装饰器: test1和test2是原代码。利用装饰器调用原功能。
import time
def timer(func): #由于形参不能是函数,所以传入的最好是函数地址,而不是函数。
def deco():
start_time=time.time()
func() #将函数的地址传入后,加上()即是调用传入的函数。
stop_time=time.time()
print('the gap is %s' %(stop_time-start_time))
return deco #返回的是函数的内存地址,而不是函数
def test1():
time.sleep(3)
print('this is test1')
def test2():
time.sleep(3)
print('this is test2')
1. 带入test1,只是带入了test1函数的内存地址
print(timer(test1)) #1. 没有(),说明传入的参数是test1的内存地址,而不是传入函数。
timer(test1) -> deco 2. 但没有调用deco()函数,而返回的是deco地址,而不是函数
print(test1) #test1的内存地址和deco的内存地址不相等,说明deco在内存中也开辟了一段内存空间。
output:
2. 带入test1()函数,这是带入了test1函数。 带入函数。
print(timer(test1)) #返回值为deco的内存地址,deco函数没有执行,是因为没有调用。而打印的是deco的内存地址。
print(timer(test1()) #传入的参数可以是函数的内存地址,也可以是函数本身。如果是函数本身,func就不能再加(),不然会报错。在这个打印中,先调用了timer(test1())中的test1(),然后调用了timer(test1()),将test1()函数传入,返回deco地址。
print(test1()) #先调用了test1(),但test1函数的返回值为空,由于test1函数没有返回值。
test1() #调用test1函数。
output:
3. 要执行deco中的函数,必须返回deco的内存地址赋值给一个变量,然后调用变量的函数从而执行deco()
test1 = timer(test1) # test1 = deco
test1() # test1 () = deco()
Output:

4. @的应用.
@timer # test1 = timer(test1)
生成器

import time
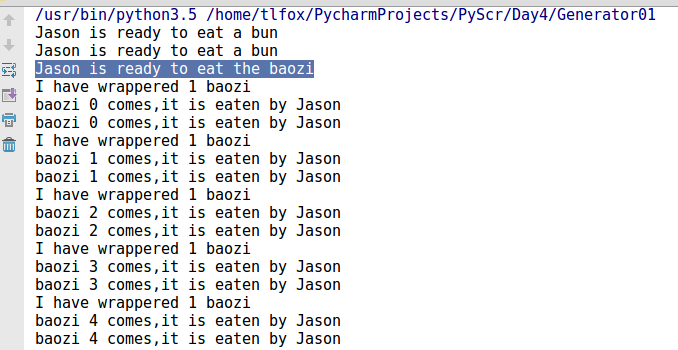
def consumer(name):
print('%s is ready to eat a bun'%name)
while True:
baozi = yield
print('baozi %s comes,it is eaten by %s' %(baozi,name))
def producer(name):
c = consumer(name) #产生generator
c2 = consumer(name) #产生generator
c.__next__() # 调用consumer(),但在yield位置中断。跳出函数并执行下一条命令。
c2.__next__() # 调用consumer(),但在yield位置中断。跳出函数并执行下一条命令。
print('%s is ready to eat the baozi' %name)
for i in range(10):
time.sleep(1)
print('I have wrappered 1 baozi')
c.send(i) # 继续执行yield中断后程序,并传入i值。
c2.send(i) # 继续执行yield中断后程序,并传入i值。
producer('Jason')
output:
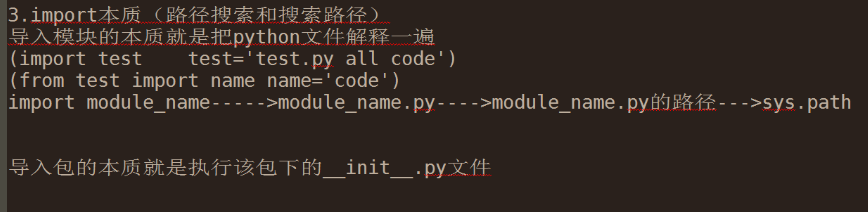
Module


