*3 pooledFeaturesTest = zeros(hiddenSize, numTestImages, ... floor((imageDim - patchDim + 1) / poolDim), ... floor((imageDim - patchDim + 1) / poolDim) );%pooledFeaturesTest大小为400*3200*3*3 tic(); for convPart = 1:(hiddenSize / stepSize)%stepSize表示分批次进行原始图片数据的特征提取,一次进行stepSize个隐含层节点 featureStart = (convPart - 1) * stepSize + 1;%选取起始的特征 featureEnd = convPart * stepSize;%选取结束的特征 fprintf('Step %d: features %d to %d\n', convPart, featureStart, featureEnd); Wt = W(featureStart:featureEnd, :); bt = b(featureStart:featureEnd); fprintf('Convolving and pooling train images\n'); convolvedFeaturesThis = cnnConvolve(patchDim, stepSize, ...%参数2表示的是当前"隐含层"节点的个数 trainImages, Wt, bt, ZCAWhite, meanPatch); pooledFeaturesThis = cnnPool(poolDim, convolvedFeaturesThis); pooledFeaturesTrain(featureStart:featureEnd, :, :, :) = pooledFeaturesThis; toc(); clear convolvedFeaturesThis pooledFeaturesThis;%这些大的变量在不用的情况下全部删除掉,因为后面用的是test部分 fprintf('Convolving and pooling test images\n'); convolvedFeaturesThis = cnnConvolve(patchDim, stepSize, ... testImages, Wt, bt, ZCAWhite, meanPatch); pooledFeaturesThis = cnnPool(poolDim, convolvedFeaturesThis); pooledFeaturesTest(featureStart:featureEnd, :, :, :) = pooledFeaturesThis; toc(); clear convolvedFeaturesThis pooledFeaturesThis; end % You might want to save the pooled features since convolution and pooling takes a long time save('cnnPooledFeatures.mat', 'pooledFeaturesTrain', 'pooledFeaturesTest'); toc(); %%====================================================================== %% STEP 4: Use pooled features for classification % Now, you will use your pooled features to train a softmax classifier, % using softmaxTrain from the softmax exercise. % Training the softmax classifer for 1000 iterations should take less than % 10 minutes. % Add the path to your softmax solution, if necessary % addpath /path/to/solution/ % Setup parameters for softmax softmaxLambda = 1e-4;%权值惩罚系数 numClasses = 4; % Reshape the pooledFeatures to form an input vector for softmax softmaxX = permute(pooledFeaturesTrain, [1 3 4 2]);%permute是调整顺序,把图片放在最后 softmaxX = reshape(softmaxX, numel(pooledFeaturesTrain) / numTrainImages,...%numel(pooledFeaturesTrain) / numTrainImages numTrainImages); %为每一张图片得到的特征向量长度 softmaxY = trainLabels; options = struct; options.maxIter = 200; softmaxModel = softmaxTrain(numel(pooledFeaturesTrain) / numTrainImages,...%第一个参数为inputSize numClasses, softmaxLambda, softmaxX, softmaxY, options); %%====================================================================== %% STEP 5: Test classifer % Now you will test your trained classifer against the test images softmaxX = permute(pooledFeaturesTest, [1 3 4 2]); softmaxX = reshape(softmaxX, numel(pooledFeaturesTest) / numTestImages, numTestImages); softmaxY = testLabels; [pred] = softmaxPredict(softmaxModel, softmaxX); acc = (pred(:) == softmaxY(:)); acc = sum(acc) / size(acc, 1); fprintf('Accuracy: %2.3f%%\n', acc * 100);%计算预测准确度 % You should expect to get an accuracy of around 80% on the test images.
