Java Executor 框架
Executor框架是指java5中引入的一系列并发库中与executor相关的功能类,包括Executor、Executors、 ExecutorService、CompletionService、Future、Callable等。(图片引用自 http://www.javaclubcn.com/a/jichuzhishi/2012/1116/170.html)
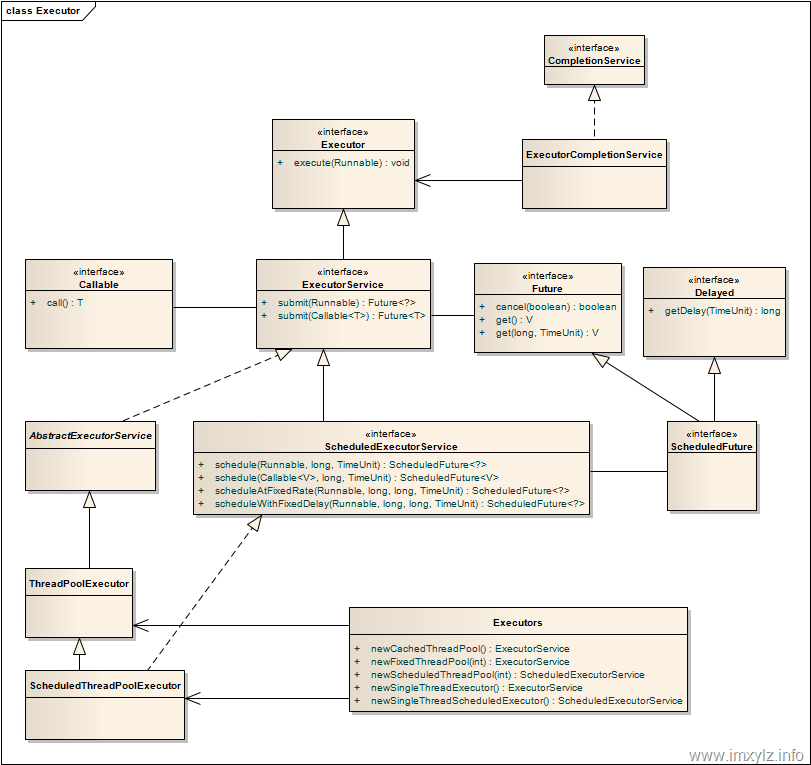
本篇博文分析Executor中几个比较重要的接口和类。
Executor
1 public interface Executor {
2 void execute(Runnable command);
3 }
Executor接口是Executor框架中最基础的部分,定义了一个用于执行Runnable的execute方法。它没有直接的实现类,有一个重要的子接口ExecutorService。
ExecutorService
1 //继承自Executor接口
2 public interface ExecutorService extends Executor {
3 /**
4 * 关闭方法,调用后执行之前提交的任务,不再接受新的任务
5 */
6 void shutdown();
7 /**
8 * 从语义上可以看出是立即停止的意思,将暂停所有等待处理的任务并返回这些任务的列表
9 */
10 List<Runnable> shutdownNow();
11 /**
12 * 判断执行器是否已经关闭
13 */
14 boolean isShutdown();
15 /**
16 * 关闭后所有任务是否都已完成
17 */
18 boolean isTerminated();
19 /**
20 * 中断
21 */
22 boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
23 throws InterruptedException;
24 /**
25 * 提交一个Callable任务
26 */
27 <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
28 /**
29 * 提交一个Runable任务,result要返回的结果
30 */
31 <T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result);
32 /**
33 * 提交一个任务
34 */
35 Future<?> submit(Runnable task);
36 /**
37 * 执行所有给定的任务,当所有任务完成,返回保持任务状态和结果的Future列表
38 */
39 <T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
40 throws InterruptedException;
41 /**
42 * 执行给定的任务,当所有任务完成或超时期满时(无论哪个首先发生),返回保持任务状态和结果的 Future 列表。
43 */
44 <T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
45 long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
46 throws InterruptedException;
47 /**
48 * 执行给定的任务,如果某个任务已成功完成(也就是未抛出异常),则返回其结果。
49 */
50 <T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
51 throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
52 /**
53 * 执行给定的任务,如果在给定的超时期满前某个任务已成功完成(也就是未抛出异常),则返回其结果。
54 */
55 <T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
56 long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
57 throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
58 }
ExecutorService接口继承自Executor接口,定义了终止、提交任务、跟踪任务返回结果等方法。
ExecutorService涉及到Runnable、Callable、Future接口,这些接口的具体内容如下。
1 // 实现Runnable接口的类将被Thread执行,表示一个基本的任务
2 public interface Runnable {
3 // run方法就是它所有的内容,就是实际执行的任务
4 public abstract void run();
5 }
6 // Callable同样是任务,与Runnable接口的区别在于它接收泛型,同时它执行任务后带有返回内容
7 public interface Callable<V> {
8 // 相对于run方法的带有返回值的call方法
9 V call() throws Exception;
10 }
 Future
Future ExecutorService有一个子接口ScheduledExecutorService和一个抽象实现类AbstractExecutorService。
ScheduledExecutorService
1 // 可以安排指定时间或周期性的执行任务的ExecutorService
2 public interface ScheduledExecutorService extends ExecutorService {
3 /**
4 * 在指定延迟后执行一个任务,只执行一次
5 */
6 public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command,
7 long delay, TimeUnit unit);
8 /**
9 * 与上面的方法相同,只是接受的是Callable任务
10 */
11 public <V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable,
12 long delay, TimeUnit unit);
13 /**
14 * 创建并执行一个周期性的任务,在initialDelay延迟后每间隔period个单位执行一次,时间单位都是unit
