1、Cluster Health 集群状态
curl 'localhost:9200/_cat/health?v'

yellow代表分片副本确实,因为我们现在只有一台机器。
curl 'localhost:9200/_cat/nodes?v'

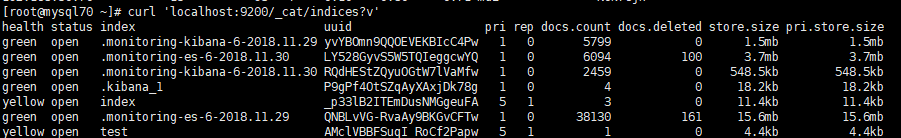
2、List All Indices 查询所有的索引
curl 'localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v'
3、Create an Index 创建索引
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/customer?pretty'
这个pretty的意思格式化返回的json,大家可以去掉试试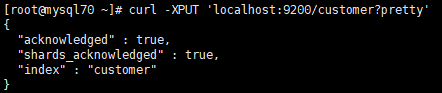
curl 'localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v'
health | index | pri | rep | docs.count | docs.deleted | store.size | pri.store.size
yellow | customer | 5 | 1 | 0 |0 | 495b | 495b4、Index and Query 索引文档操作
创建或者更新:
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -XPUT 'localhost:9200/customer/external/1?pretty' -d' { "name":"腊肉" }'
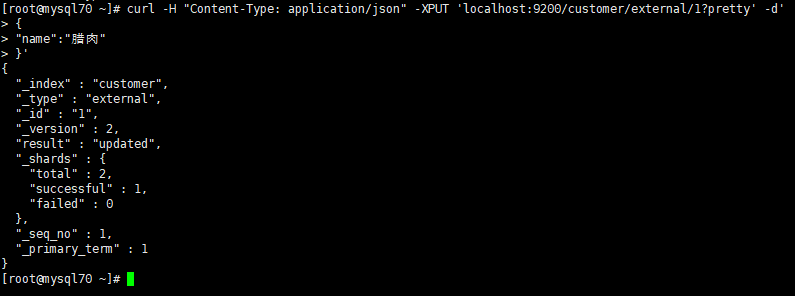
小提示:6.0的版本不允许一个index下面有多个type,并且官方说是在接下来的7.0版本中会删掉type
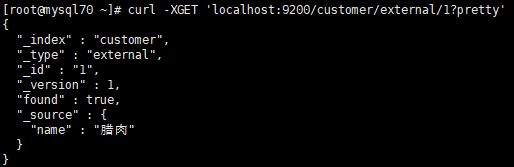
查询:
curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/customer/external/1?pretty'
更新文档
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/customer/external/1/_update?pretty' -d' { "doc": { "name": "Jane Doe" } }'
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/customer/external/1/_update?pretty' -d ' { "doc": { "name": "Jane Doe", "age": 20 } }'Script:
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/customer/external/1/_update?pretty' -d ' { "script" : "ctx._source.age += 5" }'Error:
{
"error" : {
"root_cause" : [ {
"type" : "remote_transport_exception",
"reason" : "[Angelica Jones][127.0.0.1:9300][indices:data/write/update[s]]"
} ],
"type" : "illegal_argument_exception",
"reason" : "failed to execute script",
"caused_by" : {
"type" : "script_exception",
"reason" : "scripts of type [inline], operation [update] and lang [groovy] are disabled"
}
},
"status" : 400
}Solution:elasticsearch.yml
script.inline: on
script.indexed: on删除文档
curl -XDELETE 'localhost:9200/customer/external/2?pretty’The delete-by-query plugin can delete all documents matching a specific query.
XPUT与XPOST的不同
PUT是幂等方法,而POST并不是。
PUT用于更新操作,POST用于新增操作比较合适。
PUT,DELETE操作是幂等的,所谓幂等就是指不管进行多少次操作,结果都一样。
比如,我用PUT修改一篇文章,然后在做同样的操作,每次操作后的结果并没有不同,DELETE也是一样。
POST操作不是幂等,比如常见的POST重复加载问题:当我们多次发出同样的POST请求后,其结果是创建出了若干的资源。
还有一点需要注意的是,创建操作可以使用POST,也可以使用PUT。区别在于POST是作用在一个集合资源之上的(/articles),而PUT操作是作用在一个具体资源之上的(/articles/123),比如说很多资源使用数据库自增主键作为标识信息,而创建的资源的标识信息到底是什么只能由服务端提供,这个时候就必须使用POST。
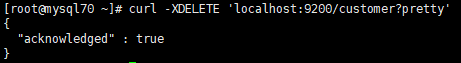
5、Delete an Index 删除索引
curl -XDELETE 'localhost:9200/customer?pretty'
curl 'localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v'
health | index | pri | rep | docs.count | docs.deleted | store.size | pri.store.sizecurl -X :///
6、批量操作
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/customer/external/_bulk?pretty' -d
'{"index":{"_id":"1”}}
{"name": "John Doe” }
{"index":{"_id":"2”}}
{"name": "Jane Doe" } ‘Delete:
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/customer/external/_bulk?pretty' -d
' {"update":{"_id":"1”}}
{
"doc": { "name": "John Doe becomes Jane Doe" }
}
{"delete":{"_id":"2"}} ‘7、The Search API
curl 'localhost:9200/customer/_search?q=*&pretty’-
took –
time in milliseconds for Elasticsearch to execute the search
-
timed_out –
tells us if the search timed out or not
-
_shards –
tells us how many shards were searched, as well as a count of the successful/failed searched shards
-
hits –
search results
-
hits.total –
total number of documents matching our search criteria
-
hits.hits –
actual array of search results (defaults to first 10 documents)
-
_score and max_score -
ignore these fields for now
XPOST:
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/customer/_search?pretty' -d ' { "query": { "match_all": {} } }'NO CURSOR DON’T LIKE SQL
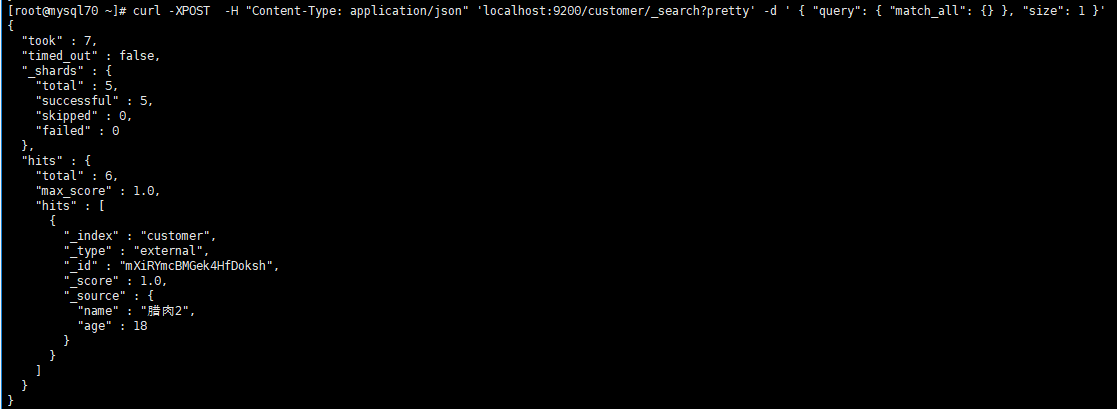
8、查询语句
curl -XPOST -H "Content-Type: application/json" 'localhost:9200/customer/_search?pretty' -d ' { "query": { "match_all": {} }, "size": 1 }'
