第1章 数据库优化简介
1-1 MySQL优化简介

第2章 SQL语句优化
2-1 数据准备
2-2 MySQL慢查日志的开启方式

2-3 MySQL慢查日志分析工具之 mysqldumpslow
www@AliYun:~$ sudo mysqldumpslow -t 3 /var/log/mysql/slow.log | more
Reading mysql slow query log from /var/log/mysql/slow.log
Count: 1 Time=0.16s (0s) Lock=0.00s (0s) Rows=0.0 (0), www[www]@[115.193.170.169]
DELETE FROM `resty_invitation`
Count: 1 Time=0.14s (0s) Lock=0.00s (0s) Rows=1000.0 (1000), www[www]@[115.193.170.169]
SELECT * FROM `resty_logs` LIMIT N, N
Count: 2 Time=0.05s (0s) Lock=0.01s (0s) Rows=0.0 (0), []@[]
throttle: N 'S' warning(s) suppressed.
2-4 MySQL慢查日志分析工具之 pt-querey-diget

2-5 如何通过慢查日志发现有问

2-6 通过explain查询和分析SQL的执行计划
mysql> explain select username,logintime,status,expire from resty_user limit 4;
+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | resty_user | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 9 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.01 sec)


2-7 Count()和Max()的优化
mysql> explain select MAX(fileSize) from resty_stream_video G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: resty_stream_video
partitions: NULL
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 177
filtered: 100.00
Extra: NULL
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
建立索引
create index idx_fileSize on resty_stream_video(fileSize);
继续查询
mysql> explain select MAX(fileSize) from resty_stream_video G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: NULL
partitions: NULL
type: NULL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: NULL
filtered: NULL
Extra: Select tables optimized away
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)

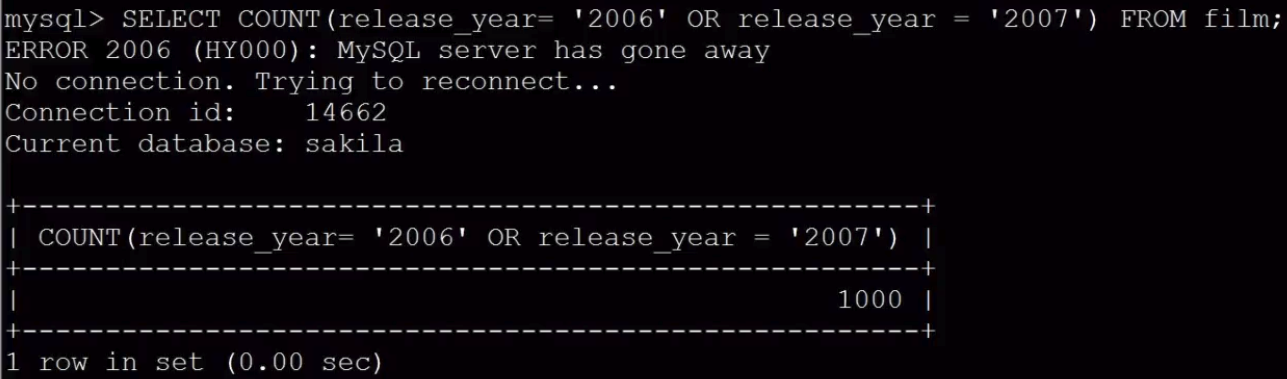

count(*)和count(某一列) 那个好?
mysql> select * from test;
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 1 |
| 2 |
| NULL |
+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(*),count(id) from test;
+----------+-----------+
| count(*) | count(id) |
+----------+-----------+
| 3 | 2 |
+----------+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
小结:count(某一列) 不包括为null的值
2-8 子查询的优化

2-9 group by的优化
2-10 Limit查询的优化
第3章 索引优化
3-1 如何选择合适的列建立索引...(03:25)
3-2 索引优化SQL的方法(07:17)
3-3 索引维护的方法(02:43)
第4章 数据库结构优化
4-1 选择合适的数据类型...(06:43)
4-2 数据库表的范式化优化...(05:03)
4-3 数据库表的反范式化优化...(04:23)
4-4 数据库表的垂直拆分...(02:59)
4-5 数据库表的水平拆分...(03:13)
第5章 系统配置优化
5-1 数据库系统配置优化...(04:24)
5-2 MySQL配置文件优化(10:26)
5-3 第三方配置工具使用...(06:17)
第6章 服务器硬件优化
6-1 服务器硬件优化(05:59)