SynchronousQueue介绍
SynchronousQueue是一种阻塞队列,该队列没有任务的容量。内部实现采用了一种性能更好的无锁算法。
代码实现里的Dual Queue,其中每一个put对应一个take方法。
简单测试代码
public class SynchronousQueueExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
final SynchronousQueue queue = new SynchronousQueue();
new Thread(new QueueProducer(queue)).start();
new Thread(new QueueConsumer(queue)).start();
}
}
public class QueueProducer implements Runnable {
private SynchronousQueue queue;
public QueueProducer(SynchronousQueue queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
String event = "FIRST_EVENT";
String another_event = "SECOND_EVENT";
try {
queue.put(event);
System.out.printf("[%s] producer event : %s %n", Thread
.currentThread().getName(), event);
queue.put(another_event);
System.out.printf("[%s] producer event : %s %n", Thread
.currentThread().getName(), another_event);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class QueueConsumer implements Runnable {
private SynchronousQueue queue;
public QueueConsumer(SynchronousQueue queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
String event = (String) queue.take();
// thread will block here
System.out.printf("[%s] consumed event : %s %n", Thread
.currentThread().getName(), event);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
--------------------------
[Thread-0] producer event : FIRST_EVENT
[Thread-1] consumed event : FIRST_EVENT
--------------------------
生产者每生产一个,如果没有消费者消费那就发生阻塞上面例子中。结果只打印了FIRST_EVENT ,因为SECOND_EVENT没有调用 queue.take()方法 ,所以没有打印。
绑定 put和take方法
/**
* Puts or takes an item.
*/
Object transfer(Object e, boolean timed, long nanos) {
/*
* Basic algorithm is to loop trying one of three actions:
*
* 1. If apparently empty or already containing nodes of same
* mode, try to push node on stack and wait for a match,
* returning it, or null if cancelled.
*
* 2. If apparently containing node of complementary mode,
* try to push a fulfilling node on to stack, match
* with corresponding waiting node, pop both from
* stack, and return matched item. The matching or
* unlinking might not actually be necessary because of
* other threads performing action 3:
*
* 3. If top of stack already holds another fulfilling node,
* help it out by doing its match and/or pop
* operations, and then continue. The code for helping
* is essentially the same as for fulfilling, except
* that it doesn't return the item.
*/
SNode s = null; // constructed/reused as needed
int mode = (e == null)? REQUEST : DATA;
for (;;) {
SNode h = head;
if (h == null || h.mode == mode) { // empty or same-mode
if (timed && nanos <= 0) { // can't wait
if (h != null && h.isCancelled())
casHead(h, h.next); // pop cancelled node
else
return null;
} else if (casHead(h, s = snode(s, e, h, mode))) {
SNode m = awaitFulfill(s, timed, nanos);
if (m == s) { // wait was cancelled
clean(s);
return null;
}
if ((h = head) != null && h.next == s)
casHead(h, s.next); // help s's fulfiller
return mode == REQUEST? m.item : s.item;
}
} else if (!isFulfilling(h.mode)) { // try to fulfill
if (h.isCancelled()) // already cancelled
casHead(h, h.next); // pop and retry
else if (casHead(h, s=snode(s, e, h, FULFILLING|mode))) {
for (;;) { // loop until matched or waiters disappear
SNode m = s.next; // m is s's match
if (m == null) { // all waiters are gone
casHead(s, null); // pop fulfill node
s = null; // use new node next time
break; // restart main loop
}
SNode mn = m.next;
if (m.tryMatch(s)) {
casHead(s, mn); // pop both s and m
return (mode == REQUEST)? m.item : s.item;
} else // lost match
s.casNext(m, mn); // help unlink
}
}
} else { // help a fulfiller
SNode m = h.next; // m is h's match
if (m == null) // waiter is gone
casHead(h, null); // pop fulfilling node
else {
SNode mn = m.next;
if (m.tryMatch(h)) // help match
casHead(h, mn); // pop both h and m
else // lost match
h.casNext(m, mn); // help unlink
}
}
}
}
说到SynchronousQueue不由的想到LinkedBlockingQueue,ArrayBlockingQueue,PriorityBlockingQueue
根据不同的需要BlockingQueue有4种具体实现:
- (1)ArrayBlockingQueue:规定大小的BlockingQueue,其构造函数必须带一个int参数来指明其大小。其所含的对象是以FIFO(先入先出)顺序排序的。
- (2)LinkedBlockingQueue:大小不定的BlockingQueue,若其构造函数带一个规定大小的参数,生成的BlockingQueue有大小限制, 若不带大小参数,所生成的BlockingQueue的大小由Integer.MAX_VALUE来决定。其所含的对象是以FIFO(先入先出)顺序排序的。LinkedBlockingQueue和ArrayBlockingQueue比较起来,它们背后所用的数据结构不一样, 导致LinkedBlockingQueue的数据吞吐量要大于ArrayBlockingQueue,但在线程数量很大时其性能的可预见性低于ArrayBlockingQueue。
- (3)PriorityBlockingQueue:类似于LinkedBlockingQueue,但其所含对象的排序不是FIFO,而是依据对象的自然排序顺序或者是构造函数所带的Comparator决定的顺序。
- (4)SynchronousQueue:特殊的BlockingQueue,对其的操作必须是放和取交替完成的。
ThreadPoolExecutor
/**
* Creates a new <tt>ThreadPoolExecutor</tt> with the given initial
* parameters and default thread factory.