curl -XPOST -H "Content-Type: application/json" 'localhost:9200/customer/_search?pretty' -d ' { "query": { "match_all": {} }, "from": 10, "size": 10 }'
curl -XPOST -H "Content-Type: application/json" 'localhost:9200/customer/_search?pretty' -d ' { "query": { "match_all": {} }, "sort": { "balance": { "order": "desc" } } }'
这里size的意思是返回多少条,from是从第几条开始。基础查询
-
Fields:字段
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/customer/_search?pretty' -d ' { "query": { "match_all": {} }, "_source": ["account_number", "balance"] }' -
返回account numbered 为20:
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/customer/_search?pretty' -d ' { "query": { "match": { "account_number": 20 } } }' -
address中包含term "mill" :
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/customer/_search?pretty' -d ' { "query": { "match": { "address": "mill" } } }' -
address中包含term "mill" 或"lane" in the address:
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/customer/_search?pretty' -d ' { "query": { "match": { "address": "mill lane" } } }' -
address中包含phrase "mill lane":
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/customer/_search?pretty' -d ' { "query": { "match_phrase": { "address": "mill lane" } } }'
-
AND
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/bank/_search?pretty' -d ' { "query": { "bool": { "must": [ { "match": { "address": "mill" } }, { "match": { "address": "lane" } } ] } } }' -
OR
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/bank/_search?pretty' -d ' { "query": { "bool": { "should": [ { "match": { "address": "mill" } }, { "match": { "address": "lane" } } ] } } }' -
NOR
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/bank/_search?pretty' -d ' { "query": { "bool": { "must_not": [ { "match": { "address": "mill" } }, { "match": { "address": "lane" } } ] } } }' -
Anybody who is 40 years old but don’t live in ID(aho):
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/bank/_search?pretty' -d ' { "query": { "bool": { "must": [ { "match": { "age": "40" } } ], "must_not": [ { "match": { "state": "ID" } } ] } } }'
Range Query:
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/bank/_search?pretty' -d ' { "query": { "bool": { "must": { "match_all": {} }, "filter": { "range": { "balance": { "gte": 20000, "lte": 30000 } } } } } }'Executing Aggregations聚合
Groups all the accounts by state, and then returns the top 10 (default) states sorted by count descending (also default):
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/bank/_search?pretty' -d '
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_state": {
"terms": {
"field": "state"
}
}
}
}'
SELECT state, COUNT(*) FROM bank GROUP BY state ORDER BY COUNT(*) DESC-
Calculates the average account balance by state:
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/bank/_search?pretty' -d ' { "size": 0, "aggs": { "group_by_state": { "terms": { "field": "state" }, "aggs": { "average_balance": { "avg": { "field": "balance" } } } } } }'
You can nest aggregations inside aggregations arbitrarily to extract pivoted summarizations that you require from your data.
-
Sort on the average balance in descending order:
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/bank/_search?pretty' -d ' { "size": 0, "aggs": { "group_by_state": { "terms": { "field": "state", "order": { "average_balance": "desc" } }, "aggs": { "average_balance": { "avg": { "field": "balance" } } } } } }' -
Group by age brackets (ages 20-29, 30-39, and 40-49), then by gender, and then finally get the average account balance, per age bracket, per gender:
curl -XPOST 'localhost:9200/bank/_search?pretty' -d '
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_age": {
"range": {
"field": "age",
"ranges": [
{
"from": 20,
"to": 30
},
{
"from": 30,
"to": 40
},
{
"from": 40,
"to": 50
}
]
},
"aggs": {
"group_by_gender": {
"terms": {
"field": "gender"
},
"aggs": {
"average_balance": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}'
Reference
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/getting-started.html