mybatis源码分析(四) mybatis与spring事务管理分析
一丶从jdbc的角度理解什么是事务
从mysql获取一个连接之后, 默认是自动提交, 即执行完sql之后, 就会提交事务. 这种事务的范围是一条sql语句.
将该连接设置非自动提交, 可以执行多条sql语句, 然后由程序决定是提交事务, 还是回滚事务. 这也是我们常说的事务.
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection(); // connection.setTransactionIsolation(level.getLevel()); //设置事务隔离级别 // 设置是否自动提交, 如果不是自动提交, 则是"开启"事务 connection.setAutoCommit(desiredAutoCommit); // connection预编译statement, 并执行sql Statement stmt=connection.preparedStatement(); stmt.execute(sql); // 提交事务, 或者回滚 connection.commit(); //connection.rollback();
从jdbc使用事务的角度来看, 事务主要是围绕connection展开的, 所以谁可获得connection, 即可控制事务.
二丶mybatis是如何使用事务的
mybatis将jdbc中的事务操作抽象封装成Transaction,用于管理connection的生命周期--创建, 准备, 提交/回滚 和关闭.
/** * Wraps a database connection. * Handles the connection lifecycle that comprises: its creation, preparation, commit/rollback and close. * * @author Clinton Begin */ public interface Transaction { /** * Retrieve inner database connection. * @return DataBase connection * @throws SQLException */ Connection getConnection() throws SQLException; /** * Commit inner database connection. * @throws SQLException */ void commit() throws SQLException; /** * Rollback inner database connection. * @throws SQLException */ void rollback() throws SQLException; /** * Close inner database connection. * @throws SQLException */ void close() throws SQLException; /** * Get transaction timeout if set. * @throws SQLException */ Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException; }
mybatis提供了两种事务实现,一种是完全由jdbc实现的事务JdbcTransaction,包括实现提交和回滚.一种是供容器管理整个生命周期的事务ManagedTransaction,其中将忽略提交和回滚事务的请求, 将提交和回滚事务由容器实现, 但其实这种事务很少用.
JdbcTransaction:

public class JdbcTransaction implements Transaction { private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(JdbcTransaction.class); protected Connection connection; protected DataSource dataSource; protected TransactionIsolationLevel level; protected boolean autoCommit; public JdbcTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel desiredLevel, boolean desiredAutoCommit) { dataSource = ds; level = desiredLevel; autoCommit = desiredAutoCommit; } public JdbcTransaction(Connection connection) { this.connection = connection; } @Override public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { if (connection == null) { openConnection(); } return connection; } @Override public void commit() throws SQLException { if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Committing JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]"); } connection.commit(); } } @Override public void rollback() throws SQLException { if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Rolling back JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]"); } connection.rollback(); } } @Override public void close() throws SQLException { if (connection != null) { resetAutoCommit(); if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Closing JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]"); } connection.close(); } } protected void setDesiredAutoCommit(boolean desiredAutoCommit) { try { if (connection.getAutoCommit() != desiredAutoCommit) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Setting autocommit to " + desiredAutoCommit + " on JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]"); } connection.setAutoCommit(desiredAutoCommit); } } catch (SQLException e) { // Only a very poorly implemented driver would fail here, // and there's not much we can do about that. throw new TransactionException("Error configuring AutoCommit. " + "Your driver may not support getAutoCommit() or setAutoCommit(). " + "Requested setting: " + desiredAutoCommit + ". Cause: " + e, e); } } protected void resetAutoCommit() { try { if (!connection.getAutoCommit()) { // MyBatis does not call commit/rollback on a connection if just selects were performed. // Some databases start transactions with select statements // and they mandate a commit/rollback before closing the connection. // A workaround is setting the autocommit to true before closing the connection. // Sybase throws an exception here. if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Resetting autocommit to true on JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]"); } connection.setAutoCommit(true); } } catch (SQLException e) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Error resetting autocommit to true " + "before closing the connection. Cause: " + e); } } } protected void openConnection() throws SQLException { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection"); } connection = dataSource.getConnection(); if (level != null) { connection.setTransactionIsolation(level.getLevel()); } setDesiredAutoCommit(autoCommit); } @Override public Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException { return null; } }
mybatis事务执行流程:
1. 由于mybatis将事务抽取成一个接口, 便于管理, 所以可以在配置中配置事务管理的实现
2. 解析配置, 将事务管理对象, 保存到Configuration中
3. SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession时, 将会同时注入tx对象
4. SqlSession执行sql语句时, 会委派给Executor执行, Executor处理主要的逻辑之外, 事务将会委派给事务对象处理, 如从事务对象中获取连接, 使用事务对象提交事务.
//BaseExecutor // 在执行器里获取Connection , 最后是委派给Transaction获取, // 事务管理, 即是Connection是否设置自动提交, 以及将事务的回滚调用交给事务管理器管理 protected Connection getConnection(Log statementLog) throws SQLException { Connection connection = transaction.getConnection(); if (statementLog.isDebugEnabled()) { return ConnectionLogger.newInstance(connection, statementLog, queryStack); } else { return connection; } }
Transaction封装了connection,然后在transaction内部封装调用connection的操作,如提供不同的Transaction, 来管理connection的生命周期.
三丶spring是如何使用事务的
1) 入口
在配置了DataSourceProperties属性之后, 会创建DataSource, 之后会创建DataSourceTransactionManager作为事务管理器

