注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//注解保留策略 public @interface MyAnno { String str(); int val(); }
@MyAnno(str = "测试注解",val = 100) public void test() { }
所有注解都只包含方法声明,不能提供方法体。应用注解时,需要为注解成员提供值
注解的保留策略,java指定三种保留策略,它们被封装到java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy枚举中,
SOURCE ,只在源文件保留,编译器会被抛弃
CLASS 在编译时存储到.class文件中,运行时不可通过jvm得到这些注解
RUNTIME 在编译时存储到.class文件中,运行时可通过jvm得到这些注解
因此,RUNTIME 是最永久的注解
使用反射在运行时获取注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//注解保留策略 public @interface MyAnno { String str() default "OK"; int val() default 500; }
public class Test { @MyAnno(str = "测试注解",val = 100) //这里不指定值得时候,将会使用默认值 public static void myMeth() { Test t = new Test(); try { Class<?> clazz = t.getClass(); Method method = clazz.getMethod("myMeth"); MyAnno anno = method.getAnnotation(MyAnno.class);//当注解策略不是RUNTIME时,这里anno会得到null System.out.println(anno.str());//输出 测试注解 System.out.println(anno.val());//输出 100 } catch (NoSuchMethodException | SecurityException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { myMeth(); } }
先获取当前对象,获取Class对象 ,根据Class对象获取当前Method,根据Method 获取表明注解的值。
获取所有注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface MyAnno { String str(); int val(); }
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface What { String desription(); }
@MyAnno(str="测试类注解",val=100) @What(desription="类描述") public class Meta2 { @MyAnno(str="测试方法注解",val=200) @What(desription="方法描述") public static void test() { Meta2 m= new Meta2(); try { Annotation[] annos = m.getClass().getAnnotations(); for (Annotation annotation : annos) { System.out.println(annotation); } // 输出如下 T8是包名 // @T8.MyAnno(str=测试类注解, val=100) // @T8.What(desription=类描述) Method test = m.getClass().getMethod("test"); Annotation[] annos2 = test.getAnnotations(); for (Annotation annotation : annos2) { System.out.println(annotation); } // 输出如下 T8是包名 // @T8.MyAnno(str=测试方法注解, val=200) // @T8.What(desription=方法描述) }catch (Exception e) { } } public static void main(String[] args) { test(); } }
单成员注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface MySingle { String value() default "aaa";//单成员注解仅仅包含一个成员 ,假设只有一个成员,使用注解时就可以直接为该成员设置,而不需要指定成员名称,前提是成员名称必须是value }
public class Single { @MySingle("this is a single annotation")//这里并没有指定 value = public static void test() throws Exception{ Single s = new Single(); Class<?> clazz = s.getClass(); Method test = clazz.getMethod("test"); MySingle mySingle = test.getAnnotation(MySingle.class); System.out.println(mySingle.value());//输出 this is a single annotation } public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { test(); } }
单值注解的其他用法
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface MySingle { String value() default "aaa";//这个仍然是单值成员 int other() default 999;//其他成员必须有默认值 }
public class Single { @MySingle("this is a single annotation")//这里并没有指定 value = public static void test() throws Exception{ Single s = new Single(); Class<?> clazz = s.getClass(); Method test = clazz.getMethod("test"); MySingle mySingle = test.getAnnotation(MySingle.class); System.out.println(mySingle.value());//输出 this is a single annotation System.out.println(mySingle.other());//输出 999 } public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { test(); } }
java的内置注解
@Retention 只能用于注解其他注解 ,用于指定保留策略
@Documented 只能用于注解其他注解 ,用于通知某个工具 注解将被文档化
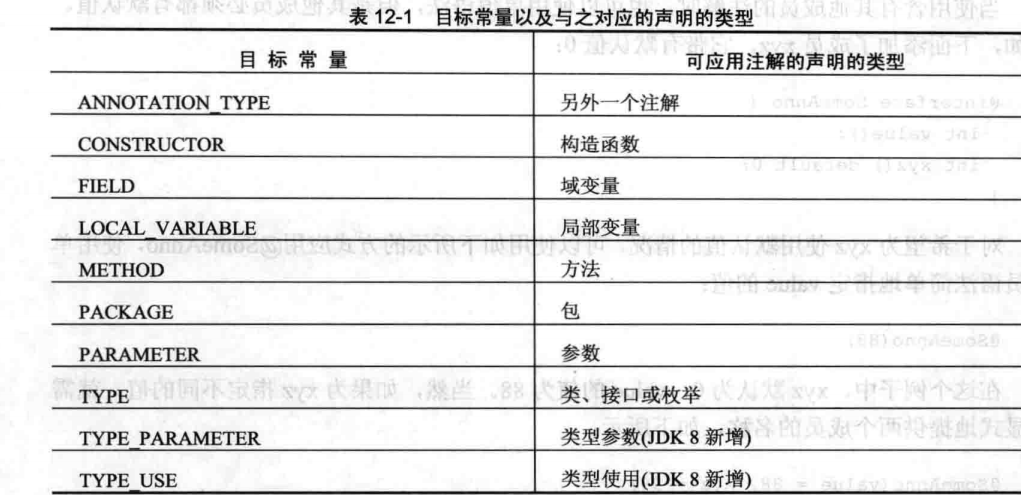
@Target 只能用于注解其他注解 用于指定注解只能使用的场合,比如一下代码
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.FIELD,ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR})//这里的作用是指定MySingle 只能作用在域变量或者构造函数 public @interface MySingle { }
ElementType枚举值如下表
@Inherited 只能用于注解其他注解 允许子类继承父类的注解。
@Override 方法重写注解
@Deprecated 过期注解
@FunctionalInterface 函数式接口注解,用于指定一个接口是一个函数式接口(并不是必须条件,该接口仅仅是提供信息)
@SuppressWarnings 抑制编译器的警告注解