import module # 导入模块,就是执行模块内的所有程序,并定义好function的内存地址。
from module import m1 #from,将模块中某个function导入,并为其定义内存。
模块间调用:
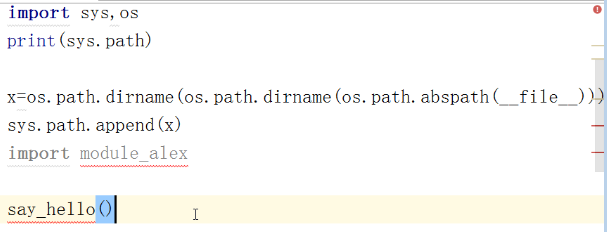
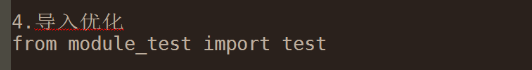
导入模块时,精确导入,会节省search的时间。



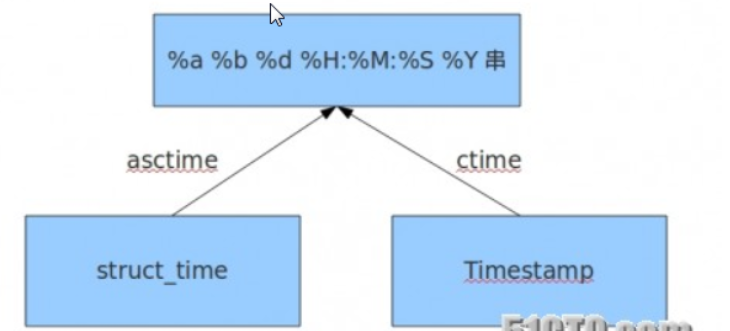
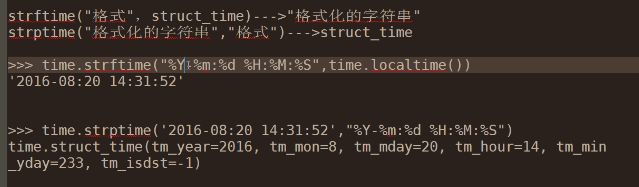
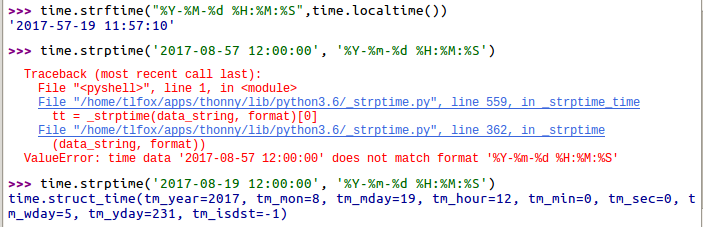
time module
time.time() #
time.localtime()
time.gmtime()

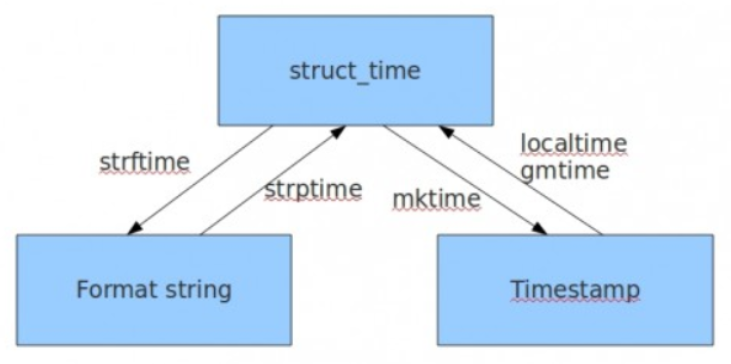
顺序可变,按不同顺序打印