201271050130-滕江南-《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十六周学习总结
博文正文开头格式:(2分)
|
项目 |
内容 |
|
这个作业属于哪个课程 |
https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ |
|
这个作业的要求在哪里 |
https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/12031970.html |
|
作业学习目标 |
(1) 掌握Java应用程序的打包操作; (2) 掌握线程概念; (3) 掌握线程创建的两种技术; |
随笔博文正文内容包括:
第一部分:总结教材14.1-14.3知识内容(20分)
1、程序与进程的概念
‐程序是一段静态的代码,它是应用程序执行的蓝本。
‐进程是程序的一次动态执行,它对应了从代码加载、执行至执行完毕的一个完整过程。
‐操作系统为每个进程分配一段独立的内存空间和系统资源,包括:代码数据以及堆栈等资源。每 一个进程的内部数据和状态都是完全独立的。
‐多任务操作系统中,进程切换对CPU资源消耗较大。
2、多线程的概念
‐多线程是进程执行过程中产生的多条执行线索。
‐线程是比进程执行更小的单位。
‐线程不能独立存在,必须存在于进程中,同一进程的各线程间共享进程空间的数据。
‐每个线程有它自身的产生、存在和消亡的过程, 是一个动态的概念。
‐多线程意味着一个程序的多行语句可以看上去几 乎在同一时间内同时运行。
‐线程创建、销毁和切换的负荷远小于进程,又称为轻量级进程(lightweight process)。
3、Java实现多线程有两种途径:
‐创建Thread类的子类
‐在程序中定义实现Runnable接口的类
4、用Thread类子类创建线程
首先需从Thread类派生出一个子类,在该子类中重写run()方法。
class hand extends Thread
{
public void run()
{……}
}
5、用Thread类的子类创建多线程的关键性操作
–定义Thread类的子类并实现用户线程操作,即 run()方法的实现。
–在适当的时候启动线程。
由于Java只支持单重继承,用这种方法定义的类不可再继承其他父类。
6、用Runnable()接口实现线程
- 首先设计一个实现Runnable接口的类;
- 然后在类中根据需要重写run方法;
- 再创建该类对象,以此对象为参数建立Thread 类的对象;
- 调用Thread类对象的start方法启动线程,将 CPU执行权转交到run方法。
实验1: 测试程序1
(1)在elipse IDE中调试运行教材585页程序13-1,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
(2)将所生成的JAR文件移到另外一个不同的目录中,再运行该归档文件,以便确认程序是从JAR文件中,而不是从当前目录中读取的资源。
(3) 掌握创建JAR文件的方法;
package resource; import java.awt.*; import java.io.*; import java.net.*; import java.util.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.41 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class ResourceTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new ResourceTestFrame(); frame.setTitle("ResourceTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } } /** * 加载图像和文本资源的框架。 */ class ResourceTestFrame extends JFrame { private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 400; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 400; public ResourceTestFrame() { setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); URL aboutURL = getClass().getResource("about.gif"); //将此图像设置为框架的图标 Image img = new ImageIcon(aboutURL).getImage(); setIconImage(img); JTextArea textArea = new JTextArea(); InputStream stream = getClass().getResourceAsStream("about.txt"); //在读取文本时使用同一编码UTF-8 try (Scanner in = new Scanner(stream, "UTF-8")) { while (in.hasNext()) textArea.append(in.nextLine() + " "); } add(textArea); } }
实验1:测试程序2(10分)
(1)在elipse IDE中调试运行ThreadTest,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
(2)掌握线程概念;
(3) 掌握用Thread的扩展类实现线程的方法;
(4)利用Runnable接口改造程序,掌握用Runnable接口创建线程的方法。
class Lefthand extends Thread { public void run() { for(int i=0;i<=5;i++) { System.out.println("You are Students!"); try{ sleep(500); } catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Lefthand error.");} } } } class Righthand extends Thread { public void run() { for(int i=0;i<=5;i++) { System.out.println("I am a Teacher!"); try{ sleep(300); } catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Righthand error.");} } } } public class ThreadTest { static Lefthand left; static Righthand right; public static void main(String[] args) { left=new Lefthand(); right=new Righthand(); left.start(); right.start(); } }
用Runnable接口实现