15 * 每次执行任务的时间点是initialDelay, initialDelay+period, initialDelay + 2 * period...
16 */
17 public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
18 long initialDelay,
19 long period,
20 TimeUnit unit);
21 /**
22 * 创建并执行一个周期性的任务,在initialDelay延迟后开始执行,在执行结束后再延迟delay个单位开始执行下一次任务,时间单位都是unit
23 * 每次执行任务的时间点是initialDelay, initialDelay+(任务运行时间+delay), initialDelay + 2 * (任务运行时间+delay)...
24 */
25 public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command,
26 long initialDelay,
27 long delay,
28 TimeUnit unit);
29 }
ScheduledExecutorService定义了四个方法,已经在上面给出基本的解释。ScheduledExecutorService有 两个实现类,分别是DelegatedScheduledExecutorService和ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor,将 在后面介绍。还需要解释的是ScheduledFuture。
ScheduledFuture继承自Future和Delayed接口,自身没有添加方法。Delayed接口定义了一个获取剩余延迟的方法。
AbstractExecutorService
1 // 提供ExecutorService的默认实现
2 public abstract class AbstractExecutorService implements ExecutorService {
3 /*
4 * 为指定的Runnable和value构造一个FutureTask,value表示默认被返回的Future
5 */
6 protected <T> RunnableFuture<T> newTaskFor(Runnable runnable, T value) {
7 return new FutureTask<T>(runnable, value);
8 }
9 /*
10 * 为指定的Callable创建一个FutureTask
11 */
12 protected <T> RunnableFuture<T> newTaskFor(Callable<T> callable) {
13 return new FutureTask<T>(callable);
14 }
15 /*
16 * 提交Runnable任务
17 */
18 public Future<?> submit(Runnable task) {
19 if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException();
20 // 通过newTaskFor方法构造RunnableFuture,默认的返回值是null
21 RunnableFuture<Object> ftask = newTaskFor(task, null);
22 // 调用具体实现的execute方法
23 execute(ftask);
24 return ftask;
25 }
26 /*
27 * 提交Runnable任务
28 */
29 public <T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result) {
30 if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException();
31 // 通过newTaskFor方法构造RunnableFuture,默认的返回值是result
32 RunnableFuture<T> ftask = newTaskFor(task, result);
33 execute(ftask);
34 return ftask;
35 }
36 /*
37 * 提交Callable任务
38 */
39 public <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task) {
40 if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException();
41 RunnableFuture<T> ftask = newTaskFor(task);
42 execute(ftask);
43 return ftask;
44 }
45
46 /*
47 * doInvokeAny的具体实现(核心内容),其它几个方法都是重载方法,都对这个方法进行调用
48 * tasks 是被执行的任务集,timed标志是否定时的,nanos表示定时的情况下执行任务的限制时间
49 */
50 private <T> T doInvokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
51 boolean timed, long nanos)
52 throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
53 // tasks空判断
54 if (tasks == null)
55 throw new NullPointerException();
56 // 任务数量
57 int ntasks = tasks.size();
58 if (ntasks == 0)
59 throw new IllegalArgumentException();
60 // 创建对应数量的Future返回集
61 List<Future<T>> futures= new ArrayList<Future<T>>(ntasks);
62 ExecutorCompletionService<T> ecs =
63 new ExecutorCompletionService<T>(this);
64 try {
65 // 执行异常
66 ExecutionException ee = null;
67 // System.nanoTime()根据系统计时器当回当前的纳秒值
