private static Calendar createCalendar(TimeZone zone,Locale aLocale) { CalendarProvider provider = LocaleProviderAdapter.getAdapter(CalendarProvider.class, aLocale) .getCalendarProvider(); if (provider != null) { try { return provider.getInstance(zone, aLocale); } catch (IllegalArgumentException iae) { // fall back to the default instantiation } } Calendar cal = null; /*根据不同的地区来创建不同的日历对象,就好比日历这个工厂,生产着世界上各地区的日历,我需要这个地区日历,我只需要传参数告诉工厂即可,不需要知道日历制作过程和实例的过程*/ if (aLocale.hasExtensions()) { String caltype = aLocale.getUnicodeLocaleType("ca"); if (caltype != null) { switch (caltype) { case "buddhist": cal = new BuddhistCalendar(zone, aLocale); break; case "japanese": cal = new JapaneseImperialCalendar(zone, aLocale); break; case "gregory": cal = new GregorianCalendar(zone, aLocale); break; } } } if (cal == null) { // If no known calendar type is explicitly specified, // perform the traditional way to create a Calendar: // create a BuddhistCalendar for th_TH locale, // a JapaneseImperialCalendar for ja_JP_JP locale, or // a GregorianCalendar for any other locales. // NOTE: The language, country and variant strings are interned. if (aLocale.getLanguage() == "th" && aLocale.getCountry() == "TH") { cal = new BuddhistCalendar(zone, aLocale); } else if (aLocale.getVariant() == "JP" && aLocale.getLanguage() == "ja" && aLocale.getCountry() == "JP") { cal = new JapaneseImperialCalendar(zone, aLocale); } else { cal = new GregorianCalendar(zone, aLocale); } } return cal; }
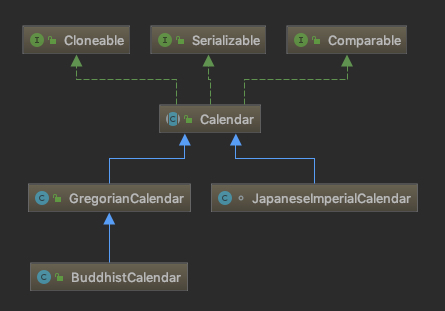
Calendar类图
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
@CallerSensitive public static Connection getConnection(String url) throws SQLException { java.util.Properties info = new java.util.Properties(); return (getConnection(url, info,Reflection.getCallerClass())); }
// Worker method called by the public getConnection() methods. private static Connection getConnection( String url, java.util.Properties info, Class<?> caller) throws SQLException { /* * When callerCl is null, we should check the application's * (which is invoking this class indirectly) * classloader, so that the JDBC driver class outside rt.jar * can be loaded from here. */ ClassLoader callerCL = caller != null ? caller.getClassLoader() : null; synchronized(DriverManager.class) { // synchronize loading of the correct classloader. if (callerCL == null) { callerCL = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); } } if(url == null) { throw new SQLException("The url cannot be null", "08001"); } println("DriverManager.getConnection("" + url + "")"); // Walk through the loaded registeredDrivers attempting to make a connection. // Remember the first exception that gets raised so we can reraise it. SQLException reason = null; for(DriverInfo aDriver : registeredDrivers) { // If the caller does not have permission to load the driver then // skip it. if(isDriverAllowed(aDriver.driver, callerCL)) { try { println(" trying " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName()); Connection con = aDriver.driver.connect(url, info); if (con != null) { // Success! println("getConnection returning " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName()); return (con); } } catch (SQLException ex) { if (reason == null) { reason = ex; } } } else { println(" skipping: " + aDriver.getClass().getName()); } } // if we got here nobody could connect. if (reason != null) { println("getConnection failed: " + reason); throw reason; } println("getConnection: no suitable driver found for "+ url); throw new SQLException("No suitable driver found for "+ url, "08001"); }
// Walk through the loaded registeredDrivers attempting to locate someone // who understands the given URL. for (DriverInfo aDriver : registeredDrivers) { // If the caller does not have permission to load the driver then // skip it. if(isDriverAllowed(aDriver.driver, callerClass)) { try { if(aDriver.driver.acceptsURL(url)) { // Success! println("getDriver returning " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName()); return (aDriver.driver); } } catch(SQLException sqe) { // Drop through and try the next driver. } } else { println(" skipping: " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName()); } }
因为这个可以看出来它是一个for循环,在遍历注册的一个驱动,
private final static CopyOnWriteArrayList<DriverInfo> registeredDrivers = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
并且它是CopyOnWriteArrayList,里面是DriverInfo,初始化的时候他是一个空的,具体是什么时候完成注册的呢,
static { try { java.sql.DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver()); } catch (SQLException E) { throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!"); } }
public static synchronized void registerDriver(java.sql.Driver driver, DriverAction da) throws SQLException { /* Register the driver if it has not already been added to our list */ if(driver != null) { registeredDrivers.addIfAbsent(new DriverInfo(driver, da)); } else { // This is for compatibility with the original DriverManager throw new NullPointerException(); } println("registerDriver: " + driver); }
if(driver != null) { registeredDrivers.addIfAbsent(new DriverInfo(driver, da)); }
此外,logback中也有简单工厂的影子。
public final class LoggerFactory public static ILoggerFactory getILoggerFactory() { }
最里面有一个getLogger方法,
public static Logger getLogger(Class clazz) { return getLogger(clazz.getName()); } public static Logger getLogger(String name) { ILoggerFactory iLoggerFactory = getILoggerFactory(); return iLoggerFactory.getLogger(name); }
这个还有个重载,一个是String name,还有一个是Class clazz,clazz是干嘛的,是clazz.getName(),
首先getLogger根据我们传来的name,从iLoggerFactory里面getLogger,先看一下
public interface ILoggerFactory package org.slf4j; //抽象产品工厂 public interface ILoggerFactory { //抽象工厂方法 public Logger getLogger(String name); }
很明显ILoggerFactory它是一个接口,下面有一个方法,那这个呢是工厂方法,那在后面我们也会讲,这里先过去,
后面我们学习工厂方法的时候,再单独来说,然后通过iLoggerFactory.getLogger,因为它是一个接口,肯定有多个实现,
LoggerContext //具体工厂实现类 public class LoggerContext extends ContextBase implements ILoggerFactory, LifeCycle { ... //具体工厂方法 @Override public final Logger getLogger(final String name) { ... }
这里面我们看一下,传入的一个name,这里面要返回Logger,这里面对name进行了判断,很明显这个方法就是一个简单工厂方法,
根据传入的入参进行选择哪个Logger,那这个还是非常简单的,刚刚也说了,在我们的LoggerFactory里面,既存在了工厂方法,
又存在了简单工厂,所以设计模式在使用的时候,不一定要局限在使用一种,例如这里就是一个组合的使用,这个简单工厂比较简单,
在很多源码中也能够找到他的影子,在前面的JDK,Logback开源框架的,对于学习设计模式的讲解呢,我们在阅读源码的时候呢,
还可以以设计模式的角度,去聚焦源码,这样对我们理解源码也是有益处的 。