题目描述
C 国有 n 个大城市和 m 条道路,每条道路连接这 n 个城市中的某两个城市。任意两个
城市之间最多只有一条道路直接相连。这 m 条道路中有一部分为单向通行的道路,一部分
为双向通行的道路,双向通行的道路在统计条数时也计为 1 条。
C 国幅员辽阔,各地的资源分布情况各不相同,这就导致了同一种商品在不同城市的价
格不一定相同。但是,同一种商品在同一个城市的买入价和卖出价始终是相同的。
商人阿龙来到 C 国旅游。当他得知同一种商品在不同城市的价格可能会不同这一信息
之后,便决定在旅游的同时,利用商品在不同城市中的差价赚回一点旅费。设 C 国 n 个城
市的标号从 1~ n,阿龙决定从 1 号城市出发,并最终在 n 号城市结束自己的旅行。在旅游的
过程中,任何城市可以重复经过多次,但不要求经过所有 n 个城市。阿龙通过这样的贸易方
式赚取旅费:他会选择一个经过的城市买入他最喜欢的商品――水晶球,并在之后经过的另
一个城市卖出这个水晶球,用赚取的差价当做旅费。由于阿龙主要是来 C 国旅游,他决定
这个贸易只进行最多一次,当然,在赚不到差价的情况下他就无需进行贸易。
假设 C 国有 5 个大城市,城市的编号和道路连接情况如下图,单向箭头表示这条道路
为单向通行,双向箭头表示这条道路为双向通行。
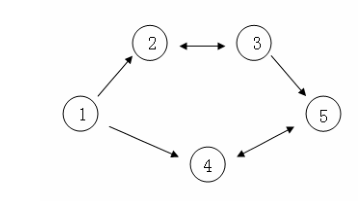
假设 1~n 号城市的水晶球价格分别为 4,3,5,6,1。
阿龙可以选择如下一条线路:1->2->3->5,并在 2 号城市以 3 的价格买入水晶球,在 3
号城市以 5 的价格卖出水晶球,赚取的旅费数为 2。
阿龙也可以选择如下一条线路 1->4->5->4->5,并在第 1 次到达 5 号城市时以 1 的价格
买入水晶球,在第 2 次到达 4 号城市时以 6 的价格卖出水晶球,赚取的旅费数为 5。
现在给出 n 个城市的水晶球价格,m 条道路的信息(每条道路所连接的两个城市的编号
以及该条道路的通行情况)。请你告诉阿龙,他最多能赚取多少旅费。
输入输出格式
输入格式:第一行包含 2 个正整数 n 和 m,中间用一个空格隔开,分别表示城市的数目和道路的
数目。
第二行 n 个正整数,每两个整数之间用一个空格隔开,按标号顺序分别表示这 n 个城
市的商品价格。
接下来 m 行,每行有 3 个正整数,x,y,z,每两个整数之间用一个空格隔开。如果 z=1,
表示这条道路是城市 x 到城市 y 之间的单向道路;如果 z=2,表示这条道路为城市 x 和城市
y 之间的双向道路。
输出格式:输出文件 trade.out 共 1 行,包含 1 个整数,表示最多能赚取的旅费。如果没有进行贸易,
则输出 0。
输入输出样例
5 5 4 3 5 6 1 1 2 1 1 4 1 2 3 2 3 5 1 4 5 2
5
说明
【数据范围】
输入数据保证 1 号城市可以到达 n 号城市。
对于 10%的数据,1≤n≤6。
对于 30%的数据,1≤n≤100。
对于 50%的数据,不存在一条旅游路线,可以从一个城市出发,再回到这个城市。
对于 100%的数据,1≤n≤100000,1≤m≤500000,1≤x,y≤n,1≤z≤2,1≤各城市
水晶球价格≤100。
NOIP 2009 提高组 第三题

#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<queue> #define maxn 100010 using namespace std; int n,m,w[maxn],num,head[maxn],ans,num2,head2[maxn]; struct node{ int to,pre; }e[500000*2],e2[500000*2]; bool mark[2][maxn],ok[maxn],vis[maxn]; void Insert(int from,int to){ e[++num].to=to; e[num].pre=head[from]; head[from]=num; } void Insert2(int from,int to){ e2[++num2].to=to; e2[num2].pre=head2[from]; head2[from]=num2; } void Bfs(int s){ queue<int>q; q.push(s); ok[s]=1; while(!q.empty()){ int now=q.front();q.pop(); for(int i=head2[now];i;i=e2[i].pre){ int to=e2[i].to; if(ok[to]==0){ ok[to]=1; q.push(to); } } } } void dfs(int now,int cost,int have){ if(now==n+1){ ans=max(ans,cost); return; } if(have==2){ ans=max(ans,cost); return; } for(int i=head[now];i;i=e[i].pre){ int to=e[i].to; if(!ok[to])continue; if(!vis[to]){ vis[to]=1; dfs(to,cost,have); if(have==0)dfs(to,-w[to],1); if(have==1&&cost+w[to]>0)dfs(to,cost+w[to],2); if(have==2)return; vis[to]=0; } } } int main(){ freopen("Cola.txt","r",stdin); scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)scanf("%d",&w[i]); int x,y,z; for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z); Insert(x,y);Insert2(y,x); if(z==2)Insert(y,x),Insert2(x,y); } Insert(n,n+1); Bfs(n);ok[n+1]=1; dfs(1,0,0); dfs(1,-w[1],1); printf("%d",ans); }

/* 两遍类spfa,认真来讲应该不算,第一遍正着建图然后得出minn[],minn[i]表示到i点最小的价格,第二遍逆着建图得出maxx[],maxx[i]表示从i可以走到n路途中最大的价格,max(minn[i]-maxx[i])即为答案。 */ #include<cstdio> #include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<queue> #include<algorithm> #define maxn 100010 using namespace std; int mn[maxn],mx[maxn],a[maxn],n,m,num,head1[maxn],head2[maxn]; bool vis[maxn]; struct node{ int to,pre; }e1[500010*2],e2[500010*2]; void Insert(int from,int to){ e1[++num].to=to; e1[num].pre=head1[from]; head1[from]=num; e2[num].to=from; e2[num].pre=head2[to]; head2[to]=num; } void spfa(){ queue<int>q;q.push(1); vis[1]=1; while(!q.empty()){ int now=q.front();q.pop();vis[now]=0; for(int i=head1[now];i;i=e1[i].pre){ int to=e1[i].to; if(mn[now]<mn[to]||mn[to]>a[to]){ mn[to]=min(mn[now],a[to]); if(!vis[to])vis[to]=1,q.push(to); } } } } void spfa1(){ queue<int>q;q.push(n); vis[n]=1; memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); while(!q.empty()){ int now=q.front();q.pop();vis[now]=0; for(int i=head2[now];i;i=e2[i].pre){ int to=e2[i].to; if(mx[now]>mx[to]||mx[to]<a[to]){ mx[to]=max(mx[now],a[to]); if(!vis[to])vis[to]=1,q.push(to); } } } } int main(){ memset(mn,0x3f,sizeof(mn)); scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); int x,y,z; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)scanf("%d",&a[i]); for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z); Insert(x,y); if(z==2)Insert(y,x); } spfa();spfa1(); int ans=0; mx[1]=a[1];mx[n]=a[n]; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)ans=max(ans,mx[i]-mn[i]); printf("%d",ans); return 0; }
