上篇博文我们写了个引子:
Ngnix技术研究系列1-通过应用场景看Nginx的反向代理
发现了新大陆,OpenResty
OpenResty 是一个基于 Nginx 与 Lua 的高性能 Web 平台,其内部集成了大量精良的 Lua 库、第三方模块以及大多数的依赖项。用于方便地搭建能够处理超高并发、扩展性极高的动态 Web 应用、Web 服务和动态网关。
OpenResty 通过汇聚各种设计精良的 Nginx 模块(主要由 OpenResty 团队自主开发),从而将 Nginx 有效地变成一个强大的通用 Web 应用平台。这样,Web 开发人员和系统工程师可以使用 Lua 脚本语言调动 Nginx 支持的各种 C 以及 Lua 模块,快速构造出足以胜任 10K 乃至 1000K 以上单机并发连接的高性能 Web 应用系统。
OpenResty的目标是让你的Web服务直接跑在 Nginx 服务内部,充分利用 Nginx 的非阻塞 I/O 模型,不仅仅对 HTTP 客户端请求,甚至于对远程后端诸如 MySQL、PostgreSQL、Memcached 以及 Redis 等都进行一致的高性能响应。
回到我们的原始需求:
http://api.***.com/action => http://192.168.0.11/api/action
Header: *** Header: ***
Body: *** Body: ***
通过Actiton获取对应的后端服务器地址
Action和服务器的对应关系(路由表)存储在Redis中.(实时更新实时获取)
根据请求的Action动态解析对应的内网服务器地址,再实现服务的转发。
Nginx原生的路由配置无法实现上述动态路由配置,因为我们要访问Redis,获取到反向代理的路由信息,再实现服务的转发。详细的实现步骤:
1. 解析URL中的Action
2.访问Redis,Key=Action Value=内网服务器地址
3.Http请求转发到内网服务器
明确了具体的实现方案后,我们需要先详细的研究一下OpenResty和Lua
http://openresty.org/cn/
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/lua/
大致了解OpenResty是什么,能做什么,同时能简单写一些Lua脚本。
然后,我们重点看OpenResty提供的样例:
Dynamic Routing Based On Redis
通过这个样例,我们就可以模仿着写一个我们自己的配置和脚本,实现上面的动态路由的需求。
Come On。
一、解析URL中的Action
首先,要解析并拆分URL字符串,各种百度和Google,需要写一段Lua代码,实现字符串按"/"拆分

其实就是定义了一个split_path函数。
然后我们将上面的Split.lua文件,配置到Nginx的配置文件中
/usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
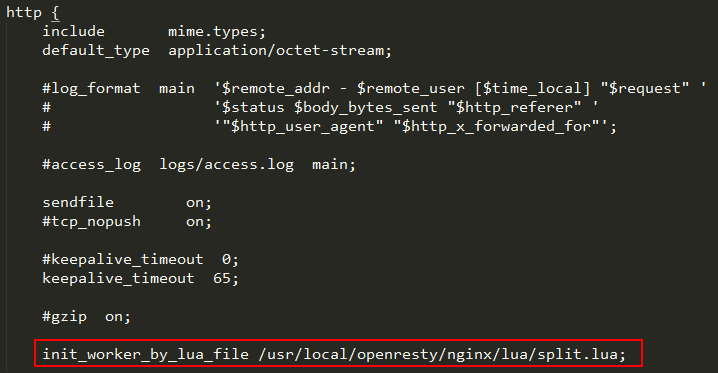
注:split.lua文件我们放在了
/usr/local/openresty/nginx/lua
编辑/usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/nginx.conf文件
http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65; #gzip on; init_worker_by_lua_file /usr/local/openresty/nginx/lua/split.lua; server { listen 80; location = /redis { internal; set_unescape_uri $key $arg_key; redis2_query get $key; redis2_pass RedisServer:6379; } location / { set $target ''; access_by_lua ' local parameters = split_path(ngx.var.uri) local action = parameters[1]
location中的access_by_lua '这一段负责执行Lua脚本和方法
local action = parameters[1]
这样,我们便解析到了Action,注:Lua中数组的下标从1开始
二.访问Redis,Key=Action Value=内网服务器地址
继续编辑Nginx配置文件
location / { set $target ''; access_by_lua ' local parameters = split_path(ngx.var.uri) local action = parameters[1] if(#parameters == 0) then ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_FORBIDDEN) end
