1. 线程运行状态
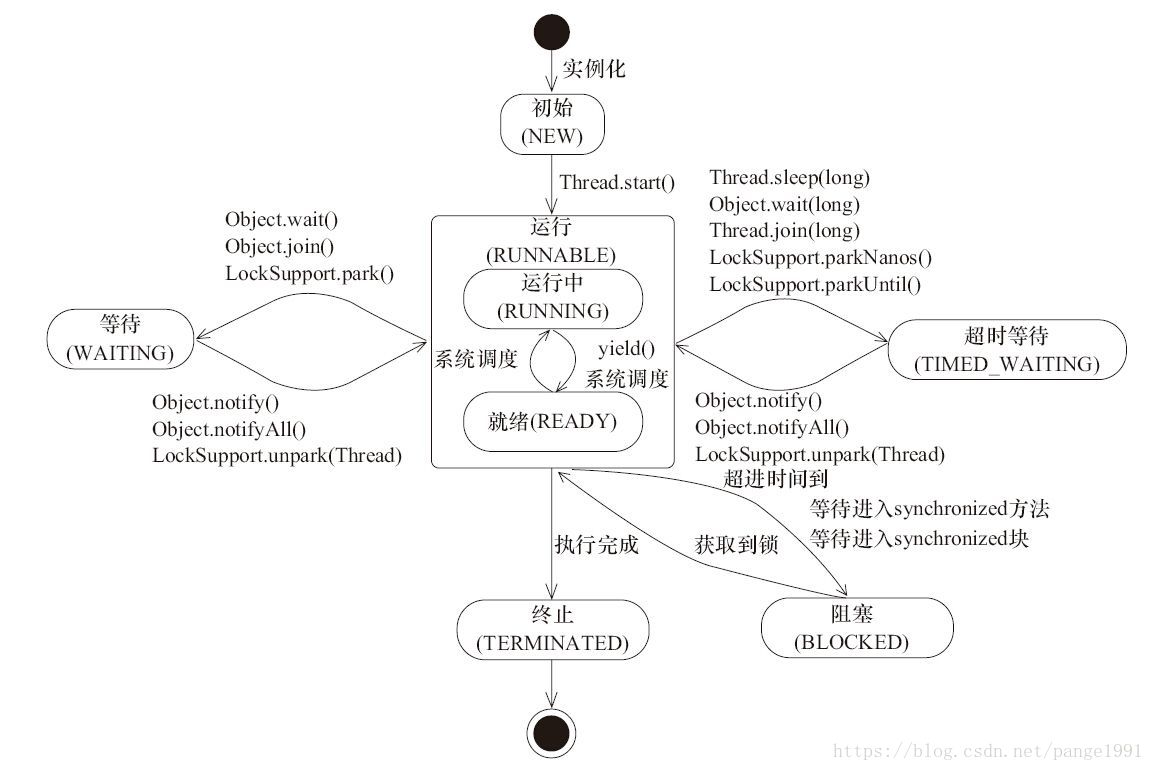
2.线程的方法
2.1 start()
public class MyThread extends Thread{
public void run() {
// this = Thread.currentThread
System.out.println(this.getName());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new MyThread();
thread.start();
}
}
2.2 run()
虚拟机实际调用的方法
2.3 setDaemon(boolean on)
设置该线程为守护线程,守护线程是一种特殊的线程,主要是为其他线程提供服务.被守护的线程一旦销毁,那么守护线程也没有存在的必要了.
示例1: innerThread设置为Thread的守护线程,模拟心跳发送.如果连接中断,则心跳中断.
public class DeamonThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// t 线程模拟网络长连接
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
// innerThread 线程模拟发送心跳的线程
Thread innerThread = new Thread(() -> {
try {
while(true) {
System.out.println("发送心跳");
Thread.sleep(500);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
innerThread.setDaemon(true);
innerThread.start();
try {
// 模拟长连接1秒以后就退出
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("T Thread done");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
t.start();
}
}
运行结果
发送心跳
发送心跳
T Thread done
2.4 sleep()
线程休眠
示例一: 线程执行2秒打印一次
public class MyThread extends Thread{
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
while(true){
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " continue to run");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果
main is running
main is running
main is running
main is running
2.5 wait(),notify(),notifyAll()
wait():线程释放锁,并进行等待,直至接到通知或被中断.