cnnConvolve.m:
function convolvedFeatures = cnnConvolve(patchDim, numFeatures, images, W, b, ZCAWhite, meanPatch) %cnnConvolve Returns the convolution of the features given by W and b with %the given images % % Parameters: % patchDim - patch (feature) dimension % numFeatures - number of features % images - large images to convolve with, matrix in the form % images(r, c, channel, image number) % W, b - W, b for features from the sparse autoencoder % ZCAWhite, meanPatch - ZCAWhitening and meanPatch matrices used for % preprocessing % % Returns: % convolvedFeatures - matrix of convolved features in the form % convolvedFeatures(featureNum, imageNum, imageRow, imageCol) patchSize = patchDim*patchDim; assert(numFeatures == size(W,1), 'W should have numFeatures rows'); numImages = size(images, 4);%第4维的大小,即图片的样本数 imageDim = size(images, 1);%第1维的大小,即图片的行数 imageChannels = size(images, 3);%第3维的大小,即图片的通道数 assert(patchSize*imageChannels == size(W,2), 'W should have patchSize*imageChannels cols'); % Instructions: % Convolve every feature with every large image here to produce the % numFeatures x numImages x (imageDim - patchDim + 1) x (imageDim - patchDim + 1) % matrix convolvedFeatures, such that % convolvedFeatures(featureNum, imageNum, imageRow, imageCol) is the % value of the convolved featureNum feature for the imageNum image over % the region (imageRow, imageCol) to (imageRow + patchDim - 1, imageCol + patchDim - 1) % % Expected running times: % Convolving with 100 images should take less than 3 minutes % Convolving with 5000 images should take around an hour % (So to save time when testing, you should convolve with less images, as % described earlier) % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE -------------------- % Precompute the matrices that will be used during the convolution. Recall % that you need to take into account the whitening and mean subtraction % steps WT = W*ZCAWhite;%等效的网络参数 b_mean = b - WT*meanPatch;%针对未均值化的输入数据需要加入该项 % -------------------------------------------------------- convolvedFeatures = zeros(numFeatures, numImages, imageDim - patchDim + 1, imageDim - patchDim + 1); for imageNum = 1:numImages for featureNum = 1:numFeatures % convolution of image with feature matrix for each channel convolvedImage = zeros(imageDim - patchDim + 1, imageDim - patchDim + 1); for channel = 1:imageChannels % Obtain the feature (patchDim x patchDim) needed during the convolution % ---- YOUR CODE HERE ---- offset = (channel-1)*patchSize; feature = reshape(WT(featureNum,offset+1:offset+patchSize), patchDim, patchDim);%取一个权值图像块出来 im = images(:,:,channel,imageNum); % Flip the feature matrix because of the definition of convolution, as explained later feature = flipud(fliplr(squeeze(feature))); % Obtain the image im = squeeze(images(:, :, channel, imageNum));%取一张图片出来 % Convolve "feature" with "im", adding the result to convolvedImage % be sure to do a 'valid' convolution % ---- YOUR CODE HERE ---- convolvedoneChannel = conv2(im, feature, 'valid'); convolvedImage = convolvedImage + convolvedoneChannel;%直接把3通道的值加起来,理由:3通道相当于有3个feature-map,类似于cnn第2层以后的输入。 % ------------------------ end % Subtract the bias unit (correcting for the mean subtraction as well) % Then, apply the sigmoid function to get the hidden activation % ---- YOUR CODE HERE ---- convolvedImage = sigmoid(convolvedImage+b_mean(featureNum)); % ------------------------ % The convolved feature is the sum of the convolved values for all channels convolvedFeatures(featureNum, imageNum, :, :) = convolvedImage; end end end function sigm = sigmoid(x) sigm = 1./(1+exp(-x)); end
cnnPool.m:
function pooledFeatures = cnnPool(poolDim, convolvedFeatures) %cnnPool Pools the given convolved features % % Parameters: % poolDim - dimension of pooling region % convolvedFeatures - convolved features to pool (as given by cnnConvolve) % convolvedFeatures(featureNum, imageNum, imageRow, imageCol) % % Returns: % pooledFeatures - matrix of pooled features in the form % pooledFeatures(featureNum, imageNum, poolRow, poolCol) % numImages = size(convolvedFeatures, 2);%图片数 numFeatures = size(convolvedFeatures, 1);%特征数 convolvedDim = size(convolvedFeatures, 3);%图片的行数 resultDim = floor(convolvedDim / poolDim); pooledFeatures = zeros(numFeatures, numImages, resultDim, resultDim); % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE -------------------- % Instructions: % Now pool the convolved features in regions of poolDim x poolDim, % to obtain the % numFeatures x numImages x (convolvedDim/poolDim) x (convolvedDim/poolDim) % matrix pooledFeatures, such that % pooledFeatures(featureNum, imageNum, poolRow, poolCol) is the % value of the featureNum feature for the imageNum image pooled over the % corresponding (poolRow, poolCol) pooling region % (see http://ufldl/wiki/index.php/Pooling ) % % Use mean pooling here. % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE -------------------- for imageNum = 1:numImages for featureNum = 1:numFeatures for poolRow = 1:resultDim offsetRow = 1+(poolRow-1)*poolDim; for poolCol = 1:resultDim offsetCol = 1+(poolCol-1)*poolDim; patch = convolvedFeatures(featureNum,imageNum,offsetRow:offsetRow+poolDim-1,... offsetCol:offsetCol+poolDim-1);%取出一个patch pooledFeatures(featureNum,imageNum,poolRow,poolCol) = mean(patch(:));%使用均值pool end end end end end
参考资料:
Deep learning:十七(Linear Decoders,Convolution和Pooling)
Exercise:Convolution and Pooling