org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration
@Configuration @ConditionalOnClass({ JdbcTemplate.class, PlatformTransactionManager.class }) @AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE) @EnableConfigurationProperties(DataSourceProperties.class) public class DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration { @Configuration @ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(DataSource.class) static class DataSourceTransactionManagerConfiguration { private final DataSource dataSource; private final TransactionManagerCustomizers transactionManagerCustomizers; DataSourceTransactionManagerConfiguration(DataSource dataSource, ObjectProvider<TransactionManagerCustomizers> transactionManagerCustomizers) { this.dataSource = dataSource; this.transactionManagerCustomizers = transactionManagerCustomizers.getIfAvailable(); } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(PlatformTransactionManager.class) public DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSourceProperties properties) {
// 默认使用DataSourceTransactionManager, 从使用的角度来说,具有通用性 DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager(this.dataSource); if (this.transactionManagerCustomizers != null) { this.transactionManagerCustomizers.customize(transactionManager); } return transactionManager; } } }
DataSourceTransactionManager继承于AbstractPlatformTransactionManager,而AbstractPlatformTransactionManager位于spring的tx子项目中 
2) spring-tx子项目
该项目最主要是用于实现事务管理.
2.1) 最核心接口就是PlatformTransactionManager接口, 定义了事务管理器.
a) #getTransaction(TransactionDefinition): TransactionStatus
Return a currently active transaction or create a new one, according to the specified propagation behavior.
b) #commit(TransactionStatus): void
Commit the given transaction, with regard to its status. If the transaction has been marked rollback-only programmatically, perform a rollback.
c) #rollback(TransactionStatus): void
Perform a rollback of the given transaction.
--更详细的文档则需要看源码或者API文档

2.2) TransactionDefinition 定义了事务的传播行为, 隔离界别, 事务超时时间等

2.3)TransactionStatus 定义了事务的状态, 以便于在提交事务或者回滚事务时决定如何后续行为.