68 long lastTime = (timed)? System.nanoTime() : 0;
69 // 获取任务集的遍历器
70 Iterator<? extends Callable<T>> it = tasks.iterator();
71
72 // 向执行器ExecutorCompletionService提交一个任务,并将结果加入futures中
73 futures.add(ecs.submit(it.next
74 // 修改任务计数器
75 --ntasks;
76 // 活跃任务计数器
77 int active = 1;
78 for (;;) {
79 // 获取并移除代表已完成任务的Future,如果不存在,返回null
80 Future<T> f = ecs.poll();
81 if (f == null) {
82 // 没有任务完成,且任务集中还有未提交的任务
83 if (ntasks > 0) {
84 // 剩余任务计数器减1
85 --ntasks;
86 // 提交任务并添加结果
87 futures.add(ecs.submit(it.next()));
88 // 活跃任务计数器加1
89 ++active;
90 }
91 // 没有剩余任务,且没有活跃任务(所有任务可能都会取消),跳过这一次循环
92 else if (active == 0)
93 break;
94 else if (timed) {
95 // 获取并移除代表已完成任务的Future,如果不存在,会等待nanos指定的纳秒数
96 f = ecs.poll(nanos, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
97 if (f == null)
98 throw new TimeoutException();
99 // 计算剩余可用时间
100 long now = System.nanoTime();
101 nanos -= now - lastTime;
102 lastTime = now;
103 }
104 else
105 // 获取并移除表示下一个已完成任务的未来,等待,如果目前不存在。
106 // 执行到这一步说明已经没有任务任务可以提交,只能等待某一个任务的返回
107 f = ecs.take();
108 }
109 // f不为空说明有一个任务完成了
110 if (f != null) {
111 // 已完成一个任务,所以活跃任务计数减1
112 --active;
113 try {
114 // 返回该任务的结果
115 return f.get();
116 } catch (InterruptedException ie) {
117 throw ie;
118 } catch (ExecutionException eex) {
119 ee = eex;
120 } catch (RuntimeException rex) {
121 ee = new ExecutionException(rex);
122 }
123 }
124 }
125 // 如果没有成功返回结果则抛出异常
126 if (ee == null)
127 ee = new ExecutionException();
128 throw ee;
129
130 } finally {
131 // 无论执行中发生异常还是顺利结束,都将取消剩余未执行的任务
132 for (Future<T> f : futures)
133 f.cancel(true);
134 }
135 }
136
137 public <T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
138 throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
139 try {
140 // 非定时任务的doInvokeAny调用
141 return doInvokeAny(tasks, false, 0);
142 } catch (TimeoutException cannotHappen) {
143 assert false;
144 return null;
145 }
146 }
147 // 定时任务的invokeAny调用,timeout表示超时时间,unit表示时间单位
148 public <T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
149 long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
150 throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
151 return doInvokeAny(tasks, true, unit.toNanos(timeout));
152 }
153 // 无超时设置的invokeAll方法
154 public <T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
155 throws InterruptedException {
156 // 空任务判断
157 if (tasks == null)
158 throw new NullPointerException();
159 // 创建大小为任务数量的结果集
160 List<Future<T>> futures = new ArrayList<Future<T>>(tasks.size());
161 // 是否完成所有任务的标记
162 boolean done = false;
163 try {
164 // 遍历并执行任务
165 for (Callable<T> t : tasks) {
166 RunnableFuture<T> f = newTaskFor(t);
167 futures.add(f);
168 execute(f);
169 }
170 // 遍历结果集
171 for (Future<T> f : futures) {
172 // 如果某个任务没完成,通过f调用get()方法
173 if (!f.isDone()) {
174 try {
175 // get方法等待计算完成,然后获取结果(会等待)。所以调用get后任务就会完成计算,否则会等待
176 f.get();
177 } catch (CancellationException ignore) {
178 } catch (ExecutionException ignore) {
179 }
180 }