*
* @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the
* pool, even if they are idle.
* @param maximumPoolSize the maximum number of threads to allow in the
* pool.
* @param keepAliveTime when the number of threads is greater than
* the core, this is the maximum time that excess idle threads
* will wait for new tasks before terminating.
* @param unit the time unit for the keepAliveTime
* argument.
* @param workQueue the queue to use for holding tasks before they
* are executed. This queue will hold only the <tt>Runnable</tt>
* tasks submitted by the <tt>execute</tt> method.
* @param handler the handler to use when execution is blocked
* because the thread bounds and queue capacities are reached.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if corePoolSize or
* keepAliveTime less than zero, or if maximumPoolSize less than or
* equal to zero, or if corePoolSize greater than maximumPoolSize.
* @throws NullPointerException if <tt>workQueue</tt>
* or <tt>handler</tt> are null.
*/
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), handler);
}
上面的每一个参数很详细的介绍了ThreadPoolExecutor的用法,保持线程的数量,最大化线程的数量,调度时间的间隔,用到的线程队列等。
主要的execute方法。
/**
* Executes the given task sometime in the future. The task
* may execute in a new thread or in an existing pooled thread.
*
* If the task cannot be submitted for execution, either because this
* executor has been shutdown or because its capacity has been reached,
* the task is handled by the current <tt>RejectedExecutionHandler</tt>.
*
* @param command the task to execute
* @throws RejectedExecutionException at discretion of
* <tt>RejectedExecutionHandler</tt>, if task cannot be accepted
* for execution
* @throws NullPointerException if command is null
*/
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (poolSize >= corePoolSize || !addIfUnderCorePoolSize(command)) {
if (runState == RUNNING && workQueue.offer(command)) {
if (runState != RUNNING || poolSize == 0)
ensureQueuedTaskHandled(command);
}
else if (!addIfUnderMaximumPoolSize(command))
reject(command); // is shutdown or saturated
}
}
在线程池中每一个任务被包装成Runnable 类型,传入到execute方法中 , 该方法中会判断是否超过最大线程,是否有空余线程,当调用停止或者达到最大容量会调用RejectedExecutionHandler。
/**
* Rechecks state after queuing a task. Called from execute when
* pool state has been observed to change after queuing a task. If
* the task was queued concurrently with a call to shutdownNow,
* and is still present in the queue, this task must be removed
* and rejected to preserve shutdownNow guarantees. Otherwise,
* this method ensures (unless addThread fails) that there is at
* least one live thread to handle this task
* @param command the task
*/
private void ensureQueuedTaskHandled(Runnable command) {
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
boolean reject = false;
Thread t = null;
try {
int state = runState;
if (state != RUNNING && workQueue.remove(command))
reject = true;
else if (state < STOP &&
poolSize < Math.max(corePoolSize, 1) &&
!workQueue.isEmpty())
t = addThread(null);
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
if (reject)
reject(command);
else if (t != null)
t.start();
}
/**
* Invokes the rejected execution handler for the given command.
*/
void reject(Runnable command) {
handler.rejectedExecution(command, this);
}
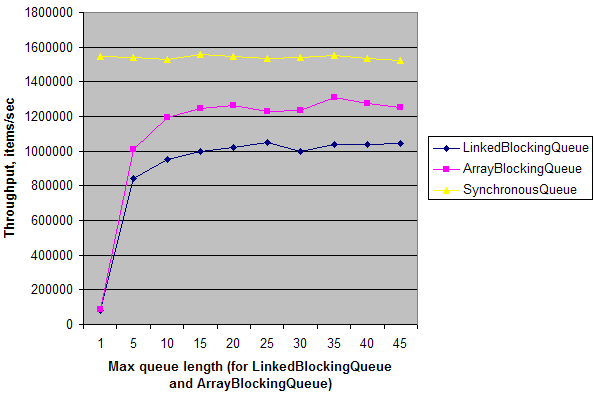
网上的一个测试
public class Test {
static ExecutorService e = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
static int N = 1000000;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int length = (i == 0) ? 1 : i * 5;
System.out.print(length + " ");
System.out.print(doTest(new LinkedBlockingQueue<Integer>(length), N) + " ");
System.out.print(doTest(new ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer>(length), N) + " ");
System.out.print(doTest(new SynchronousQueue<Integer>(), N));
System.out.println();
}
e.shutdown();
}
private static long doTest(final BlockingQueue<Integer> q, final int n) throws Exception {
long t = System.nanoTime();
e.submit(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
try { q.put(i); } catch (InterruptedException ex) {}
}
});
Long r = e.submit(new Callable<Long>() {
public Long call() {
long sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
try { sum += q.take(); } catch (InterruptedException ex) {}
return sum;
}
}).get();
t = System.nanoTime() - t;
return (long)(1000000000.0 * N / t); // Throughput, items/sec
}
}