缓存简介
比如我们要查询数据,我们先从缓冲中查找有没有,如果没有再调用该方法,并且加入到缓冲中,下次调用的时候直接从缓冲中去数据。
导读
未使用缓存
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.1.xsd">
<context:annotation-config />
<context:component-scan base-package="com.tony.test" />
</beans>
//执行任务类
@Component
public class Worker {
public void longTask(final long id) {
System.out.printf("长任务ID %d...%n", id);
}
public void shortTask(final long id) {
System.out.printf("短任务ID %d...%n", id);
}
}
//Main方法测试
public class App {
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final String xmlFile = "classpath*:*/spring.xml";
try (ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlFile)) {
final Worker worker = (Worker)context.getBean(Worker.class);
worker.longTask(1);
worker.longTask(1);
worker.longTask(1);
worker.longTask(2);
worker.longTask(2);
}
}
}
测试结果
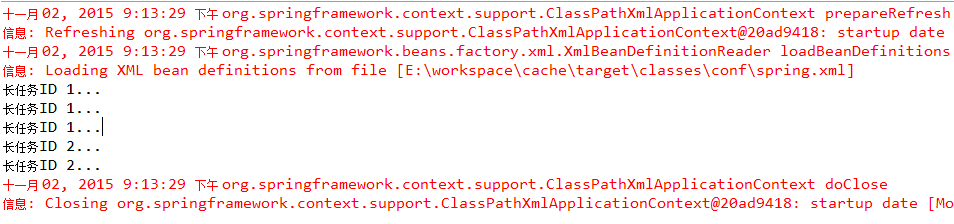
未使用缓存每次都会进行数据调用
使用缓存
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.1.xsd">
<context:annotation-config />
<context:component-scan base-package="com.tony.test" />
<cache:annotation-driven />
<bean id="cacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.support.SimpleCacheManager">
<property name="caches">
<set>
<bean
class="org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCacheFactoryBean"
p:name="task" />
</set>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
//执行任务类
@Component
public class Worker {
@Cacheable("task")
public void longTask(final long id) {
System.out.printf("长任务ID %d...%n", id);
}
public void shortTask(final long id) {
System.out.printf("短任务ID %d...%n", id);
}
}
//Main方法测试
public class App {
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final String xmlFile = "classpath*:*/spring.xml";
try (ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlFile)) {
final Worker worker = (Worker)context.getBean(Worker.class);
worker.longTask(1);
worker.longTask(1);
worker.longTask(1);
worker.longTask(2);
worker.longTask(2);
worker.shortTask(1);
worker.shortTask(1);
}
}
}
测试结果
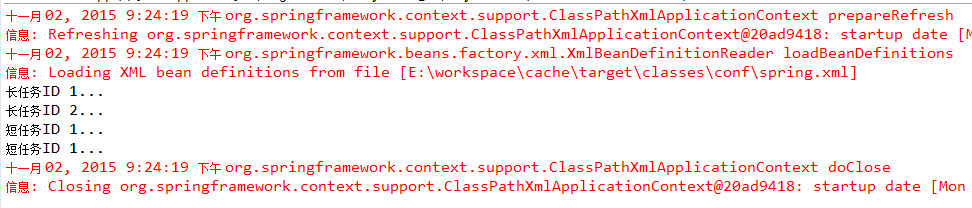
上面测试可以看到,定义了@Cacheable("task"),只打印《长任务ID 1...》和《长任务ID 2...》各执行一次,说明缓存起作用了。
简单概述
`private String name = "";
private ConcurrentMap<Object, Object> store;
private boolean allowNullValues = true;
private ConcurrentMapCache cache;
/**
* Specify the name of the cache.
* <p>Default is "" (empty String).
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* Specify the ConcurrentMap to use as an internal store
* (possibly pre-populated).
* <p>Default is a standard {@link java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap}.
*/
public void setStore(ConcurrentMap<Object, Object> store) {
this.store = store;
}
/**
* Set whether to allow {@code null} values
* (adapting them to an internal null holder value).
* <p>Default is "true".
*/
public void setAllowNullValues(boolean allowNullValues) {
this.allowNullValues = allowNullValues;
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String beanName) {
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(this.name)) {
setName(beanName);
}
}
//重写InitializingBean 中的afterPropertiesSet方法
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
this.cache = (this.store != null ? new ConcurrentMapCache(this.name, this.store, this.allowNullValues) :
new ConcurrentMapCache(this.name, this.allowNullValues));
}
@Override
public ConcurrentMapCache getObject() {
return this.cache;
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return ConcurrentMapCache.class;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
####基于代理存储cache数据
```java
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final String xmlFile = "classpath*:*/spring.xml";
try (ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlFile)) {
final Worker worker = (Worker) context.getBean(Worker.class);
System.out.println(worker.getClass().getCanonicalName());
}
}
上面getCanonicalName方法打印结果:com.tony.test.Worker$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$9bdaf924 ,当我们调用Worker的,其实是调用的一个代理对象,当调用方法上面加上cache之后,代理对象将cache存储起来,下次请求过来之后直接返回cache的value值。