181 }
182 // 标志所有任务执行完成
183 done = true;
184 // 返回结果
185 return futures;
186 } finally {
187 // 假如没有完成所有任务(可能是发生异常等情况),将任务取消
188 if (!done)
189 for (Future<T> f : futures)
190 f.cancel(true);
191 }
192 }
193 // 超时设置的invokeAll方法
194 public <T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
195 long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
196 throws InterruptedException {
197 // 需要执行的任务集为空或时间单位为空,抛出异常
198 if (tasks == null || unit == null)
199 throw new NullPointerException();
200 // 将超时时间转为纳秒单位
201 long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
202 // 创建任务结果集
203 List<Future<T>> futures = new ArrayList<Future<T>>(tasks.size());
204 // 是否全部完成的标志
205 boolean done = false;
206 try {
207 // 遍历tasks,将任务转为RunnableFuture
208 for (Callable<T> t : tasks)
209 futures.add(newTaskFor(t));
210 // 记录当前时间(单位是纳秒)
211 long lastTime = System.nanoTime();
212 // 获取迭代器
213 Iterator<Future<T>> it = futures.iterator();
214 // 遍历
215 while (it.hasNext()) {
216 // 执行任务
217 execute((Runnable)(it.next()));
218 // 记录当前时间
219 long now = System.nanoTime();
220 // 计算剩余可用时间
221 nanos -= now - lastTime;
222 // 更新上一次执行时间
223 lastTime = now;
224 // 超时,返回保存任务状态的结果集
225 if (nanos <= 0)
226 return futures;
227 }
228
229 for (Future<T> f : futures) {
230 // 如果有任务没完成
231 if (!f.isDone()) {
232 // 时间已经用完,返回保存任务状态的结果集
233 if (nanos <= 0)
234 return futures;
235 try {
236 // 获取计算结果,最多等待给定的时间nanos,单位是纳秒
237 f.get(nanos, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
238 } catch (CancellationException ignore) {
239 } catch (ExecutionException ignore) {
240 } catch (TimeoutException toe) {
241 return futures;
242 }
243 // 计算可用时间
244 long now = System.nanoTime();
245 nanos -= now - lastTime;
246 lastTime = now;
247 }
248 }
249 // 修改是否全部完成的标记
250 done = true;
251 // 返回结果集
252 return futures;
253 } finally {
254 // 假如没有完成所有任务(可能是时间已经用完、发生异常等情况),将任务取消
255 if (!done)
256 for (Future<T> f : futures)
257 f.cancel(true);
258 }
259 }
260 }
AbstractExecutor实现了ExecutorService接口的部分方法。具体代码的分析在上面已经给出。
AbstractExecutor有两个子类:DelegatedExecutorService、ThreadPoolExecutor。将在后面介绍。
下面是AbstractExecutor中涉及到的RunnableFuture、FutureTask、ExecutorCompletionService。
RunnableFuture继承自Future和Runnable,只有一个run()方法(Runnable中已经有一个run方法了,为什么 RunnableFuture还要重新写一个run方法呢?求高手指教)。RunnableFuture接口看上去就像是Future和Runnable 两个接口的组合。
FutureTask实现了RunnableFuture接口,除了实现了Future和Runnable中的方法外,它还有自己的方法和一个内部类Sync。
ExecutorCompletionService实现了CompletionService接口,将结果从复杂的一部分物种解耦出来。这些内容后续会介绍,不过这里先介绍框架中的其它内容,弄清整体框架。
下面看继承自AbstractExecutorService的ThreadPoolExecutor。
ThreadPoolExecutor
 ThreadPoolExecutor(好长)
ThreadPoolExecutor(好长) 可以参考http://xtu-xiaoxin.iteye.com/blog/647744
从上面的框架结构图中可以可以看出剩下的就是ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor和Executors。Executors是一个工具类,提供一些工厂和实用方法。
下面看ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor,它继承自ThreadPoolExecutor并实现了ScheduledExecutorService接口。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 在代码中都加了注释,我想大致能解释清楚吧。
