第二十三节 inotify事件监控工具
标签(空格分隔): Linux实战教学笔记-陈思齐
---本教学笔记是本人学习和工作生涯中的摘记整理而成,此为初稿(尚有诸多不完善之处),为原创作品,允许转载,转载时请务必以超链接形式标明文章原始出处,作者信息和本声明。否则将追究法律责任。http://www.cnblogs.com/chensiqiqi/
第1章,NFS存储服务器与backup备份服务器的搭建。
详细细节知识与搭建请关注:
http://www.cnblogs.com/chensiqiqi/p/6514315.html Rsync数据同步工具
http://www.cnblogs.com/chensiqiqi/p/6530859.html 企业级NFS网络文件共享服务
http://www.cnblogs.com/chensiqiqi/p/6531003.html【Rsync项目实战】备份全网服务器数据
第2章:rsync + inotify 组合的起源
Rsync(remote sync)远程同步工具,通过rsync可以实现对远程服务器数据的增量备份同步,但rsync自身也有瓶颈,同步数据时,rsync采用核心算法对远程服务器的目标文件进行比对,只进行差异同步。我们可以想象一下,如果服务器的文件数量达到了百万甚至千万量级,那么文件对比将是非常耗时的。而且发生变化的往往是其中很少的一部分,这是非常低效的方式。inotify的出现,可以缓解rsync不足之处,取长补短。
第3章 inotify简介
- Inotify是一种强大的,细粒度的,异步的文件系统事件监控机制(软件),linux内核从2.6.13起,加入了Inotify支持,通过Inotify可以监控文件系统中添加,删除,修改,移动等各种事件,利用这个内核接口,第三方软件就可以监控文件系统下文件的各种变化情况,而inotify-tools正是实施这样监控的软件。还有国人周洋在金山公司开发的sersync。
- Inotify实际是一种事件驱动机制,它为应用程序监控文件系统事件提供了实时响应事件的机制,而无须通过诸如cron等的轮询机制来获取事件。cron等机制不仅无法做到实时性,而且消耗大量系统资源。相比之下,inotify基于事件驱动,可以做到对事件处理的实时响应,也没有轮询造成的系统资源消耗,是非常自然的事件通知接口,也与自然世界的事件机制相符合。
- inotify 的实现有几款软件
1)inotify-tools,
2)sersync(金山周洋)
3)lsyncd
特别说明:
下面的inotify配置是建立在rsync服务基础上的配置过程。

第4章 inotify 实施准备
大前提rsync daemon 服务配置成功,可以再rsync客户端推送拉取数据,然后才能配置inotify服务。
第5章 开始安装
默认yum源:
base + extras + updates
扩展的yum源:
epel
1.网易163源
2。阿里云epel源
在安装inotify-tools前请先确认你的linux内核是否达到了2.6.13,并且在编译时开启CONFIG_INOTIFY选项,也可以通过以下命令检测。
5.1 查看当前系统是否支持inotify
[root@backup ~]# uname -r
2.6.32-642.el6.x86_64
[root@backup ~]# ls -l /proc/sys/fs/inotify
总用量 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 3月 11 05:01 max_queued_events
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 3月 11 05:01 max_user_instances
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 3月 11 05:01 max_user_watches
#显示这三个文件证明支持关键参数说明:
在/proc/sys/fs/inotify目录下有三个文件,对inotify机制有一定的限制
max_user_watches:设置inotifywait或inotifywatch命令可以监视的文件数量(单进程)
max_user_instances:设置每个用户可以运行的inotifywait或inotifywatch命令的进程数。
max_queued_events:设置inotify实例事件(event)队列可容纳的事件数量。5.2 Yum安装inotify-tools:
#wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-6.repo
yum -y install inotify-tools
rpm -qa inotify-tools一共安装了2个工具,即inotifywait和inotifywatch
inotifywait:在被监控的文件或目录上等待特定文件系统事件(open,close,delete等)发生,执行后处于阻塞状态,适合shell脚本中使用。
inotifywatch:收集被监视的文件系统使用度统计数据,指文件系统事件发生的次数统计。
5.3 inotifywait命令常用参数详解
inotifywait --help
[root@backup ~]# inotifywait --help
inotifywait 3.14
Wait for a particular event on a file or set of files.
