简介
Thrift最初由Facebook研发,主要用于各个服务之间的RPC通信,支持跨语言,常用的语言比如C++, Java, Python, PHP, Ruby, Erlang, Perl, Haskell, C#, Cocoa, JavaScript, Node.js, Smalltalk, and OCaml都支持。Thrift是一个典型的CS(客户端/服务端)结构,客户端和服务端可以使用不同的语言开发。既然客户端和服务端能使用不同的语言开发,那么一定就要有一种中间语言来关联客户端和服务端的语言,没错,这种语言就是IDL(Interface Description Language)。

下载配置
下载地址
windows 下面下载exe,thrift在linux下面也有对应的安装方式。将thrift-0.9.3.exe 下载下来重命名为thrift.exe,并拷贝到windows--->system32里面。
Maven artifact
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.thrift</groupId>
<artifactId>libthrift</artifactId>
<version>0.9.3</version>
</dependency>
GIT Checkout
git clone https://git-wip-us.apache.org/repos/asf/thrift.git thrift
cd thrift
基本概念
1.数据类型
- bool:布尔值,true 或 false,对应 Java 的 boolean
- byte:8 位有符号整数,对应 Java 的 byte
- i16:16 位有符号整数,对应 Java 的 short
- i32:32 位有符号整数,对应 Java 的 int
- i64:64 位有符号整数,对应 Java 的 long
- double:64 位浮点数,对应 Java 的 double
- string:utf-8编码的字符串,对应 Java 的 String
结构体类型: - struct:定义公共的对象,类似于 C 语言中的结构体定义,在 Java 中是一个 JavaBean
容器类型: - list:对应 Java 的 ArrayList
- set:对应 Java 的 HashSet
- map:对应 Java 的 HashMap
异常类型: - exception:对应 Java 的 Exception
服务类型: - service:对应服务的类
2.服务端编码基本步骤:
- 实现服务处理接口impl
- 创建TProcessor
- 创建TServerTransport
- 创建TProtocol
- 创建TServer
- 启动Server
3.客户端编码基本步骤:
- 创建Transport
- 创建TProtocol
- 基于TTransport和TProtocol创建 Client
- 调用Client的相应方法
4.数据传输协议
- TBinaryProtocol : 二进制格式.
- TCompactProtocol : 压缩格式
- TJSONProtocol : JSON格式
- TSimpleJSONProtocol : 提供JSON只写协议, 生成的文件很容易通过脚本语言解析
- tips:客户端和服务端的协议要一致
代码测试
1.创建文件,在D: hrift下建立hello.thrift文件
namespace java com.tony.thrift.demo
service HelloWorldService {
string sayHello(1:string username)
}
thrift -r -gen java hello.thrift
根据thrift 文件自动生成
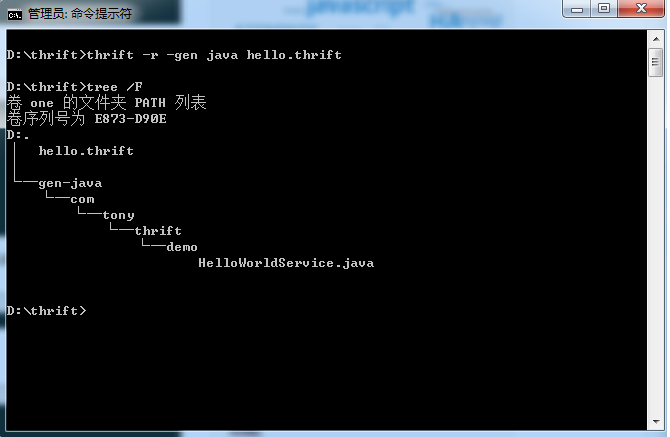
2,将上述截图生成的文件拷贝到工程中。
HelloWorldService
public class HelloWorldService {
public interface Iface {
public String sayHello(String username) throws org.apache.thrift.TException;
}
}
HelloWorldImpl
public class HelloWorldImpl implements HelloWorldService.Iface{
@Override
public String sayHello(String username) throws TException {
return "Hi," + username + " welcome to thrift";
}
}
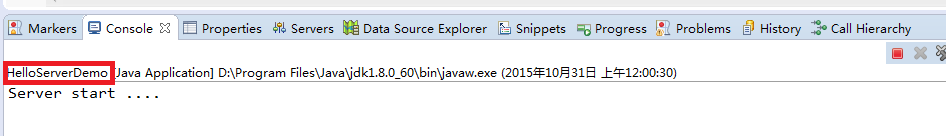
HelloServerDemo
public class HelloServerDemo {
public static final int SERVER_PORT = 7911;
public void startServer() {
try {
System.out.println("Server start ....");
TProcessor tprocessor = new HelloWorldService.Processor<HelloWorldService.Iface>(new HelloWorldImpl());
TServerSocket serverTransport = new TServerSocket(SERVER_PORT);
TServer.Args tArgs = new TServer.Args(serverTransport);
tArgs.processor(tprocessor);
tArgs.protocolFactory(new TBinaryProtocol.Factory());
TServer server = new TSimpleServer(tArgs);
server.serve();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Server start error!!!");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
HelloServerDemo server = new HelloServerDemo();
server.startServer();
}
}
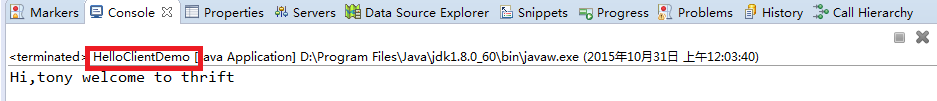
HelloClientDemo
public class HelloClientDemo
{
public static final String SERVER_IP = "localhost";
public static final int SERVER_PORT = 7911;
public static final int TIMEOUT = 30000;
public void startClient(String userName) {
TTransport transport = null;
try {
transport = new TSocket(SERVER_IP, SERVER_PORT, TIMEOUT);
TProtocol protocol = new TBinaryProtocol(transport);
HelloWorldService.Client client = new HelloWorldService.Client(protocol);
transport.open();
String result = client.sayHello(userName);
System.out.println(result);
} catch (TTransportException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (TException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (null != transport) {
transport.close();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HelloClientDemo client = new HelloClientDemo();
client.startClient("tony");
}
}
服务端启动后,可以测试客户端。