Executor涉及的类还是比较多的,到此为止剩下的还有Executors
Executors
Executors中所定义的 Executor、ExecutorService、ScheduledExecutorService、ThreadFactory 和 Callable 类的工厂和实用方法。此类支持以下各种方法:
- 创建并返回设置有常用配置字符串的
ExecutorService的方法。 - 创建并返回设置有常用配置字符串的
ScheduledExecutorService的方法。 - 创建并返回“包装的”ExecutorService 方法,它通过使特定于实现的方法不可访问来禁用重新配置。
- 创建并返回
ThreadFactory的方法,它可将新创建的线程设置为已知的状态。 - 创建并返回非闭包形式的
Callable的方法,这样可将其用于需要 Callable 的执行方法中。
Executors提供的都是工具形式的方法,所以都是static的,并且这个类也没有必要实例化,所以它的构造方法时private的。下面主要看一下几个内部类。
RunnableAdapter
1 static final class RunnableAdapter<T> implements Callable<T> {
2 final Runnable task;
3 final T result;
4 RunnableAdapter(Runnable task, T result) {
5 this.task = task;
6 this.result = result;
7 }
8 public T call() {
9 task.run();
10 return result;
11 }
12 }
适配器。以Callable的形式执行Runnable并且返回给定的result。
PrivilegedCallable
1 static final class PrivilegedCallable<T> implements Callable<T> {
2 private final AccessControlContext acc;
3 private final Callable<T> task;
4 private T result;
5 private Exception exception;
6 PrivilegedCallable(Callable<T> task) {
7 this.task = task;
8 this.acc = AccessController.getContext();
9 }
10
11 public T call() throws Exception {
12 AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<T>() {
13 public T run() {
14 try {
15 result = task.call();
16 } catch (Exception ex) {
17 exception = ex;
18 }
19 return null;
20 }
21 }, acc);
22 if (exception != null)
23 throw exception;
24 else
25 return result;
26 }
27 }
在访问控制下运行的Callable。涉及到Java.security包中的内容。
PrivilegedCallableUsingCurrentClassLoader类与上面的PrivilegedCallable类似,只是使用的是CurrentClassLoader。
DefaultThreadFactory
1 static class DefaultThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
2 static final AtomicInteger poolNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
3 final ThreadGroup group;
4 final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
5 final String namePrefix;
6
7 DefaultThreadFactory() {
8 SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager();
9 group = (s != null)? s.getThreadGroup() :
10 Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
11 namePrefix = "pool-" +
12 poolNumber.getAndIncrement() +
13 "-thread-";
14 }
15
16 public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
17 // 调用Thread构造方法创建线程
18 Thread t = new Thread(group, r,
19 namePrefix + threadNumber.getAndIncrement(),
20 0);
21 // 取消守护线程设置
22 if (t.isDaemon())
23 t.setDaemon(false);
24 // 设置默认优先级
25 if (t.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY)
26 t.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
27 return t;
28 }
29 }
DefaultThreadFactory 是默认的线程工程,提供创建线程的方法。
PrivilegedThreadFactory继承自DefaultThreadFactory,区别在于线程执行的run方法指定了classLoader并受到权限的控制。
DelegatedExecutorService继承自AbstractExecutorService,是一个包装类,暴露ExecutorService的方法。
DelegatedScheduledExecutorService继承自DelegatedExecutorService,实现了 ScheduledExecutorService接口。它也是一个包装类,公开ScheduledExecutorService方法。