Usage: inotifywait [ options ] file1 [ file2 ] [ file3 ] [ ... ]
Options:
-h|--help Show this help text.
@<file> Exclude the specified file from being watched.
--exclude <pattern>
Exclude all events on files matching the
extended regular expression <pattern>.
--excludei <pattern>
Like --exclude but case insensitive.
-m|--monitor Keep listening for events forever. Without
this option, inotifywait will exit after one
event is received.
-d|--daemon Same as --monitor, except run in the background
logging events to a file specified by --outfile.
Implies --syslog.
-r|--recursive Watch directories recursively.
--fromfile <file>
Read files to watch from <file> or `-' for stdin.
-o|--outfile <file>
Print events to <file> rather than stdout.
-s|--syslog Send errors to syslog rather than stderr.
-q|--quiet Print less (only print events).
-qq Print nothing (not even events).
--format <fmt> Print using a specified printf-like format
string; read the man page for more details.
--timefmt <fmt> strftime-compatible format string for use with
%T in --format string.
-c|--csv Print events in CSV format.
-t|--timeout <seconds>
When listening for a single event, time out after
waiting for an event for <seconds> seconds.
If <seconds> is 0, inotifywait will never time out.
-e|--event <event1> [ -e|--event <event2> ... ]
Listen for specific event(s). If omitted, all events are
listened for.
Exit status:
0 - An event you asked to watch for was received.
1 - An event you did not ask to watch for was received
(usually delete_self or unmount), or some error occurred.
2 - The --timeout option was given and no events occurred
in the specified interval of time.
Events:
access file or directory contents were read
modify file or directory contents were written
attrib file or directory attributes changed
close_write file or directory closed, after being opened in
writeable mode
close_nowrite file or directory closed, after being opened in
read-only mode
close file or directory closed, regardless of read/write mode
open file or directory opened
moved_to file or directory moved to watched directory
moved_from file or directory moved from watched directory
move file or directory moved to or from watched directory
**create** file or directory created within watched directory
**delete** file or directory deleted within watched directory
delete_self file or directory was deleted
unmount file system containing file or directory unmounted下面用列表详细解释一下各个参数的含义
| inotifywait参数 | 含义说明 |
|---|---|
| -r --recursive | 递归查询目录 |
| -q --quiet | 打印很少的信息,仅仅打印监控事件的信息 |
| -m,--monitor | 始终保持事件监听状态 |
| --exclude | 排除文件或目录时,不区分大小写。 |
| --timefmt | 指定时间输出的格式 |
| --format | 打印使用指定的输出类似格式字符串 |
| -e,--event | 通过此参数可以指定需要监控的事件,如下一个列表所示 |
-e :--event的各种事件含义
| Events | 含义 |
|---|---|
| access | 文件或目录被读取 |
| modify | 文件或目录内容被修改 |
| attrib | 文件或目录属性被改变 |
| close | 文件或目录封闭,无论读/写模式 |
| open | 文件或目录被打开 |
| moved_to | 文件或目录被移动至另外一个目录 |
| move | 文件或目录被移动到另一个目录或从另一个目录移动至当前目录 |
| create | 文件或目录被创建在当前目录 |
| delete | 文件或目录被删除 |
| umount | 文件系统被卸载 |
5.4 人工测试监控事件
开启两个窗口
5.4.1 测试create
在第一个窗口输入如下内容:
[root@backup ~]# ls /backup
[root@backup ~]# inotifywait -mrq --timefmt '%y %m %d %H %M' --format '%T %w%f' -e create /backup
在第二个窗口:输入如下内容
[root@backup ~]# cd /backup
[root@backup backup]# touch chensiqi
此时回到第一个窗口出现如下内容:
17 03 11 07 19 /backup/chensiqi
#命令说明
inotifywait:ionotify的命令工具
-mrq:-q只输入简短信息 -r,递归监控整个目录包括子目录 -m进行不间断持续监听
--timefmt 指定输出的时间格式
