import tensorflow as tf
a = 3
# Create a variable.
w = tf.Variable([[0.5,1.0]])
x = tf.Variable([[2.0],[1.0]])
y = tf.matmul(w, x) #Tensor("MatMul:0", shape=(1, 1), dtype=float32)
#variables have to be explicitly initialized before you can run Ops
init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()#全局变量初始化
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
print(y.eval())#打印y的值 [[2.]]
# tensorflow中尽量用float32格式,不要用别的,这样会减少错误
tf.zeros([3, 4], int32) ==> [[0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0]]
# 'tensor' is [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]
tf.zeros_like(tensor) ==> [[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0]]
tf.ones([2, 3], int32) ==> [[1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1]]
# 'tensor' is [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]
tf.ones_like(tensor) ==> [[1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1]]
# Constant 1-D Tensor populated with value list.
tensor = tf.constant([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]) => [1 2 3 4 5 6 7]
# Constant 2-D tensor populated with scalar value -1.
tensor = tf.constant(-1.0, shape=[2, 3]) => [[-1. -1. -1.]
[-1. -1. -1.]]
tf.linspace(10.0, 12.0, 3, name="linspace") => [ 10.0 11.0 12.0]
# 'start' is 3
# 'limit' is 18
# 'delta' is 3
tf.range(start, limit, delta) ==> [3, 6, 9, 12, 15]
#生成2行3列的均值为1,方差为4的高斯分布随机矩阵 norm = tf.random_normal([2, 3], mean=-1, stddev=4) # Shuffle the first dimension of a tensor c = tf.constant([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]) shuff = tf.random_shuffle(c)#洗牌操作 # Each time we run these ops, different results are generated sess = tf.Session() print (sess.run(norm)) print (sess.run(shuff))
结果:
[[-0.30886292 3.11809683 3.29861784] [-7.09597015 -1.89811802 1.75282788]] [[3 4] [5 6] [1 2]]
state = tf.Variable(0)#创建变量0
new_value = tf.add(state, tf.constant(1))#加1操作
update = tf.assign(state, new_value)#将new_value的值赋值给state
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())#将前三行变量初始化
print(sess.run(state))#计算
for _ in range(3):
sess.run(update)
print(sess.run(state))
结果:
0 1 2 3
#tf.train.Saver 保存当前状态到硬盘,以后可以调用
w = tf.Variable([[0.5,1.0]])
x = tf.Variable([[2.0],[1.0]])
y = tf.matmul(w, x)
init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
# Do some work with the model.
# Save the variables to disk.
save_path = saver.save(sess, "C://tensorflow//model//test")
print ("Model saved in file: ", save_path)#Model saved in file: C://tensorflow//model//test
#少用这样方法,最好用tensorflow自己的格式创造
import numpy as np
a = np.zeros((3,3))
ta = tf.convert_to_tensor(a)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run(ta))
结果:
[[ 0. 0. 0.] [ 0. 0. 0.] [ 0. 0. 0.]]
input1 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
input2 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
output = tf.mul(input1, input2)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run([output], feed_dict={input1:[7.], input2:[2.]}))#[array([ 14.], dtype=float32)]
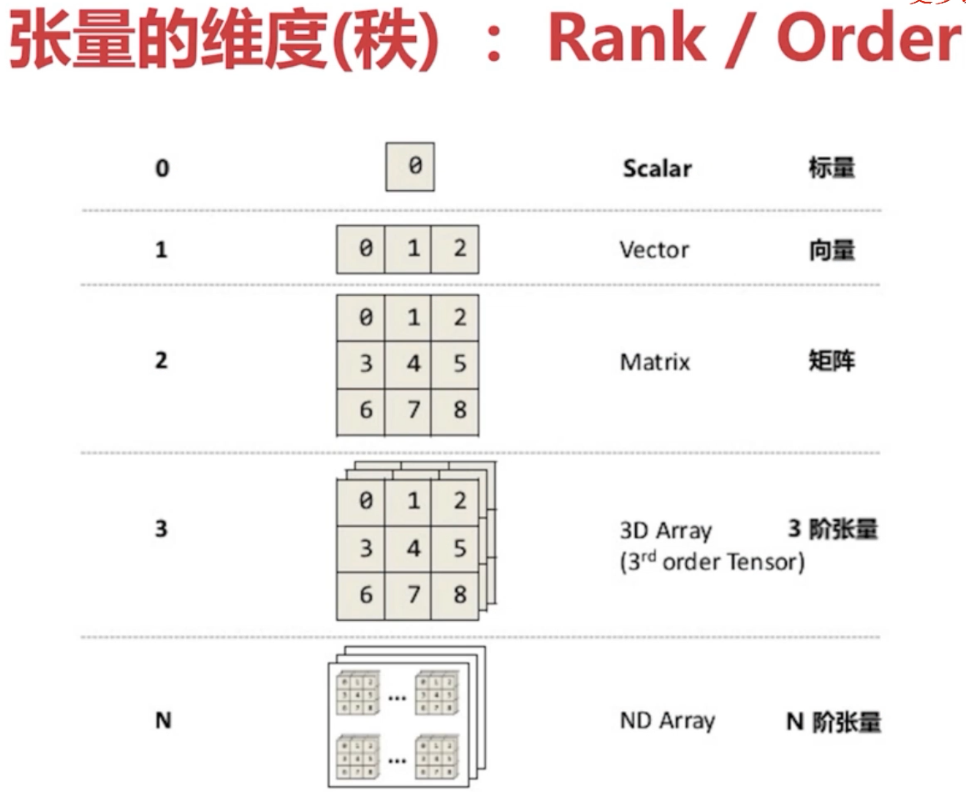
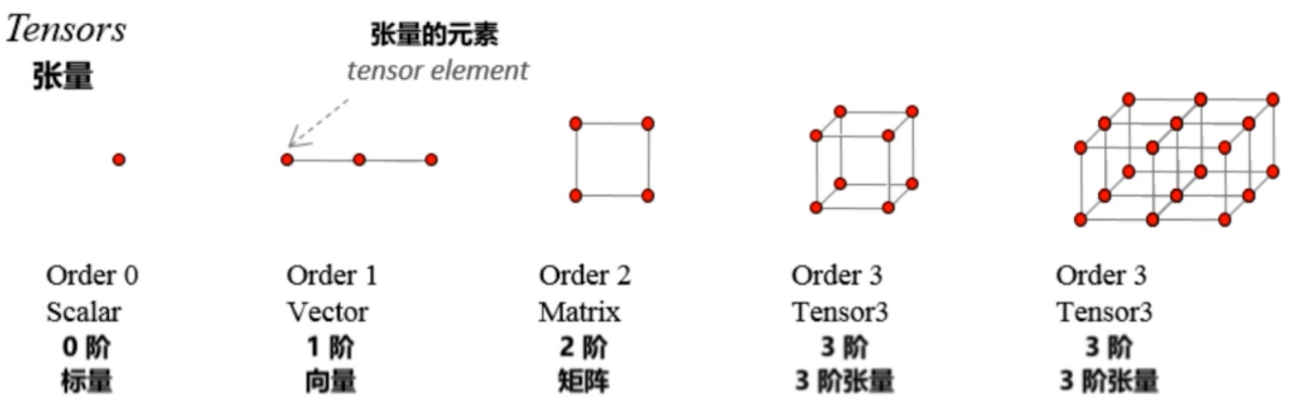
Tensor的属性:
几种Tensor:
- Constant(常量):值不能改变的一种Tensor。tf.constant
- Placeholder(占位符):先占住一个固定的位置,等着你之后往里面添加值的一种Tensor。tf.placeholder
- Variable(变量):值可以改变的一种Tensor。tf.Variable
- SparseTensor(稀疏张量):一种“稀疏”的Tensor,类似线性代数里的稀疏矩阵的概念。tf.SparseTensor
Tensor 表示法: 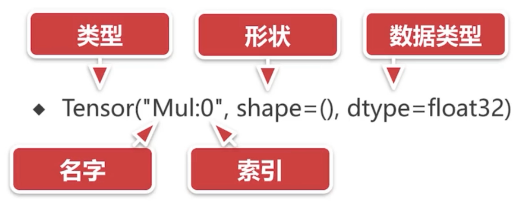
var1 = tf.Variable(4, dtype=tf.int64)
print(var1)#Tensor("Variable/read:0", shape=(), dtype=int64)
var2 = tf.Variable([3, 4])
print(var2)#Tensor("Variable_1/read:0", shape=(2,), dtype=int32)
var3 = tf.Variable([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
print(var3)#Tensor("Variable_2/read:0", shape=(2, 2), dtype=int32)
named_var = tf.Variable([5, 6], name='named_var')
print(named_var)#Tensor("named_var/read:0", shape=(2,), dtype=int32)
const = tf.constant(3)
print(const)#Tensor("Const_1:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
TensorFlow 程序的流程:
1.定义算法的计算图(Graph)结构
2.使用会话(Session)执行图的一部分(计算)
#引入TensorFlow库
import tensorflow as tf
#创建一个常量 Operation(操作)
hw = tf.constant("hello world")
#启动一个Tensorflow的Session(会话)
sess = tf.Session()
#运行Graph(计算图)
print(sess.run(hw))
#关闭Session(会话)
sess.close()
if hw.graph is tf.get_default_graph():#hw的图就是默认的图,不用自己创建,会默认存在
print("The graph of hw is the default graph of the context")
完整的一段示例:
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
# 引入 TensorFlow
import tensorflow as tf
# 创建两个常量 Tensor
const1 = tf.constant([[2, 2]])
const2 = tf.constant([[4],
[4]])
# print(const1)#Tensor("Const_1:0", shape=(1, 2), dtype=int32)
# print(const2)#Tensor("Const_2:0", shape=(2, 1), dtype=int32)
# 张量相乘(multiply 是 相乘 的意思)
multiply = tf.matmul(const1, const2)
# 尝试用 print 输出 multiply 的值
print("sess.run() 之前,尝试输出 multiply 的值: {}".format(multiply))
# 创建了 Session(会话)对象
sess = tf.Session()
# 用 Session 的 run 方法来实际运行 multiply 这个矩阵乘法操作
# 并把操作执行的结果赋值给 result
result = sess.run(multiply)
# 用 print 打印矩阵乘法的结果
print("sess.run() 之后,输出 multiply 的值: {}".format(result))
if const1.graph is tf.get_default_graph():#const1的图就是默认的图
print("const1 所在的图(Graph)是当前上下文默认的图")
# const1所在的图(Graph)是当前上下文默认的图
# 关闭已用完的 Session(会话)
sess.close()
# 第二种方法来创建和关闭Session,更为安全,防止忘记关闭Session
# 用了 Python 的上下文管理器(with ... as ... :)
with tf.Session() as sess:
result2 = sess.run(multiply)
print("multiply 的结果是 {} ".format(result2))
# Multiple的结果是[[16]]