public class WaitTest {
public void waitMethod(Object lock) {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("start");
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object lock = new Object();
WaitTest thread = new WaitTest();
thread.waitMethod(lock);
}
执行结果:
Connected to the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:55626', transport: 'socket'
start
notify(): 如果有多个线程等待,那么线程规划器随机挑选出一个wait的线程,对其发出通知notify(),并使它等待获取该对象的对象锁。注意"等待获取该对象的对象锁",这意味着,即使收到了通知,wait的线程也不会马上获取对象锁,必须等待notify()方法的线程释放锁才可以。和wait()一样,notify()也要在同步方法/同步代码块中调用。
示例: 调用notify方法后,notify线程执行完毕释放锁的时候wait()方法才可以继续持有锁执行
package com.company;
public class MyThread1 extends Thread {
private Object lock;
public MyThread1(Object lock) {
this.lock = lock;
}
@Override
public void run() {
ThreadDomain threadDomain = new ThreadDomain();
threadDomain.waitMethod(lock);
}
}
package com.company;
public class MyThread2 extends Thread {
private Object lock;
public MyThread2(Object lock) {
this.lock = lock;
}
@Override
public void run() {
ThreadDomain threadDomain = new ThreadDomain();
threadDomain.notifyMethod(lock);
}
}
package com.company;
public class ThreadDomain {
public void waitMethod(Object lock) {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "start to wait");
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "end to wait");
}
}
public void notifyMethod(Object lock) {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "start to notify");
lock.notify();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "end to notify");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object lock = new Object();
MyThread1 myThread1 = new MyThread1(lock);
MyThread2 myThread2 = new MyThread2(lock);
MyThread2 myThread3 = new MyThread2(lock);
myThread1.start();
myThread2.start();
myThread3.start();
}
}
执行结果:
Connected to the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:56026', transport: 'socket'
Thread-0start to wait
Thread-2start to notify
Thread-2end to notify
Thread-1start to notify
Thread-1end to notify
Thread-0end to wait
Disconnected from the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:56026', transport: 'socket'
Process finished with exit code 0
notifyAll(): 利用Object对象的notifyAll()方法可以唤醒处于同一监视器下的所有处于wait的线程
package com.company;
public class MyThread2 extends Thread {
private Object lock;
public MyThread2(Object lock) {
this.lock = lock;
}
@Override
public void run() {
ThreadDomain threadDomain = new ThreadDomain();
threadDomain.notifyMethod(lock);
}
}
package com.company;
public class ThreadDomain {
public void waitMethod(Object lock) {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "start to wait");
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "end to wait");
}
}
public void notifyMethod(Object lock) {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "start to notify");
lock.notifyAll();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "end to notify");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object lock = new Object();
MyThread1 myThread1 = new MyThread1(lock);
MyThread1 myThread2 = new MyThread1(lock);
MyThread1 myThread3 = new MyThread1(lock);
MyThread2 myThread4 = new MyThread2(lock);
myThread1.start();
myThread2.start();
myThread3.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
myThread4.start();
}
}
执行结果:
Thread-1start to wait
Thread-2start to wait
Thread-0start to wait
Thread-3start to notify
Thread-3end to notify
Thread-0end to wait
Thread-2end to wait
Thread-1end to wait
interrupt()打断wait() : interrupt()方法的作用不是中断线程,而是在线程阻塞的时候给线程一个中断标识,表示该线程中断
2.6 interrupt(),isInterrupted()
,interrupted()
interuppt(): 在一个线程中调用另一个线程的interrupt()方法,即会向那个线程发出信号——线程中断状态已被设置。 通俗来讲就是:只是给另外一个线程打上一个标识,标记这个线程需要被中断.
package com.company;
public class InterruptTest extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "is interrupted,but still run");
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "is not interrupted,still run");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
InterruptTest interruptTest = new InterruptTest();
interruptTest.start();
interruptTest.interrupt();
}
}
执行结果: 线程并没有被中断
Thread-0is interrupted,but still run
Thread-0is interrupted,but still run
Thread-0is interrupted,but still run
Thread-0is interrupted,but still run
Thread-0is interrupted,but still run
Thread-0is interrupted,but still run
isInterrupted():判断线程是否被中断
interrupted(): 清除中断标记
- 线程被中断时,``interrupted()``返回true
- 线程未被中断时,``interrupted()``返回false
2.7 join()
join():会使调用join()的线程所在的线程无限阻塞,直至调用join()方法的线程销毁为止.
public class MyThread extends Thread {
private static volatile int count = 0;
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
count++;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
MyThread mt = new MyThread();
mt.start();
// 注释join()时,打印count=0;不注释时打印count=3
mt.join();
System.out.println("count = " + count);
}
}