3)使用@Transactional注解声明事务
声明式事务,s是基于AOP实现的.Spring会对使用@Transactinal注解声明的方法进行动态代理, 生成使用org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionInterceptor增强对应方法的对象..
3.1) 事务切面方法实现
// org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport
@Override @Nullable public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable { // Work out the target class: may be {@code null}. // The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class // as well as the method, which may be from an interface. Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null); // Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction... return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, invocation::proceed); }
/** * General delegate for around-advice-based subclasses, delegating to several other template * methods on this class. Able to handle {@link CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager} * as well as regular {@link PlatformTransactionManager} implementations. * @param method the Method being invoked * @param targetClass the target class that we're invoking the method on * @param invocation the callback to use for proceeding with the target invocation * @return the return value of the method, if any * @throws Throwable propagated from the target invocation */ @Nullable protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass, final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable { // If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional. TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource(); final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null); final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr); final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr); if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) { // Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls. TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification); Object retVal; try { // This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain. // This will normally result in a target object being invoked. retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation(); } catch (Throwable ex) { // target invocation exception completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex); throw ex; } finally { cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo); } commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo); return retVal; } else { final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder(); // It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in. try { Object result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) tm).execute(txAttr, status -> { TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status); try { return invocation.proceedWithInvocation(); } catch (Throwable ex) { if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) { // A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback. if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) { throw (RuntimeException) ex; } else { throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex); } } else { // A normal return value: will lead to a commit. throwableHolder.throwable = ex; return null; } } finally { cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo); } }); // Check result state: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow. if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) { throw throwableHolder.throwable; } return result; } catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) { throw ex.getCause(); } catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) { if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) { logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable); ex2.initApplicationException(throwableHolder.throwable); } throw ex2; } catch (Throwable ex2) { if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) { logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable); } throw ex2; } } }
/** * Create a transaction if necessary based on the given TransactionAttribute. * <p>Allows callers to perform custom TransactionAttribute lookups through * the TransactionAttributeSource. * @param txAttr the TransactionAttribute (may be {@code null}) * @param joinpointIdentification the fully qualified method name * (used for monitoring and logging purposes) * @return a TransactionInfo object, whether or not a transaction was created. * The {@code hasTransaction()} method on TransactionInfo can be used to * tell if there was a transaction created. * @see #getTransactionAttributeSource() */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") protected TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm, @Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, final String joinpointIdentification) { // If no name specified, apply method identification as transaction name. if (txAttr != null && txAttr.getName() == null) { txAttr = new DelegatingTransactionAttribute(txAttr) { @Override public String getName() { return joinpointIdentification; } }; } TransactionStatus status = null; if (txAttr != null) { if (tm != null) { status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr); // 这里使用了配置的PlatformTransactionManager获取事务状态 } else { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Skipping transactional joinpoint [" + joinpointIdentification + "] because no transaction manager has been configured"); } } } return prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status); }
3.2) 查看springboot自动配置DataSourceTransactionManager实现
@Override protected Object doGetTransaction() { DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = new DataSourceTransactionObject(); txObject.setSavepointAllowed(isNestedTransactionAllowed()); ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(obtainDataSource()); txObject.setConnectionHolder(conHolder, false); return txObject; // 刚开始获取事务时, 由于没有开启事务, 所以为null }
/** * This implementation sets the isolation level but ignores the timeout. */ @Override protected void doBegin(Object transaction, TransactionDefinition definition) { DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction; Connection con = null; try { if (!txObject.hasConnectionHolder() || txObject.getConnectionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) { // 从数据源中获取connection Connection newCon = obtainDataSource().getConnection(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Acquired Connection [" + newCon + "] for JDBC transaction"); } txObject.setConnectionHolder(new ConnectionHolder(newCon), true); } txObject.getConnectionHolder().setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true); con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection(); Integer previousIsolationLevel = DataSourceUtils.prepareConnectionForTransaction(con, definition); txObject.setPreviousIsolationLevel(previousIsolationLevel); // Switch to manual commit if necessary. This is very expensive in some JDBC drivers, // so we don't want to do it unnecessarily (for example if we've explicitly // configured the connection pool to set it already). if (con.getAutoCommit()) { txObject.setMustRestoreAutoCommit(true); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Switching JDBC Connection [" + con + "] to manual commit"); } con.setAutoCommit(false); } prepareTransactionalConnection(con, definition); txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTransactionActive(true); int timeout = determineTimeout(definition); if (timeout != TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) { txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTimeoutInSeconds(timeout); } // Bind the connection holder to the thread. if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
// 将Connection和datasource关联, 交由事务同步管理器保存管理, 使用ThreadLocal隔离
// TranscationSynchronizationManager也是Spring和mybatis-spring共同合作管理事务的桥梁
// ThreadLocal与当前线程绑定, 即线程隔离, 并且使用了同一个DataSource作为key, 可以获取到同一个ConnectionHolder
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(obtainDataSource(), txObject.getConnectionHolder()); } } catch (Throwable ex) { if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) { DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, obtainDataSource()); txObject.setConnectionHolder(null, false); } throw new CannotCreateTransactionException("Could not open JDBC Connection for transaction", ex); } }
四丶mybatis和spring的事务是如何结合使用的
mybatis-spring项目,用于将Spring和mybatis整合
mybatis源码分析(三) mybatis-spring整合源码分析
mybatis-spring整合,需要配置SqlSessionFactoryBean构建生成SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactoryBean#buildSqlSessionFactory()
//如果为空,则使用默认的SpringManagedTransactionFactory生成SpringManagedTransaction targetConfiguration.setEnvironment(new Environment(this.environment, this.transactionFactory == null ? new SpringManagedTransactionFactory() : this.transactionFactory, this.dataSource));
SpringManagedTransaction#openConnection()
/** * Gets a connection from Spring transaction manager and discovers if this * {@code Transaction} should manage connection or let it to Spring. * <p> * It also reads autocommit setting because when using Spring Transaction MyBatis * thinks that autocommit is always false and will always call commit/rollback * so we need to no-op that calls. */ private void openConnection() throws SQLException {
// 从Spring transaction manager获取之前由Spring获取的connection this.connection = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(this.dataSource); this.autoCommit = this.connection.getAutoCommit(); this.isConnectionTransactional = DataSourceUtils.isConnectionTransactional(this.connection, this.dataSource); LOGGER.debug(() -> "JDBC Connection [" + this.connection + "] will" + (this.isConnectionTransactional ? " " : " not ") + "be managed by Spring"); }
有本文第二节可知, mybatis执行事务相关操作, 如获取Connection, 使用connection执行多条sql, 使用connection提交事务或者回滚事务, 都是委派给Transacation执行的,
要想将sql语句的执行由mybatis执行, 事务的提交或者回滚操作由Spring控制, 两者需要关联使用同一个connection, 在不同的方法中调用connection的相关方法操作, (所以, Spring并没有直接使用mybatis sqlSession中提供的提交或者回滚方法) . 如何安全的获取同一个connection?这就需要使用TransactionSynchronizationManager
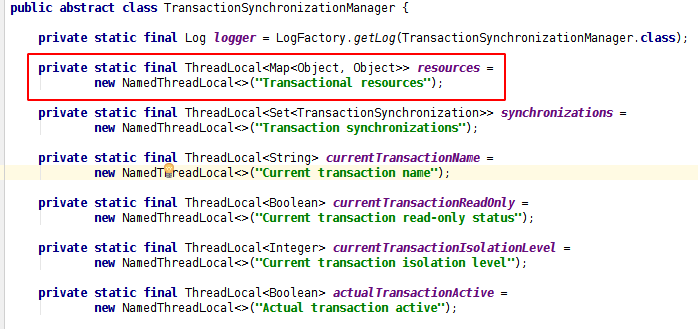
ThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>> resources
保存connection资源,的 key为DataSource, value为ConnectionHolder
(所以, 事务只支持在一个数据源中, 0.0)
学习资料:
