前提:
在chrome网上应用商店安装postman 和 Postman Interceptor.
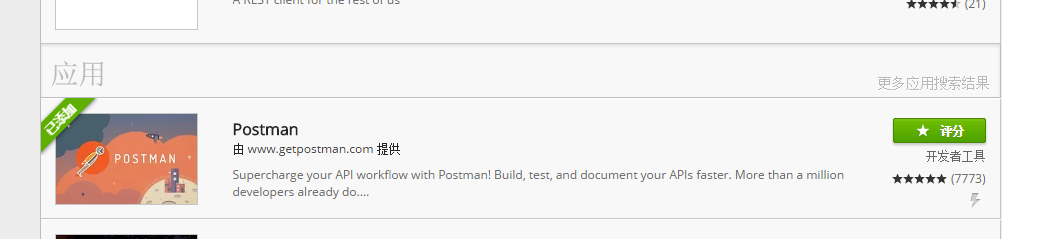
如下图:

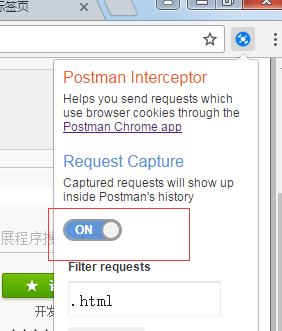
使用postman的时候,最后开启postman Interceptor,如下图:
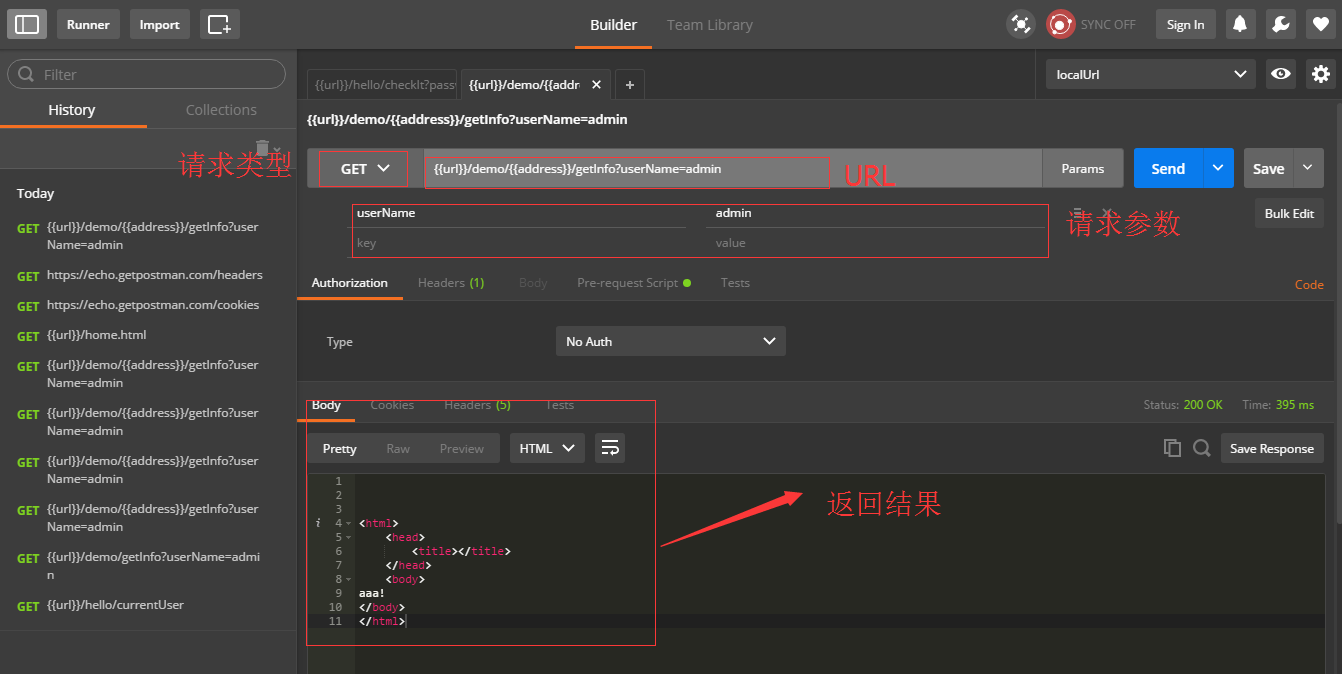
然后启动,postman工具,开始使用。
其中{{url}}的使用,是因为在设置了环境变量,如下图:

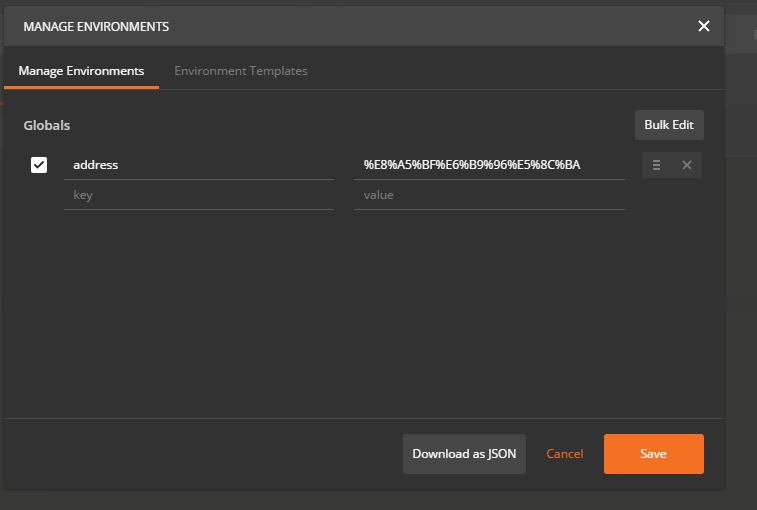
使用{{address}}是因为设置了全局变量,如下图:
Testing 实例
来看一些Postman用于test的例子。这些例子中的大多数在Postman中是有效的,他们像一行JavaScript语句一样简答。在你的request中你可以有很多的test。
注意:test脚本在从服务器收到response后执行
1.设置环境变量:
postman.setEnvironmentVariable("key", "value");2.设置全局变量:
postman.setGlobalVariable("key", "value");3.检查response的body中是否包含字符串:
tests["Body matches string"] = responseBody.has("string_you_want_to_search");4.把XML的body转换成JSON对象:
var jsonObject = xml2Json(responseBody);5.检查response的body是都为一个字符串:
tests["Body is correct"] = responseBody === "response_body_string";6.检查JSON的值:
var data = JSON.parse(responseBody);
tests["Your test name"] = data.value === 100;7.内容类型存在(检查不区分大小写)
tests["Content-Type is present"] = postman.getResponseHeader("Content-Type"); //Note: the getResponseHeader() method returns the header value, if it exists.8.内容类型存在(区分大小写):
tests["Content-Type is present"] = responseHeaders.hasOwnProperty("Content-Type");9.response的响应时间小于200ms:
tests["Response time is less than 200ms"] = responseTime < 200;10.状态码为200:
tests["Status code is 200"] = responseCode.code === 200;11.Code name contains a string:
tests["Status code name has string"] = responseCode.name.has("Created");12.成功的POST request状态码:
tests["Successful POST request"] = responseCode.code === 201 || responseCode.code === 202;