--format:指定输出信息的格式
-e create:制定监控的时间类型,监控创建create事件。5.4.2 测试delte
第一个窗口输入如下信息:
[root@backup ~]# inotifywait -mrq --timefmt '%y %m %d %H %M' --format '%T %w%f' -e delete /backup
第二个窗口输入如下信息:
[root@backup backup]# rm -rf chensiqi
此时第一个窗口会出现如下信息:
17 03 11 07 29 /backup/chensiqi
#命令说明:
-e delete:指定监听的事件类型。监听删除delete事件5.4.3 测试close_write
第一个窗口输入如下信息:
inotifywait -mrq --timefmt '%y %m %d %H %M' --format '%T %w%f' -e close_write /backup
第二个窗口输入如下信息:
[root@backup backup]# touch close_write.log
[root@backup backup]# echo 111 >> close_write.log
[root@backup backup]# rm -f close_write.log
此时第一个窗口会出现如下信息:
17 03 11 07 38 /backup/close_write.log
17 03 11 07 39 /backup/close_write.log
#命令说明:
-e close_write:指定监听类型。监听文件写模式的关闭。5.4.4 测试move_to
第一个窗口输入如下信息:
[root@backup ~]# inotifywait -mrq --timefmt '%y %m %d %H %M' --format '%T %w%f' -e moved_to /backup
第二个窗口输入如下信息:
此时第一个窗口会出现如下信息:
[root@backup backup]# touch chensiqi
[root@backup backup]# mv chensiqi chen
[root@backup backup]# mkdir ddddd
[root@backup backup]# mv chen ddddd/5.5 编写inotify实时监控脚本
#!/bin/bash
backup_Server=172.16.1.41
/usr/bin/inotifywait -mrq --format '%w%f' -e create,close_write,delete /data | while read line
do
cd /data
rsync -az ./ --delete rsync_backup@$backup_Server::nfsbackup --password-file=/etc/rsync.password
done提示:
- 上边那个脚本效率很低,效率低的原因在于只要目录出现变化就都会导致我整个目录下所有东西都被推送一遍。因此,我们可以做如下改动提高效率
#!/bin/bash
Path=/data
backup_Server=172.16.1.41
/usr/bin/inotifywait -mrq --format '%w%f' -e create,close_write,delete /data | while read line
do
if [ -f $line ];then
rsync -az $line --delete rsync_backup@$backup_Server::nfsbackup --password-file=/etc/rsync.password
else
cd $Path &&
rsync -az ./ --delete rsync_backup@$backup_Server::nfsbackup --password-file=/etc/rsync.password
fi
done脚本可以加入开机启动:
echo "/bin/sh /server/scripts/inotify.sh &" >> /etc/rc.local
提示:
一个& 代表从后台开始运行该条命令。
5.6 关键参数调整
在/proc/sys/fs/inotify目录下有三个文件,对inotify机制有一定的限制
max_user_watches:设置inotifywait或inotifywatch命令可以监视的文件数量(单进程)
max_user_instances:设置每个用户可以运行的inotifywait或inotifywatch命令的进程数
max_queued_events:设置inotify实例事件(event)队列可容纳的事件数量。
实战调整:
[root@nfs01 data]# cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_
max_queued_events max_user_instances max_user_watches
[root@nfs01 data]# cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches
8192
[root@nfs01 data]# echo "50000000" > /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches
[root@nfs01 data]# cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches
50000000
[root@nfs01 data]# cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_queued_events
16384
[root@nfs01 data]# echo "326790" > /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_queued_events
[root@nfs01 data]# cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_queued_events
326790
[root@nfs01 data]# sysctl -p5.7 Rsync+inotify实时数据同步并发简单测试
10K-100K
每秒100个并发
[root@nfs01 data]# paste inotify_100_server.log
inotify_100_backup_server.log > inotify_100.txt
[root@nfs01 data]# cat inotify_100.txt
23:05 34227 23:05 34227
23:05 34387 23:05 34387
23:05 35027 23:05 35027
23:05 35587 23:05 35587
23:05 36473 23:05 36473
23:05 36707 23:05 36707
23:05 37587 23:05 37587
以下省略...Inotify实时并发:
结论:经过测试,每秒200文件并发,数据同步几乎无延迟(小于1秒)
5.8 inotify 优点:
1)监控文件系统事件变化,通过同步工具实现实时数据同步。
5.9 inotify 缺点
1)并发如果大于200个文件(10-100k),同步就会有延迟
2)我们前面写的脚本,每次都是全部推送一次,但确实是增量的。也可以只同步变化的文件,不变化的不理。
3)监控到事件后,调用rsync同步是单进程的,而sersync为多进程同步。既然有了inotify-tools,为什么还要开发sersync?
