function A = warmUpExercise() %WARMUPEXERCISE Example function in octave % A = WARMUPEXERCISE() is an example function that returns the 5x5 identity matrix A = []; % ============= YOUR CODE HERE ============== % Instructions: Return the 5x5 identity matrix % In octave, we return values by defining which variables % represent the return values (at the top of the file) % and then set them accordingly. A = eye(5); % =========================================== end
function J = computeCost(X, y, theta) %COMPUTECOST Compute cost for linear regression % J = COMPUTECOST(X, y, theta) computes the cost of using theta as the % parameter for linear regression to fit the data points in X and y % Initialize some useful values m = length(y); % number of training examples % You need to return the following variables correctly J = 0; % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta % You should set J to the cost. predictions = X*theta; sqrErrors = (predictions - y) .^2;%每个元素取平方 J = 1/(2*m) *sum(sqrErrors); % ========================================================================= end
function plotData(x, y) %PLOTDATA Plots the data points x and y into a new figure % PLOTDATA(x,y) plots the data points and gives the figure axes labels of % population and profit. figure; % open a new figure window % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: Plot the training data into a figure using the % "figure" and "plot" commands. Set the axes labels using % the "xlabel" and "ylabel" commands. Assume the % population and revenue data have been passed in % as the x and y arguments of this function. % % Hint: You can use the 'rx' option with plot to have the markers % appear as red crosses. Furthermore, you can make the % markers larger by using plot(..., 'rx', 'MarkerSize', 10); plot(x,y,'rx','MarkerSize',10);% rx 红色的 叉号 ‘x’。大小为10 ylabel('Profit in $10,000s'); xlabel('population of City in 10,000s'); % ============================================================ end

执行ex1 回依次执行所有不得.m文件,直至结束。若想中途停止shift+ctrl+c
function [theta, J_history] = gradientDescent(X, y, theta, alpha, num_iters) %GRADIENTDESCENT Performs gradient descent to learn theta % theta = GRADIENTDESCENT(X, y, theta, alpha, num_iters) updates theta by % taking num_iters gradient steps with learning rate alpha % Initialize some useful values m = length(y); % number of training examples J_history = zeros(num_iters, 1); for iter = 1:num_iters % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: Perform a single gradient step on the parameter vector % theta. % % Hint: While debugging, it can be useful to print out the values % of the cost function (computeCost) and gradient here. % theta1=theta(1,1)-alpha/m*sum(X*theta-y); theta2=theta(2,1)-alpha/m*sum((X*theta-y) .* X(:,2)); theta(1,1)=theta1; theta(2,1)=theta2; % ============================================================ % Save the cost J in every iteration J_history(iter) = computeCost(X, y, theta); end end

function [X_norm, mu, sigma] = featureNormalize(X) %FEATURENORMALIZE Normalizes the features in X % FEATURENORMALIZE(X) returns a normalized version of X where % the mean value of each feature is 0 and the standard deviation % is 1. This is often a good preprocessing step to do when % working with learning algorithms. % You need to set these values correctly X_norm = X; mu = zeros(1, size(X, 2)); sigma = zeros(1, size(X, 2)); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: First, for each feature dimension, compute the mean % of the feature and subtract it from the dataset, % storing the mean value in mu. Next, compute the % standard deviation of each feature and divide % each feature by it's standard deviation, storing % the standard deviation in sigma. % % Note that X is a matrix where each column is a % feature and each row is an example. You need % to perform the normalization separately for % each feature. % % Hint: You might find the 'mean' and 'std' functions useful. % m = size(X,2)%列数 for i=1:m, mu(i)=mean(X(:,i))%X第i列的平均数 sigma(i) =std(X(:,i))%X第i列的标准差 end X_norm =(X_norm-mu)./sigma;%这里同样是对应元素的运算 % ============================================================ end
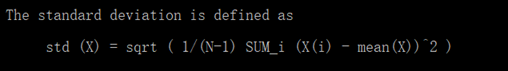
元素间的加减,点乘、除要保证列数一致
>> A =[1 2;3 4;5 6]
A =
>> A =[1 2;3 4;5 6]
A =
1 2
3 4
5 6
3 4
5 6
>> B = [1 2]
B =
B =
1 2
>> A-B
ans =
ans =
0 0
2 2
4 4
2 2
4 4
>> A./B
ans =
ans =
1 1
3 2
5 3
3 2
5 3
function [theta, J_history] = gradientDescentMulti(X, y, theta, alpha, num_iters) %GRADIENTDESCENTMULTI Performs gradient descent to learn theta % theta = GRADIENTDESCENTMULTI(x, y, theta, alpha, num_iters) updates theta by % taking num_iters gradient steps with learning rate alpha % Initialize some useful values m = length(y); % number of training examples J_history = zeros(num_iters, 1); temp = theta; for iter = 1:num_iters % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: Perform a single gradient step on the parameter vector % theta. % % Hint: While debugging, it can be useful to print out the values % of the cost function (computeCostMulti) and gradient here. % for i =1:length(theta), temp(i,1) = temp(i,1)-alpha/m*sum((X*theta-y).*X(:,i)); end theta = temp; % ============================================================ % Save the cost J in every iteration J_history(iter) = computeCostMulti(X, y, theta); end end
length(v) 这个命令将返回 最大维度的大小
function [theta] = normalEqn(X, y) %NORMALEQN Computes the closed-form solution to linear regression % NORMALEQN(X,y) computes the closed-form solution to linear % regression using the normal equations. theta = zeros(size(X, 2), 1); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: Complete the code to compute the closed form solution % to linear regression and put the result in theta. % % ---------------------- Sample Solution ---------------------- theta = pinv(X'*X)*X'*y; % ------------------------------------------------------------- % ============================================================ end
function J = computeCostMulti(X, y, theta) %COMPUTECOSTMULTI Compute cost for linear regression with multiple variables % J = COMPUTECOSTMULTI(X, y, theta) computes the cost of using theta as the % parameter for linear regression to fit the data points in X and y % Initialize some useful values m = length(y); % number of training examples % You need to return the following variables correctly J = 0; % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta % You should set J to the cost. predictions = X*theta; sqrErrors = (predictions -y).^2; J = 1/(2*m)*sum(sqrErrors); % ========================================================================= end