package threadTest; class Lefthand implements Runnable { public void run() { for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) { System.out.println("You are Students!"); try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Lefthand error."); } } } } class Righthand implements Runnable { public void run() { for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) { System.out.println("I am a Teacher!"); try { Thread.sleep(300); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Righthand error."); } } } } public class ThreadTest { static Thread left; static Thread right; public static void main(String[] args) { Runnable a = new Lefthand(); Runnable b = new Righthand(); left = new Thread(a); right = new Thread(b); left.start(); right.start(); } }
运行结果:
 实验1:测试程序3(10分)
实验1:测试程序3(10分)
(1)在Elipse环境下调试教材625页程序14-1、14-2 、14-3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
(2)在Elipse环境下调试教材631页程序14-4,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
(3)对比两个程序,理解线程的概念和用途;
(4)掌握线程创建的两种技术。
package bounce; import java.awt.geom.*; /** * A ball that moves and bounces off the edges of a rectangle * @version 1.33 2007-05-17 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Ball { private static final int XSIZE = 15; private static final int YSIZE = 15; private double x = 0; private double y = 0; private double dx = 1; private double dy = 1; /** * Moves the ball to the next position, reversing direction if it hits one of the edges */ public void move(Rectangle2D bounds) { x += dx; y += dy; if (x < bounds.getMinX()) { x = bounds.getMinX(); dx = -dx; } if (x + XSIZE >= bounds.getMaxX()) { x = bounds.getMaxX() - XSIZE; dx = -dx; } if (y < bounds.getMinY()) { y = bounds.getMinY(); dy = -dy; } if (y + YSIZE >= bounds.getMaxY()) { y = bounds.getMaxY() - YSIZE; dy = -dy; } } /** * Gets the shape of the ball at its current position. */ public Ellipse2D getShape() { return new Ellipse2D.Double(x, y, XSIZE, YSIZE); } }
packagebounceThread;
import java.awt.*;import java.util.*;import javax.swing.*;/** * 画球的部件。 * @version 1.34 2012-01-26 * @author Cay Horstmann */public class BallComponent extends JComponent{ private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 450; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 350; private java.util.List<Ball> balls = new ArrayList<>(); /** * 向面板中添加一个球。 * @param b把球加到面板上 */ public void add(Ball b) { balls.add(b); } public void paintComponent(Graphics g) { Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g; for (Ball b : balls) { g2.fill(b.getShape()); } } public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); }}packagebounceThread;
import java.awt.geom.*;/** 从长方形边缘上移动和弹跳的球 * @version 1.33 2007-05-17 * @author Cay Horstmann*/public class Ball{ private static final int XSIZE = 15; private static final int YSIZE = 15; private double x = 0; private double y = 0; private double dx = 1; private double dy = 1; /** 将球移动到下一个位置,如果球碰到其中一条边,则反向移动 */ public void move(Rectangle2D bounds) { x += dx; y += dy; if (x < bounds.getMinX()) { x = bounds.getMinX(); dx = -dx; } if (x + XSIZE >= bounds.getMaxX()) { x = bounds.getMaxX() - XSIZE; dx = -dx; } if (y < bounds.getMinY()) { y = bounds.getMinY(); dy = -dy; } if (y + YSIZE >= bounds.getMaxY()) { y = bounds.getMaxY() - YSIZE; dy = -dy; } } /** 获取球在当前位置的形状。 */ public Ellipse2D getShape() { return new Ellipse2D.Double(x, y, XSIZE, YSIZE); }}运行结果:

package bounceThread; import java.awt.geom.*; /** 弹球从矩形的边缘上移动和弹出的球 * @version 1.33 2007-05-17 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Ball { private static final int XSIZE = 15; private static final int YSIZE = 15; private double x = 0; private double y = 0; private double dx = 1; private double dy = 1; /** 将球移动到下一个位置,如果球击中一个边缘,则向相反的方向移动。 */ public void move(Rectangle2D bounds) { x += dx; y += dy; if (x < bounds.getMinX()) { x = bounds.getMinX(); dx = -dx; } if (x + XSIZE >= bounds.getMaxX()) { x = bounds.getMaxX() - XSIZE; dx = -dx; } if (y < bounds.getMinY()) { y = bounds.getMinY(); dy = -dy; } if (y + YSIZE >= bounds.getMaxY()) { y = bounds.getMaxY() - YSIZE; dy = -dy; } } /** 获取当前位置的球的形状。 */ public Ellipse2D getShape() { return new Ellipse2D.Double(x, y, XSIZE, YSIZE); } } Ball
package bounceThread; import java.awt.*; import java.util.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * 拉球的部件。 * @version 1.34 2012-01-26 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class BallComponent extends JComponent { private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 450; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 350; private java.util.List<Ball> balls = new ArrayList<>(); /** * 在面板上添加一个球。 * @param b要添加的球 */ public void add(Ball b) { balls.add(b); } public void paintComponent(Graphics g) { Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g; for (Ball b : balls) { g2.fill(b.getShape()); } } public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); } } BallComponent
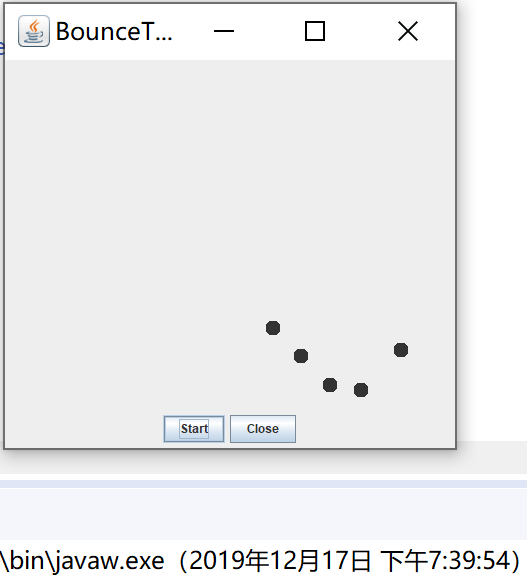
package bounceThread; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * 显示动画弹跳球。 * @version 1.34 2015-06-21 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class BounceThread { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new BounceFrame(); frame.setTitle("BounceThread"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } } /** * 带有面板和按钮的框架。 */ class BounceFrame extends JFrame { private BallComponent comp; public static final int STEPS = 1000; public static final int DELAY = 5; /** * 用显示弹跳球以及开始和关闭按钮的组件构建框架 */ public BounceFrame() { comp = new BallComponent(); add(comp, BorderLayout.CENTER); JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel(); addButton(buttonPanel, "Start", event -> addBall()); addButton(buttonPanel, "Close", event -> System.exit(0)); add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack(); } /** * 向容器添加按钮。 * @param c 容器 * @param title 按钮标题 * @param listener 按钮的操作监听器 */ public void addButton(Container c, String title, ActionListener listener) { JButton button = new JButton(title); c.add(button); button.addActionListener(listener); } /** * 在画布上添加一个弹跳球,并启动一个线程使其弹跳 */ public void addBall() { Ball ball = new Ball(); comp.add(ball); Runnable r = () -> { try { for (int i = 1; i <= STEPS; i++) { ball.move(comp.getBounds()); comp.repaint(); Thread.sleep(DELAY); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { } }; Thread t = new Thread(r); t.start(); } } BounceThread
运行结果:
实验2:
结对编程练习:采用GUI界面设计以下程序,并创建程序归档文件。
设计一个100以内整数小学生四则运算练习程序,由计算机随机产生10道加减乘除练习题,学生输入答案,由程序检查答案是否正确,每道题正确计10分,错误不计分,10道题测试结束后给出测试总分;
将程序中测试练习题及学生答题结果输出到文件,文件名为test.txt。
实验总结:(15分)
本周学习了有关线程的知识,线程创建有两种方式,第一种是实现runnable接口,第二种是采用Thread类方法,在实验课上进行了实现Runnable接口。但是在测试程序1操作过程中,还存在着很大的问题不理解题目的要求,也不知道该怎么打包回归文档。因为缺了一次课,所以自己看书看同学们的操作步骤完成了程序1。