local key = action local res = ngx.location.capture( "/redis", { args = { key = key } } )if res.status ~= 200 then ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "redis server returned bad status: ", res.status) ngx.exit(res.status) end if not res.body then ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "redis returned empty body") ngx.exit(500) end local parser = require "redis.parser" local server, typ = parser.parse_reply(res.body) if typ ~= parser.BULK_REPLY or not server then ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "bad redis response: ", res.body) ngx.exit(500) end if server == "" then server = "default.com" end
三.Http请求转发到内网服务器
继续编辑Nginx.Conf文件
init_worker_by_lua_file /usr/local/openresty/nginx/lua/split.lua; server { listen 80; location = /redis { internal; set_unescape_uri $key $arg_key; redis2_query get $key; redis2_pass RedisServer:6379; } location / { set $target ''; access_by_lua ' local parameters = split_path(ngx.var.uri) local action = parameters[1] if(#parameters == 0) then ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_FORBIDDEN) end local key = action local res = ngx.location.capture( "/redis", { args = { key = key } } ) if res.status ~= 200 then ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "redis server returned bad status: ", res.status) ngx.exit(res.status) end if not res.body then ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "redis returned empty body") ngx.exit(500) end local parser = require "redis.parser" local server, typ = parser.parse_reply(res.body) if typ ~= parser.BULK_REPLY or not server then ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "bad redis response: ", res.body) ngx.exit(500) end if server == "" then server = "default.com" end
server = server .. "/api/" .. action if ngx.var.QUERY_STRING ~= nil and ngx.var.QUERY_STRING ~= "" then server = server .."&"..ngx.var.QUERY_STRING end ngx.var.target = server '; resolver 8.8.8.8; proxy_pass http://$target; } }
至此,我们完成了Nginx的配置文件。
启动Nginx测试:
sudo /usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/Nginx.conf
PostMan发起一次请求: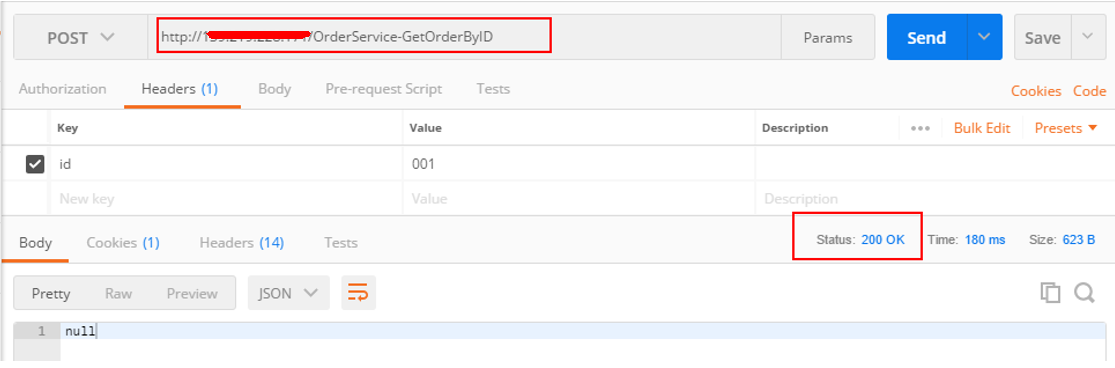
查看Nginx日志
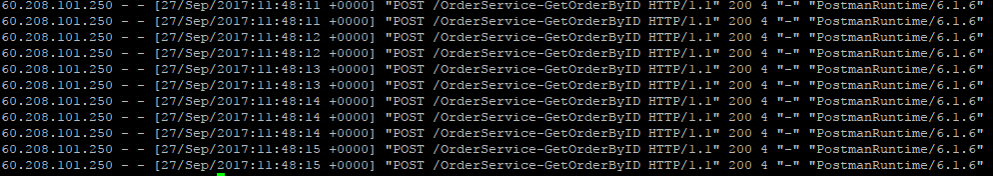
以上就是使用Nginx+lua+redis实现动态路由。分享给大家
周国庆
2017/10/01