5.10 serysync功能多:(inotify+rsync命令)
1)支持通过配置文件管理
2)真正的守护进程socket
3)可以对失败文件定时重传(定时任务功能)
4)第三方的HTTP接口(例如:更新cdn缓存)
5)默认多进程rsync同步
5.11 高并发数据实时同步方案小结:
1)inotify(sersync)+ rsync,是文件级别的。
2)drbd文件系统级别,文件系统级别,基于block块同步,缺点:备节点数据不可用
3)第三方软件的同步功能:mysql同步(主从复制),oracle,mongodb
4)程序双写,直接写两台服务器。
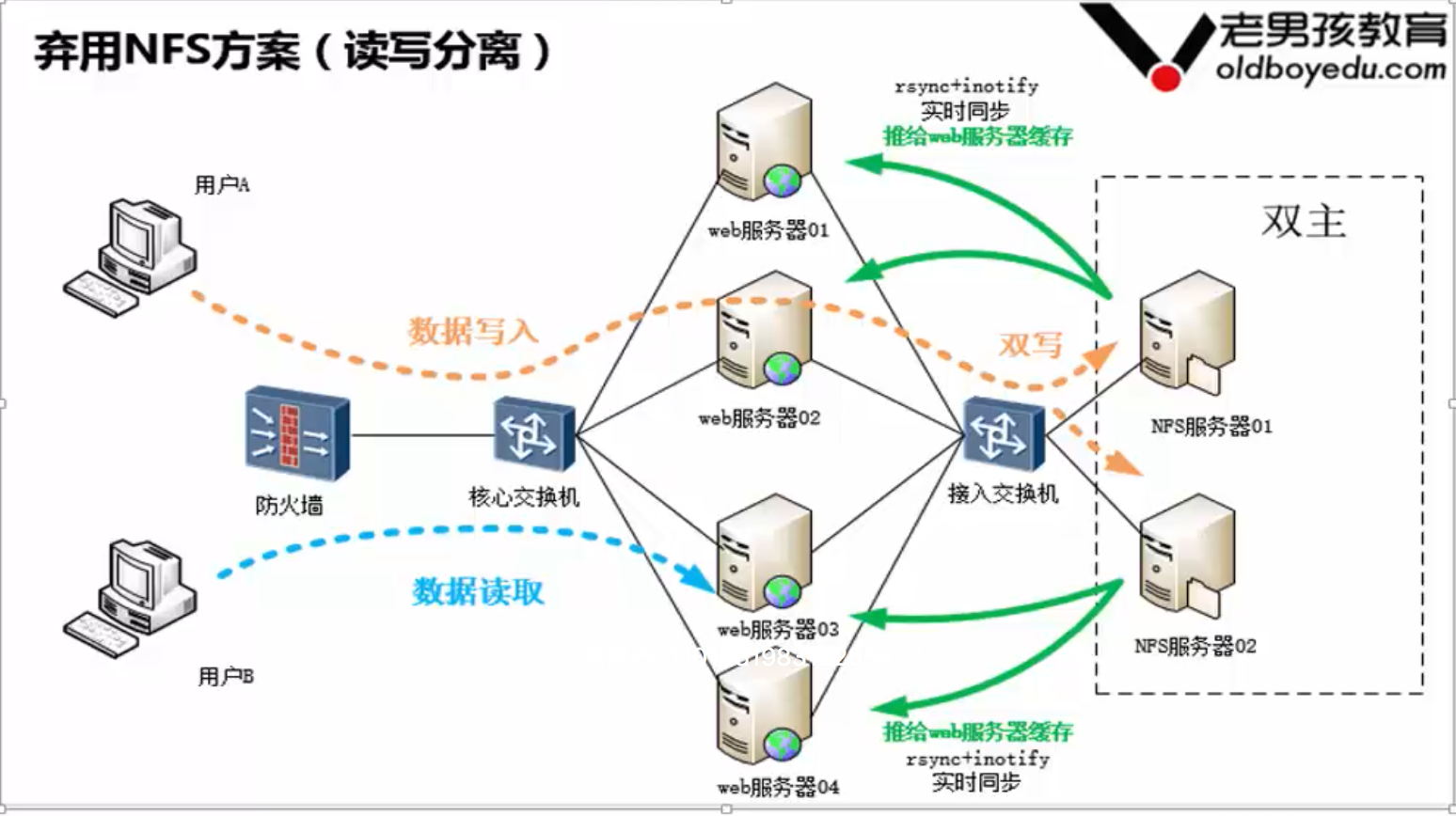
5)利用产品业务逻辑解决(读写分离,备份读不到,读主)
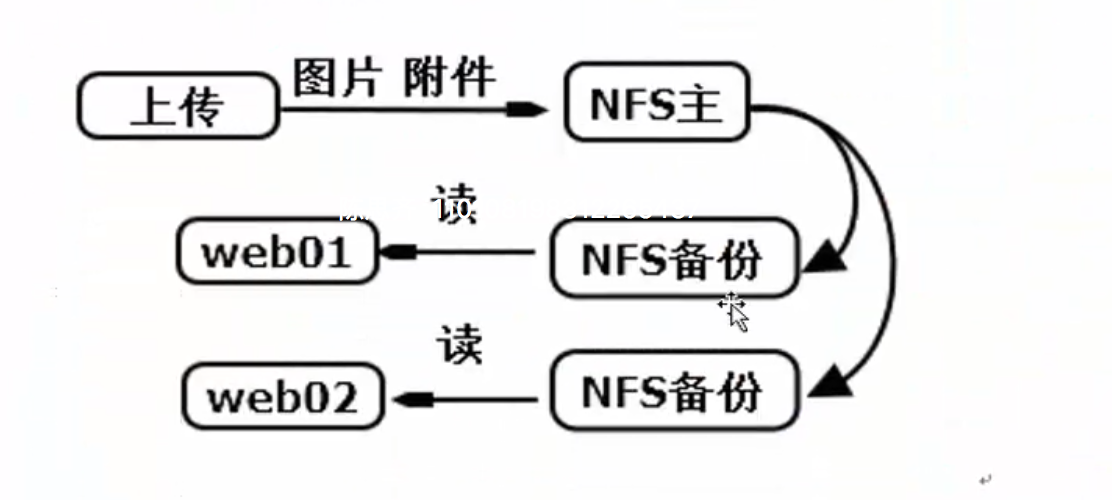
说明:
用户上传的图片或者附件单独存在NFS主服务器上;
用户读取数据从两台NFS备份服务器上读取;
NFS主和两台NFS备份通过inotify+rsync方式进行实时同步。
6)NFS集群(1,4,5方案整合)(双写主存储,备存储用inotify(sersync)+rsync